Flutter三方库适配OpenHarmony【flutter_speech】— MethodChannel 双向通信实现
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net前面几篇我们分别讲了权限申请、引擎创建、监听器、启动停止、资源释放。这些功能散落在不同的方法中,是时候把它们串起来了。MethodChannel是连接Dart层和原生层的桥梁,所有的交互都通过它完成。flutter_speech的通信是双向的——Dart层可以调用原生方法(如activat
前言
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
前面几篇我们分别讲了权限申请、引擎创建、监听器、启动停止、资源释放。这些功能散落在不同的方法中,是时候把它们串起来了。
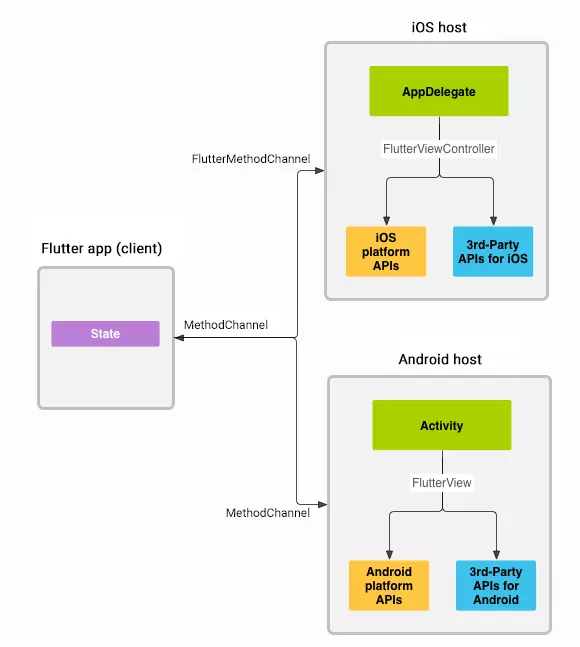
MethodChannel是连接Dart层和原生层的桥梁,所有的交互都通过它完成。flutter_speech的通信是双向的——Dart层可以调用原生方法(如activate、listen),原生层也可以主动通知Dart层(如识别结果、错误事件)。
我在适配过程中发现,理解通信的全貌比理解单个方法更重要。很多bug不是某个方法写错了,而是通信时序搞混了——比如在引擎还没创建好的时候就发了onSpeechAvailability,或者在channel已经被注销后还在invokeMethod。
今天我们把flutter_speech中所有的通信路径都梳理一遍,画一张完整的通信地图。
💡 本文重点:不是讲某个方法的实现细节(前面已经讲过了),而是从通信协议的角度把所有交互串起来。
一、Dart → Native:onMethodCall 方法分发
1.1 通信方向
Dart层 Native层(OpenHarmony)
────── ────────────────────
_channel.invokeMethod(...) → onMethodCall(call, result)
← result.success / result.error
Dart层通过invokeMethod发起调用,Native层通过result返回结果。这是一个请求-响应模式。
1.2 flutter_speech中的所有Dart→Native调用
| Dart方法 | Channel方法名 | 参数 | 返回值 | 对应Native方法 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| activate(locale) | “speech.activate” | String locale | bool | activate() |
| listen() | “speech.listen” | 无 | bool | startListening() |
| cancel() | “speech.cancel” | 无 | bool | cancel() |
| stop() | “speech.stop” | 无 | bool | stop() |
| (预留) | “speech.destroy” | 无 | bool | destroyEngine() |
1.3 Dart层的调用代码
class SpeechRecognition {
static const MethodChannel _channel =
const MethodChannel('com.flutter.speech_recognition');
Future activate(String locale) =>
_channel.invokeMethod("speech.activate", locale);
Future listen() =>
_channel.invokeMethod("speech.listen");
Future cancel() =>
_channel.invokeMethod("speech.cancel");
Future stop() =>
_channel.invokeMethod("speech.stop");
}
1.4 Native层的分发代码
onMethodCall(call: MethodCall, result: MethodResult): void {
switch (call.method) {
case "speech.activate":
this.activate(String(call.args), result).catch((e: Error) => {
console.error(TAG, `activate unhandled error: ${e.message}`);
result.error('SPEECH_ACTIVATION_ERROR', e.message, null);
});
break;
case "speech.listen":
this.startListening(result);
break;
case "speech.cancel":
this.cancel(result);
break;
case "speech.stop":
this.stop(result);
break;
case "speech.destroy":
this.destroyEngine();
result.success(true);
break;
default:
result.notImplemented();
break;
}
}
1.5 参数传递方式
| 方法 | Dart传参方式 | Native取参方式 | 参数类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| activate | invokeMethod(“speech.activate”, locale) | String(call.args) | String |
| listen | invokeMethod(“speech.listen”) | 无参数 | - |
| cancel | invokeMethod(“speech.cancel”) | 无参数 | - |
| stop | invokeMethod(“speech.stop”) | 无参数 | - |
flutter_speech的参数传递非常简单——只有activate需要传一个locale字符串,其他方法都不需要参数。
📌 注意:Dart层用
call.arguments(复数),OpenHarmony用call.args(缩写)。这个命名差异在第8篇已经提过,这里再强调一下。
1.6 结果返回方式
每个方法都必须通过result对象返回结果:
// 成功
result.success(true);
// 错误
result.error('ERROR_CODE', 'Error message', null);
// 未实现
result.notImplemented();
Dart层的Future会根据返回方式不同而有不同的表现:
| Native返回 | Dart Future行为 | Dart代码 |
|---|---|---|
| result.success(value) | 正常完成,值为value | .then((res) => …) |
| result.error(code, msg, details) | 抛出PlatformException | .catchError((e) => …) |
| result.notImplemented() | 抛出MissingPluginException | .catchError((e) => …) |
二、Native → Dart:channel.invokeMethod 回调通知
2.1 通信方向
Native层(OpenHarmony) Dart层
──────────────────── ──────
channel.invokeMethod(...) → _platformCallHandler(call)
Native层通过channel.invokeMethod主动向Dart层发送事件。这是一个推送模式,不需要Dart层先发起请求。
2.2 flutter_speech中的所有Native→Dart事件
| Native调用 | Channel方法名 | 参数 | 触发时机 | Dart回调 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 引擎就绪 | “speech.onSpeechAvailability” | bool | activate成功/失败 | availabilityHandler |
| 识别开始 | “speech.onRecognitionStarted” | null | onStart回调 | recognitionStartedHandler |
| 识别结果 | “speech.onSpeech” | String | onResult回调 | recognitionResultHandler |
| 识别完成 | “speech.onRecognitionComplete” | String | onResult(isLast=true) | recognitionCompleteHandler |
| 错误 | “speech.onError” | int | onError回调 | errorHandler |
2.3 Native层的发送代码
// 1. 引擎可用性通知
this.channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeechAvailability', true);
this.channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeechAvailability', false);
// 2. 识别开始通知
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onRecognitionStarted', null);
// 3. 实时识别结果
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeech', result.result);
// 4. 识别完成
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onRecognitionComplete', result.result);
// 5. 错误通知
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onError', errorCode);
2.4 Dart层的接收代码
SpeechRecognition._internal() {
_channel.setMethodCallHandler(_platformCallHandler);
}
Future _platformCallHandler(MethodCall call) async {
switch (call.method) {
case "speech.onSpeechAvailability":
availabilityHandler(call.arguments);
break;
case "speech.onSpeech":
recognitionResultHandler(call.arguments);
break;
case "speech.onRecognitionStarted":
recognitionStartedHandler();
break;
case "speech.onRecognitionComplete":
recognitionCompleteHandler(call.arguments);
break;
case "speech.onError":
errorHandler();
break;
}
}
2.5 可选链操作符的使用
注意Native层发送事件时使用了?.(可选链操作符):
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeech', result.result);
// ↑ 可选链
这是因为channel可能为null(在onDetachedFromEngine之后)。使用?.可以安全地跳过null的情况,不会抛异常。
💡 防御性编程:在回调中使用channel时,总是用
?.而不是.。因为回调可能在引擎销毁后才触发(异步时序问题),此时channel可能已经是null了。
三、speech.onSpeechAvailability 事件传递
3.1 事件含义
speech.onSpeechAvailability告诉Dart层"语音识别是否可用"。
3.2 触发场景
| 场景 | 参数值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| activate成功 | true | 引擎就绪,可以开始识别 |
| onError触发 | false | 引擎出错,不可用 |
3.3 发送位置
// 位置1:activate成功后
this.channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeechAvailability', true);
// 位置2:onError回调中
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeechAvailability', false);
3.4 Dart层的处理
_speech.setAvailabilityHandler((bool result) {
setState(() => _speechRecognitionAvailable = result);
});
UI根据_speechRecognitionAvailable的值来控制按钮的可用状态:
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _speechRecognitionAvailable && !_isListening
? () => _speech.listen()
: null, // 不可用时按钮灰色
child: Text('Listen'),
)
3.5 时序分析
activate("zh_CN")
│
├── 权限申请 → 成功
├── 能力检测 → 支持
├── 引擎创建 → 成功
├── 设置监听器
│
├── invokeMethod('speech.onSpeechAvailability', true) ← 通知可用
│ → Dart: availabilityHandler(true)
│ → UI: "Listen"按钮变为可点击
│
└── result.success(true)
→ Dart: activate() Future完成
📌 注意时序:
onSpeechAvailability(true)是在result.success(true)之前发送的。这意味着Dart层可能先收到可用性通知,再收到activate的返回值。不过在实际使用中,这个顺序差异不影响功能。
四、speech.onSpeech 实时识别结果推送
4.1 事件含义
speech.onSpeech推送实时的识别文本,每次识别引擎产生新的结果都会触发。
4.2 触发频率
一次识别过程中,speech.onSpeech会被触发多次:
用户说"打开设置页面":
t=0.3s: speech.onSpeech("打")
t=0.5s: speech.onSpeech("打开")
t=0.8s: speech.onSpeech("打开设置")
t=1.2s: speech.onSpeech("打开设置页面")
t=1.5s: speech.onSpeech("打开设置页面") ← 最终结果(同时触发onRecognitionComplete)
4.3 参数类型
// Native端发送
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeech', result.result);
// result.result 是 string 类型
// Dart端接收
case "speech.onSpeech":
recognitionResultHandler(call.arguments);
// call.arguments 是 String 类型
4.4 UI更新
_speech.setRecognitionResultHandler((String text) {
setState(() {
_transcription = text; // 更新显示的文本
});
});
每次收到新的结果,UI都会更新显示。用户能看到文字一个个蹦出来的效果。
五、speech.onRecognitionComplete 完成事件处理
5.1 事件含义
speech.onRecognitionComplete表示识别已完成,携带最终的识别文本。
5.2 触发位置
这个事件可能从两个地方发出:
// 位置1:onResult回调中(isLast=true时)
onResult(sessionId, result) {
if (result.isLast) {
plugin.isListening = false;
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onRecognitionComplete', result.result);
}
}
// 位置2:onComplete回调中(兜底)
onComplete(sessionId, eventMessage) {
if (plugin.isListening) {
plugin.isListening = false;
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onRecognitionComplete', plugin.lastTranscription);
}
}
通过isListening标志保证只发送一次。
5.3 与speech.onSpeech的区别
| 维度 | speech.onSpeech | speech.onRecognitionComplete |
|---|---|---|
| 触发次数 | 多次 | 1次 |
| 含义 | 实时部分结果 | 最终完整结果 |
| 用途 | 更新UI显示 | 标记识别结束 |
| 参数 | 当前文本 | 最终文本 |
5.4 Dart层的处理
_speech.setRecognitionCompleteHandler((String text) {
setState(() {
_transcription = text;
_isListening = false; // 标记识别结束
});
});
收到完成事件后,UI会:
- 显示最终文本
- 将"正在监听"状态改为"已停止"
- 按钮状态恢复
六、完整通信协议图
6.1 一次完整识别的通信时序
Dart层 Native层
────── ──────
1. activate("zh_CN") ──────────────────► onMethodCall("speech.activate", "zh_CN")
│ 权限申请...
│ 引擎创建...
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeechAvailability", true)
◄────────────────── result.success(true)
2. listen() ───────────────────────────► onMethodCall("speech.listen")
│ startListening...
◄────────────────── result.success(true)
│
│ (引擎开始采集音频)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onRecognitionStarted")
│
│ (用户说话中...)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeech", "你好")
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeech", "你好世界")
│
│ (用户停止说话,VAD超时)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeech", "你好世界")
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onRecognitionComplete", "你好世界")
3. (识别自然结束,无需手动stop)
6.2 用户手动stop的时序
Dart层 Native层
────── ──────
(识别进行中...)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeech", "今天天气")
stop() ────────────────────────────────► onMethodCall("speech.stop")
│ finish(sessionId)
◄────────────────── result.success(true)
│
│ (引擎处理剩余音频)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeech", "今天天气怎么样")
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onRecognitionComplete", "今天天气怎么样")
6.3 错误场景的时序
Dart层 Native层
────── ──────
activate("en_US") ─────────────────────► onMethodCall("speech.activate", "en_US")
│ 语言校验失败
◄────────────────── result.error("ERROR_LANGUAGE_NOT_SUPPORTED", ...)
Dart层 Native层
────── ──────
(识别进行中,网络断开)
│ onError(1, "network timeout")
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onSpeechAvailability", false)
◄────────────────── invokeMethod("speech.onError", 1)
七、通信安全性保障
7.1 Channel名称一致性
// Dart层
static const MethodChannel _channel =
const MethodChannel('com.flutter.speech_recognition');
// Native层
this.channel = new MethodChannel(
binding.getBinaryMessenger(),
"com.flutter.speech_recognition" // 必须完全一致
);
如果两端的Channel名称不一致,所有通信都会失效,但不会报错——方法调用会触发MissingPluginException。
7.2 方法名一致性
所有方法名都以speech.为前缀,形成了一个简单的命名空间:
Dart → Native:
speech.activate
speech.listen
speech.cancel
speech.stop
speech.destroy
Native → Dart:
speech.onSpeechAvailability
speech.onRecognitionStarted
speech.onSpeech
speech.onRecognitionComplete
speech.onError
📌 命名规范:Dart→Native的方法名用动词(activate、listen),Native→Dart的事件名用
on前缀(onSpeech、onError)。这种命名方式让通信方向一目了然。
7.3 空值安全
// Native端:channel可能为null
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeech', result.result);
// Native端:asrEngine可能为null
if (!this.asrEngine) {
result.error('ERROR_ENGINE_NOT_INITIALIZED', ...);
return;
}
// Dart端:回调可能未设置(late变量)
case "speech.onSpeech":
recognitionResultHandler(call.arguments); // 如果未设置会抛异常
⚠️ Dart层的潜在问题:
recognitionResultHandler是late声明的,如果在设置回调之前收到了事件,会抛出LateInitializationError。这是flutter_speech的一个已知限制——必须在调用activate之前设置好所有回调。
7.4 类型安全
| 事件 | Native发送类型 | Dart接收类型 | 是否匹配 |
|---|---|---|---|
| onSpeechAvailability | boolean | dynamic → bool | ✅ |
| onRecognitionStarted | null | 不使用参数 | ✅ |
| onSpeech | string | dynamic → String | ✅ |
| onRecognitionComplete | string | dynamic → String | ✅ |
| onError | number | dynamic → int | ✅ |
Platform Channel会自动处理基本类型的序列化和反序列化,所以类型匹配通常不是问题。
八、通信调试技巧
8.1 日志追踪
在关键通信节点添加日志:
// Native端发送事件时
console.info(TAG, `>>> invokeMethod: speech.onSpeech, args=${result.result}`);
channel?.invokeMethod('speech.onSpeech', result.result);
// Native端收到调用时
onMethodCall(call: MethodCall, result: MethodResult): void {
console.info(TAG, `<<< onMethodCall: ${call.method}, args=${call.args}`);
// ...
}
# 查看所有通信日志
hdc hilog | grep "FlutterSpeechPlugin" | grep -E "invokeMethod|onMethodCall"
8.2 常见通信问题
| 问题 | 症状 | 原因 | 解决 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dart调用无响应 | Future不完成 | 某个分支没有调用result | 检查所有switch分支 |
| 事件收不到 | Dart回调不触发 | channel为null或Handler未注册 | 检查生命周期 |
| 类型错误 | 运行时异常 | 参数类型不匹配 | 检查发送和接收的类型 |
| 重复事件 | 回调触发多次 | 监听器注册了多次 | 确保setupListener只调用一次 |
| 事件顺序错乱 | UI状态不一致 | 异步时序问题 | 用isListening等标志做状态保护 |
8.3 通信协议检查清单
- Channel名称两端完全一致
- 所有Dart→Native方法都有对应的switch分支
- 所有switch分支都有result响应
- 所有Native→Dart事件都有对应的_platformCallHandler分支
- Native端发送事件时使用
?.操作符 - Dart端在使用前设置了所有回调Handler
- 参数类型两端匹配
总结
本文从通信协议的角度完整梳理了flutter_speech的MethodChannel双向通信:
- Dart→Native:5个方法调用(activate、listen、cancel、stop、destroy)
- Native→Dart:5个事件通知(onSpeechAvailability、onRecognitionStarted、onSpeech、onRecognitionComplete、onError)
- 通信安全:Channel名称一致、方法名一致、空值安全、类型安全
- 完整时序:从activate到识别完成的所有通信步骤
下一篇我们讲语言支持与Locale处理——OpenHarmony的语言限制和flutter_speech的应对策略。
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞👍、收藏⭐、关注🔔,你的支持是我持续创作的动力!
相关资源:
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献45条内容
已为社区贡献45条内容







所有评论(0)