基础入门 Flutter for OpenHarmony:InteractiveViewer 交互式查看器详解
在移动应用开发中,图片或内容的缩放、平移是一种常见的交互需求。用户可以通过双指缩放、拖拽平移来查看大图或详细内容。Flutter 提供了 InteractiveViewer 组件,专门用于实现这种交互式的查看体验。InteractiveViewer 是 Flutter 中用于实现缩放、平移交互的组件,适合需要手势交互的查看场景。InteractiveViewer 的基本用法和核心概念Transfo
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
🎯 欢迎来到 Flutter for OpenHarmony 社区!本文将深入讲解 Flutter 中 InteractiveViewer 交互式查看器组件的使用方法,带你从基础到精通,掌握图片缩放、平移、旋转等手势交互功能。
一、InteractiveViewer 组件概述
在移动应用开发中,图片或内容的缩放、平移是一种常见的交互需求。用户可以通过双指缩放、拖拽平移来查看大图或详细内容。Flutter 提供了 InteractiveViewer 组件,专门用于实现这种交互式的查看体验。
📋 InteractiveViewer 组件特点
| 特点 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 缩放支持 | 支持双指缩放手势 |
| 平移支持 | 支持拖拽平移内容 |
| 边界限制 | 支持设置内容的边界约束 |
| 缩放限制 | 支持设置最小和最大缩放比例 |
| 对齐支持 | 支持内容对齐方式 |
| 动画效果 | 内置平滑的交互动画 |
| 手势拦截 | 支持拦截和处理手势事件 |
InteractiveViewer 与其他缩放方案对比
| 方案 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| InteractiveViewer | 功能全面、易于使用 | 仅支持单一子组件 |
| GestureDetector | 灵活度高 | 需要手动处理手势计算 |
| Transform | 完全自定义 | 需要手动处理所有交互 |
| photo_view 插件 | 功能丰富、开箱即用 | 需要额外依赖 |
💡 使用场景:InteractiveViewer 适合需要缩放、平移交互的场景,如图片查看器、地图查看、PDF阅读器、图表查看等。
二、InteractiveViewer 基础用法
InteractiveViewer 的使用非常简单,只需要将需要交互的内容作为子组件传入。让我们从最基础的用法开始学习。
2.1 最简单的 InteractiveViewer
最基础的 InteractiveViewer 只需要提供一个子组件:
InteractiveViewer(
child: Image.network('https://example.com/image.jpg'),
)
2.2 设置缩放限制
通过 minScale 和 maxScale 参数设置缩放限制:
InteractiveViewer(
minScale: 0.5,
maxScale: 4.0,
child: Image.network('https://example.com/image.jpg'),
)
2.3 设置边界限制
通过 boundaryMargin 参数设置边界边距:
InteractiveViewer(
boundaryMargin: const EdgeInsets.all(double.infinity),
child: Image.network('https://example.com/image.jpg'),
)
2.4 完整示例
下面是一个完整的可运行示例,展示了 InteractiveViewer 的基础用法:
class InteractiveViewerBasicExample extends StatelessWidget {
const InteractiveViewerBasicExample({super.key});
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('InteractiveViewer 基础示例')),
body: Center(
child: InteractiveViewer(
minScale: 0.5,
maxScale: 4.0,
boundaryMargin: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Container(
width: 300,
height: 300,
color: Colors.blue[100],
child: const Center(
child: Text(
'双指缩放\n拖拽平移',
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 24),
),
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
三、InteractiveViewer 核心属性详解
InteractiveViewer 提供了丰富的属性来控制交互行为。
3.1 缩放相关属性
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| minScale | double | 0.8 | 最小缩放比例 |
| maxScale | double | 2.5 | 最大缩放比例 |
| scaleEnabled | bool | true | 是否启用缩放 |
| scaleFactor | double | 1.0 | 初始缩放比例 |
3.2 平移相关属性
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| panEnabled | bool | true | 是否启用平移 |
| boundaryMargin | EdgeInsetsGeometry | EdgeInsets.zero | 边界边距 |
| alignment | Alignment | Alignment.center | 内容对齐方式 |
3.3 约束相关属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| constrained | 是否约束子组件大小 |
| clipBehavior | 裁剪行为 |
3.4 交互回调
| 回调 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| onInteractionStart | 交互开始回调 |
| onInteractionUpdate | 交互更新回调 |
| onInteractionEnd | 交互结束回调 |
四、InteractiveViewer 实际应用场景
InteractiveViewer 在实际开发中有着广泛的应用,让我们通过具体示例来学习。
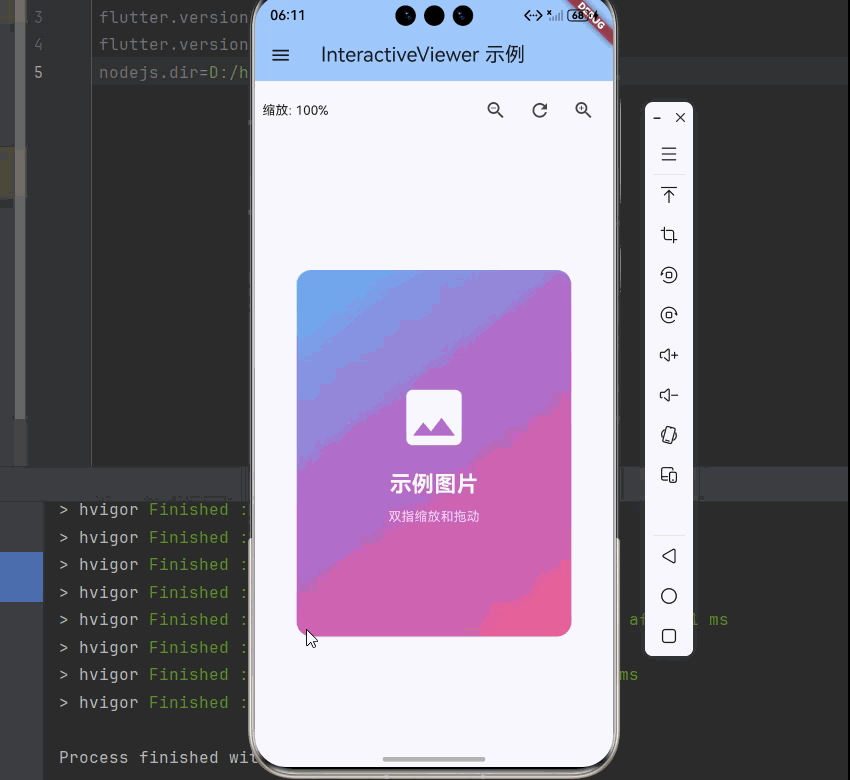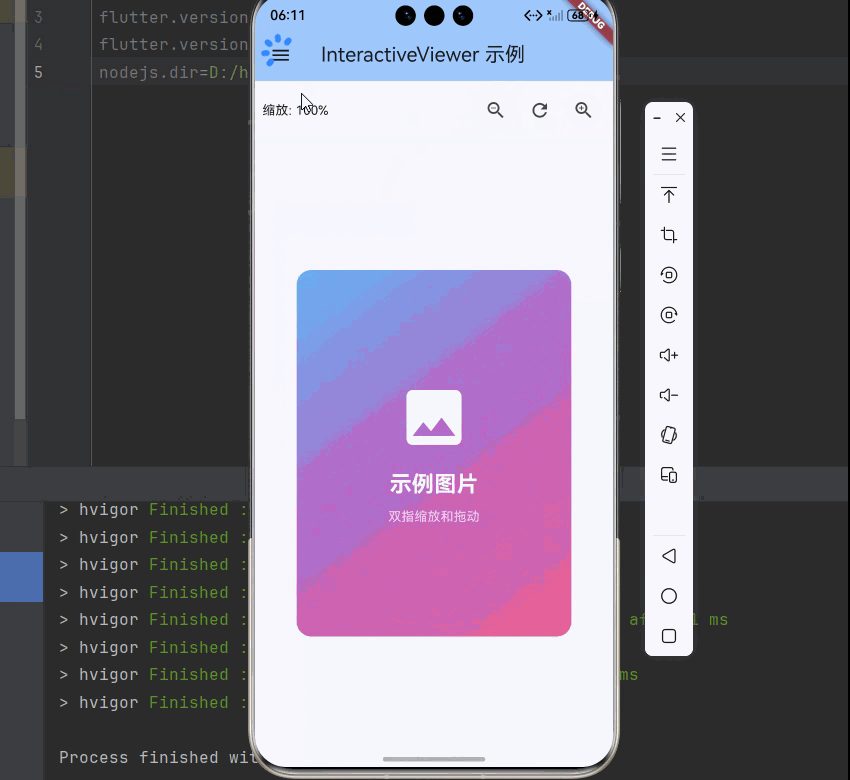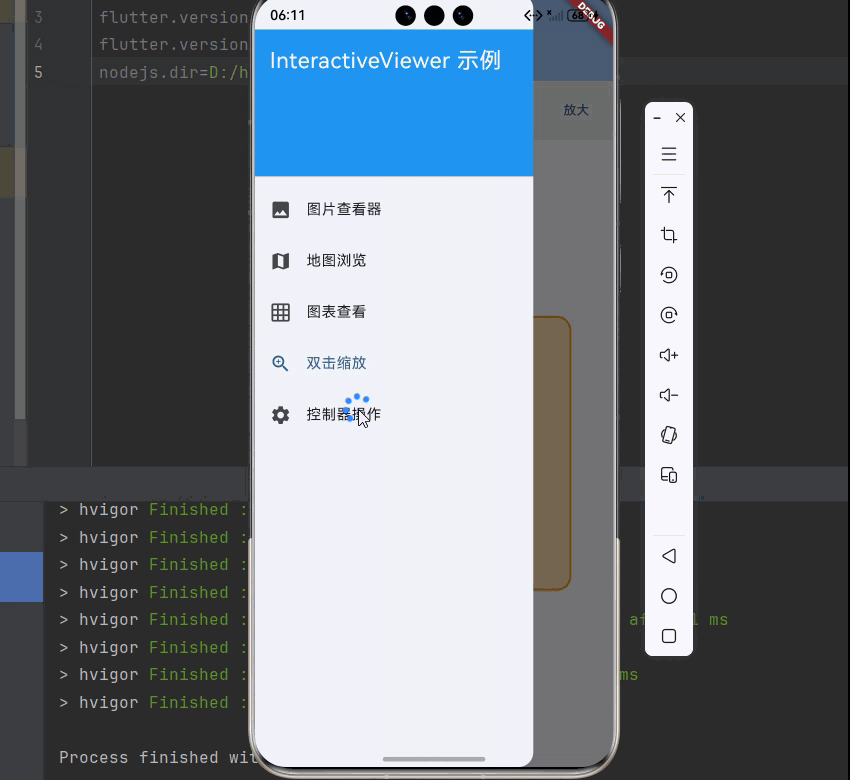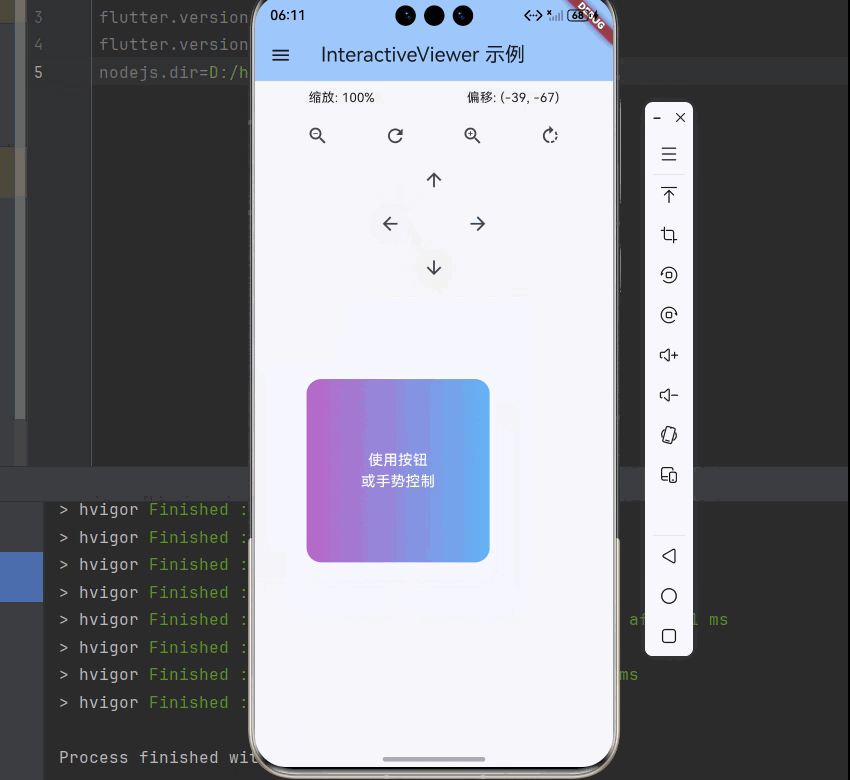
4.1 图片查看器
使用 InteractiveViewer 创建图片查看器:
class ImageViewerPage extends StatefulWidget {
const ImageViewerPage({super.key});
State<ImageViewerPage> createState() => _ImageViewerPageState();
}
class _ImageViewerPageState extends State<ImageViewerPage> {
final TransformationController _controller = TransformationController();
double _currentScale = 1.0;
void _resetView() {
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity();
setState(() {
_currentScale = 1.0;
});
}
void _zoomIn() {
final newScale = (_currentScale * 1.2).clamp(0.5, 4.0);
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(newScale);
setState(() {
_currentScale = newScale;
});
}
void _zoomOut() {
final newScale = (_currentScale / 1.2).clamp(0.5, 4.0);
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(newScale);
setState(() {
_currentScale = newScale;
});
}
void dispose() {
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('图片查看器'),
actions: [
IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.refresh),
onPressed: _resetView,
tooltip: '重置',
),
],
),
body: Stack(
children: [
Center(
child: InteractiveViewer(
transformationController: _controller,
minScale: 0.5,
maxScale: 4.0,
boundaryMargin: const EdgeInsets.all(double.infinity),
onInteractionUpdate: (details) {
setState(() {
_currentScale = _controller.value.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
});
},
child: Image.network(
'https://picsum.photos/800/600',
fit: BoxFit.contain,
loadingBuilder: (context, child, loadingProgress) {
if (loadingProgress == null) return child;
return Center(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(
value: loadingProgress.expectedTotalBytes != null
? loadingProgress.cumulativeBytesLoaded /
loadingProgress.expectedTotalBytes!
: null,
),
);
},
errorBuilder: (context, error, stackTrace) {
return const Center(
child: Icon(Icons.error, size: 48, color: Colors.red),
);
},
),
),
),
Positioned(
bottom: 20,
left: 0,
right: 0,
child: Center(
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16, vertical: 8),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: Colors.black54,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20),
),
child: Text(
'${(_currentScale * 100).round()}%',
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
),
),
),
],
),
floatingActionButton: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: [
FloatingActionButton(
heroTag: 'zoomIn',
mini: true,
onPressed: _zoomIn,
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
FloatingActionButton(
heroTag: 'zoomOut',
mini: true,
onPressed: _zoomOut,
child: const Icon(Icons.remove),
),
],
),
);
}
}
4.2 图表查看器
使用 InteractiveViewer 查看大型图表:
class ChartViewerPage extends StatelessWidget {
const ChartViewerPage({super.key});
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('图表查看器')),
body: InteractiveViewer(
minScale: 0.3,
maxScale: 2.0,
constrained: false,
child: Container(
width: 800,
height: 600,
color: Colors.white,
child: CustomPaint(
painter: ChartPainter(),
),
),
),
);
}
}
class ChartPainter extends CustomPainter {
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
final paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[300]!
..strokeWidth = 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
final x = i * size.width / 10;
canvas.drawLine(Offset(x, 0), Offset(x, size.height), paint);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
final y = i * size.height / 10;
canvas.drawLine(Offset(0, y), Offset(size.width, y), paint);
}
final dataPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.blue
..strokeWidth = 3
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke;
final path = Path();
final points = [
const Offset(0, 400),
const Offset(80, 350),
const Offset(160, 300),
const Offset(240, 320),
const Offset(320, 250),
const Offset(400, 200),
const Offset(480, 220),
const Offset(560, 150),
const Offset(640, 180),
const Offset(720, 100),
const Offset(800, 80),
];
path.moveTo(points[0].dx, points[0].dy);
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
path.lineTo(points[i].dx, points[i].dy);
}
canvas.drawPath(path, dataPaint);
final dotPaint = Paint()..color = Colors.blue;
for (final point in points) {
canvas.drawCircle(point, 6, dotPaint);
}
final textPainter = TextPainter(
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
);
final labels = ['一月', '二月', '三月', '四月', '五月', '六月', '七月', '八月', '九月', '十月', '十一月'];
for (int i = 0; i < labels.length; i++) {
textPainter.text = TextSpan(
text: labels[i],
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.black87, fontSize: 12),
);
textPainter.layout();
textPainter.paint(canvas, Offset(i * 80 - 20, size.height - 30));
}
}
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => false;
}
4.3 地图查看器
使用 InteractiveViewer 查看自定义地图:
class MapViewerPage extends StatefulWidget {
const MapViewerPage({super.key});
State<MapViewerPage> createState() => _MapViewerPageState();
}
class _MapViewerPageState extends State<MapViewerPage> {
final TransformationController _controller = TransformationController();
void dispose() {
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('地图查看器'),
actions: [
IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.my_location),
onPressed: () {
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity();
},
),
],
),
body: InteractiveViewer(
transformationController: _controller,
minScale: 0.5,
maxScale: 3.0,
constrained: false,
boundaryMargin: const EdgeInsets.all(100),
child: Container(
width: 1000,
height: 800,
color: Colors.green[50],
child: Stack(
children: [
CustomPaint(
size: const Size(1000, 800),
painter: MapPainter(),
),
..._buildMarkers(),
],
),
),
),
);
}
List<Widget> _buildMarkers() {
return [
_buildMarker(200, 300, 'A区', Colors.red),
_buildMarker(400, 200, 'B区', Colors.blue),
_buildMarker(600, 400, 'C区', Colors.green),
_buildMarker(800, 300, 'D区', Colors.orange),
];
}
Widget _buildMarker(double x, double y, String label, Color color) {
return Positioned(
left: x - 20,
top: y - 40,
child: GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text('点击了 $label')),
);
},
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 8, vertical: 4),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(4),
),
child: Text(
label,
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 12),
),
),
Icon(Icons.location_on, color: color, size: 30),
],
),
),
);
}
}
class MapPainter extends CustomPainter {
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
final roadPaint = Paint()
..color = Colors.grey[400]!
..strokeWidth = 8
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke;
final path1 = Path();
path1.moveTo(0, size.height / 2);
path1.lineTo(size.width, size.height / 2);
canvas.drawPath(path1, roadPaint);
final path2 = Path();
path2.moveTo(size.width / 2, 0);
path2.lineTo(size.width / 2, size.height);
canvas.drawPath(path2, roadPaint);
final path3 = Path();
path3.moveTo(0, 100);
path3.quadraticBezierTo(size.width / 2, 200, size.width, 100);
canvas.drawPath(path3, roadPaint);
final buildingPaint = Paint()..color = Colors.grey[300]!;
canvas.drawRect(const Rect.fromLTWH(100, 350, 200, 150), buildingPaint);
canvas.drawRect(const Rect.fromLTWH(300, 100, 200, 150), buildingPaint);
canvas.drawRect(const Rect.fromLTWH(500, 450, 200, 150), buildingPaint);
canvas.drawRect(const Rect.fromLTWH(700, 150, 200, 150), buildingPaint);
}
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => false;
}
五、TransformationController 控制器
TransformationController 用于程序化控制 InteractiveViewer 的变换。
5.1 基本用法
final TransformationController _controller = TransformationController();
InteractiveViewer(
transformationController: _controller,
child: Image.network('...'),
)
void resetView() {
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity();
}
5.2 程序化缩放
void zoomTo(double scale) {
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(scale);
}
void zoomIn() {
final currentScale = _controller.value.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
final newScale = (currentScale * 1.2).clamp(0.5, 4.0);
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(newScale);
}
void zoomOut() {
final currentScale = _controller.value.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
final newScale = (currentScale / 1.2).clamp(0.5, 4.0);
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(newScale);
}
5.3 程序化平移
void panTo(Offset offset) {
final matrix = _controller.value.clone();
matrix.translate(offset.dx, offset.dy);
_controller.value = matrix;
}
5.4 动画变换
void animatedZoom(double targetScale) {
final animation = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 300),
vsync: this,
);
final startScale = _controller.value.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
final animationCurve = CurvedAnimation(
parent: animation,
curve: Curves.easeInOut,
);
animation.addListener(() {
final currentScale = startScale + (targetScale - startScale) * animationCurve.value;
_controller.value = Matrix4.identity()..scale(currentScale);
});
animation.forward();
}
六、交互回调详解
InteractiveViewer 提供了三个交互回调函数。
6.1 onInteractionStart
交互开始时触发:
InteractiveViewer(
onInteractionStart: (details) {
print('交互开始');
print('焦点: ${details.localFocalPoint}');
print('指针数量: ${details.pointerCount}');
},
child: Image.network('...'),
)
6.2 onInteractionUpdate
交互更新时触发:
InteractiveViewer(
onInteractionUpdate: (details) {
print('缩放比例: ${details.scale}');
print('水平平移: ${details.focalPointDelta.dx}');
print('垂直平移: ${details.focalPointDelta.dy}');
},
child: Image.network('...'),
)
6.3 onInteractionEnd
交互结束时触发:
InteractiveViewer(
onInteractionEnd: (details) {
print('交互结束');
print('速度: ${details.velocity}');
},
child: Image.network('...'),
)
📊 ScaleUpdateDetails 属性速查表
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| focalPoint | 焦点位置(全局坐标) |
| localFocalPoint | 焦点位置(本地坐标) |
| scale | 当前缩放比例 |
| horizontalScale | 水平缩放比例 |
| verticalScale | 垂直缩放比例 |
| rotation | 旋转角度 |
| pointerCount | 触摸点数量 |
七、高级用法
7.1 双击缩放
实现双击缩放功能:
class DoubleTapZoomViewer extends StatefulWidget {
const DoubleTapZoomViewer({super.key});
State<DoubleTapZoomViewer> createState() => _DoubleTapZoomViewerState();
}
class _DoubleTapZoomViewerState extends State<DoubleTapZoomViewer>
with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
final TransformationController _controller = TransformationController();
Animation<Matrix4>? _animation;
AnimationController? _animationController;
void initState() {
super.initState();
_animationController = AnimationController(
vsync: this,
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 300),
);
}
void dispose() {
_controller.dispose();
_animationController?.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
void _handleDoubleTap(Offset tapPosition) {
final currentScale = _controller.value.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
final targetScale = currentScale > 1.5 ? 1.0 : 2.5;
final position = tapPosition;
final x = -position.dx * (targetScale - 1);
final y = -position.dy * (targetScale - 1);
final targetMatrix = Matrix4.identity()
..translate(x, y)
..scale(targetScale);
_animation = Matrix4Tween(
begin: _controller.value,
end: targetMatrix,
).animate(CurvedAnimation(
parent: _animationController!,
curve: Curves.easeInOut,
));
_animationController!.reset();
_animationController!.forward();
_animationController!.addListener(() {
_controller.value = _animation!.value;
});
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('双击缩放')),
body: Center(
child: GestureDetector(
onDoubleTapDown: (details) {
_handleDoubleTap(details.localPosition);
},
child: InteractiveViewer(
transformationController: _controller,
minScale: 0.5,
maxScale: 4.0,
child: Image.network(
'https://picsum.photos/800/600',
fit: BoxFit.contain,
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
7.2 限制平移范围
限制内容只能在特定范围内平移:
class BoundedViewer extends StatefulWidget {
const BoundedViewer({super.key});
State<BoundedViewer> createState() => _BoundedViewerState();
}
class _BoundedViewerState extends State<BoundedViewer> {
final TransformationController _controller = TransformationController();
static const double _minScale = 1.0;
static const double _maxScale = 4.0;
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller.addListener(_onTransformChanged);
}
void dispose() {
_controller.removeListener(_onTransformChanged);
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
void _onTransformChanged() {
final matrix = _controller.value;
final scale = matrix.getMaxScaleOnAxis();
if (scale < _minScale || scale > _maxScale) {
final clampedScale = scale.clamp(_minScale, _maxScale);
final correctedMatrix = Matrix4.identity()..scale(clampedScale);
_controller.value = correctedMatrix;
}
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('限制范围')),
body: Center(
child: InteractiveViewer(
transformationController: _controller,
minScale: _minScale,
maxScale: _maxScale,
boundaryMargin: const EdgeInsets.all(50),
child: Container(
width: 300,
height: 300,
color: Colors.blue[100],
child: const Center(child: Text('内容')),
),
),
),
);
}
}
八、最佳实践
8.1 性能优化
| 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 使用 constrained | 大内容设置 constrained: false |
| 避免复杂子组件 | 简化 InteractiveViewer 的子组件 |
| 合理设置缩放范围 | 避免过大的缩放范围 |
8.2 交互设计
| 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 提供重置按钮 | 允许用户一键恢复初始状态 |
| 显示缩放比例 | 实时显示当前缩放比例 |
| 双击缩放 | 提供双击快速缩放功能 |
8.3 样式设计
| 建议 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 合理的边界 | 设置合适的 boundaryMargin |
| 平滑动画 | 使用动画过渡变换效果 |
九、总结
InteractiveViewer 是 Flutter 中用于实现缩放、平移交互的组件,适合需要手势交互的查看场景。通过本文的学习,你应该已经掌握了:
- InteractiveViewer 的基本用法和核心概念
- TransformationController 的程序化控制
- 如何实现图片查看器、图表查看器、地图查看器
- 交互回调的使用方法
- 双击缩放等高级功能的实现
在实际开发中,InteractiveViewer 常用于图片查看、地图浏览、图表查看等场景。结合 TransformationController,可以实现更丰富的交互功能。
参考资料
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献30条内容
已为社区贡献30条内容






所有评论(0)