Flutter三方库适配OpenHarmony【apple_product_name】lookup查询方法使用技巧
本文介绍了开源鸿蒙跨平台社区中apple_product_name库的lookup方法,这是一个灵活的设备型号查询接口,支持通过任意型号标识符获取产品名称。文章详细解析了方法定义、降级策略、原生侧实现以及典型应用场景。核心内容包括: 功能特点:lookup方法支持跨设备查询,未命中时返回原始值而非抛出异常 变体方法:lookupOrNull在未命中时返回null,便于区分已知/未知设备 性能优化:
前言
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
lookup方法是apple_product_name库中功能最灵活的查询接口,它突破了"只能查询当前设备"的限制,允许开发者通过传入任意型号标识符来查询对应的产品名称。这意味着你可以在一台设备上查询另一台设备的产品名称,这在处理服务器端返回的设备列表数据、进行设备统计分析以及构建设备管理后台等场景中非常实用。
本文将从方法定义出发,逐步深入介绍lookup方法的各种使用技巧和典型应用场景。先给出结论式摘要:
lookup做了什么:将任意machineId(如"ALN-AL00")通过原生侧映射表转换为友好名称(如"HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro"),未命中则返回原始值而非抛异常lookupOrNull的区别:未命中时返回null而非原始值,适合需要区分"已知/未知设备"的场景- 性能关键点:每次调用都走 MethodChannel,批量场景建议用并行查询 + 缓存
提示:如果你还不了解
getProductName的三级降级策略,建议先阅读 getProductName方法实战应用;lookup的原生侧查询逻辑与其中的"第一级映射表查找"完全一致。
目录
- lookup 方法定义与降级策略
- lookupOrNull 变体方法
- 原生侧实现与O(1)查找
- 调用链路总览(附图)
- 基础查询与返回值约定
- 批量查询与并行优化
- 缓存查询结果
- 设备列表UI展示
- 设备支持检测
- 统计分析应用
- 错误处理模式
- 服务器数据转换实战
- 单元测试策略
- 常见坑与排查清单
- 总结
一、lookup 方法定义与降级策略
1.1 Dart侧API签名
/// 根据型号标识符查找产品名称
///
/// [machineId] 设备型号标识符,如 "ALN-AL00"
/// 返回产品名称,如 "HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro",如果未找到则返回原始 machineId
Future<String> lookup(String machineId) async {
final String? productName = await _channel.invokeMethod('lookup', {
'machineId': machineId,
});
return productName ?? machineId;
}
lookup方法接受一个 machineId 参数,通过 MethodChannel 将其传递给原生侧映射表进行查找。核心的降级策略是:当映射表中不存在该型号时,不会抛异常或返回空值,而是通过 ?? machineId 直接返回原始值。这意味着调用方始终能获得一个有意义的字符串,可以放心用于 UI 展示。
1.2 与 getMachineId / getProductName 的定位对比
| 方法 | 输入 | 输出 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
getMachineId() |
无(读取当前设备) | 原始型号编码 | 日志、兼容性匹配 |
getProductName() |
无(读取当前设备) | 友好名称(三级降级) | UI展示当前设备 |
lookup(machineId) |
任意型号字符串 | 友好名称或原始值 | 查询任意设备、批量转换 |
lookupOrNull(machineId) |
任意型号字符串 | 友好名称或 null |
设备支持检测 |
提示:
lookup是唯一支持传入参数的查询方法,其他方法都只能查询当前设备。
二、lookupOrNull 变体方法
2.1 方法签名
/// 根据型号标识符查找产品名称
///
/// [machineId] 设备型号标识符
/// 返回产品名称,如果未找到则返回 null
Future<String?> lookupOrNull(String machineId) async {
final String? productName = await _channel.invokeMethod('lookup', {
'machineId': machineId,
});
return productName;
}
与 lookup 的唯一区别:未命中时返回 null 而非原始值。这在需要**明确区分"已知设备"和"未知设备"**时非常有用。
2.2 lookup vs lookupOrNull 选择指南
- 用
lookup:需要展示设备名称,未知设备也要显示点什么(显示原始型号) - 用
lookupOrNull:需要判断设备是否在映射表中,null作为"未知"的信号
注意:在 Dart 的空安全体系下,
String?返回类型能让编译器帮你在编译期发现潜在的空指针问题。
三、原生侧实现与O(1)查找
3.1 TypeScript 实现
private lookup(call: MethodCall, result: MethodResult): void {
try {
const machineId = call.argument("machineId") as string;
if (!machineId) {
result.error("INVALID_ARGUMENT", "machineId is required", null);
return;
}
const productName = HUAWEI_DEVICE_MAP[machineId];
result.success(productName); // 未找到返回 undefined → Dart 侧收到 null
} catch (e) {
const errorMsg = e instanceof Error ? e.message : String(e);
result.error("LOOKUP_ERROR", errorMsg, null);
}
}
几个关键设计细节:
- 参数校验:空
machineId会返回INVALID_ARGUMENT错误码,Dart 侧触发PlatformException - O(1) 查找:
HUAWEI_DEVICE_MAP本质是 JS 对象(哈希表),查找时间复杂度恒定 - 未命中处理:JS 属性访问返回
undefined,经平台通道传输后 Dart 侧收到null
3.2 onMethodCall 路由
onMethodCall(call: MethodCall, result: MethodResult): void {
switch (call.method) {
case "getMachineId":
this.getMachineId(result);
break;
case "getProductName":
this.getProductName(result);
break;
case "lookup":
this.lookup(call, result);
break;
default:
result.notImplemented();
break;
}
}
注意 lookup 是三个方法中唯一需要传递 call 参数的,因为它需要从 call.argument("machineId") 中提取查询参数。
提示:关于
onMethodCall路由机制的详细说明,参考 MethodChannel通信机制详解。
四、终端数据打印
五、基础查询与返回值约定
5.1 基础查询示例
Future<void> queryDevice() async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
// 查询已知设备 → 返回友好名称
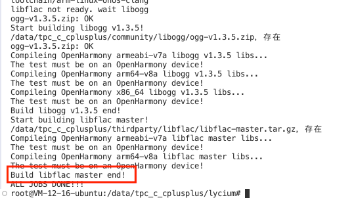
final mate60Pro = await ohos.lookup('ALN-AL00');
print(mate60Pro); // HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro
// 查询未知设备 → 返回原始值
final unknown = await ohos.lookup('XXX-XX00');
print(unknown); // XXX-XX00
// lookupOrNull:未知设备 → 返回 null
final nullResult = await ohos.lookupOrNull('XXX-XX00');
print(nullResult); // null
}
5.2 返回值约定表
| 输入 | lookup 返回 |
lookupOrNull 返回 |
说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
"ALN-AL00" |
"HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro" |
"HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro" |
映射表命中 |
"XXX-XX00" |
"XXX-XX00" |
null |
映射表未命中 |
"" (空串) |
抛 PlatformException |
抛 PlatformException |
参数校验失败 |
提示:建议将
OhosProductName实例作为单例管理,避免每次查询都创建新实例。关于 Dart 异步编程基础,参考 Dart async/await。
六、批量查询与并行优化
6.1 顺序批量查询
Future<List<String>> batchLookup(List<String> machineIds) async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
final results = <String>[];
for (final id in machineIds) {
final name = await ohos.lookup(id);
results.add(name);
}
return results;
}
顺序查询简单直观,但总耗时 = 所有单次查询耗时之和。列表较长时(50+)建议用并行方式。
6.2 并行批量查询(推荐)
Future<List<String>> parallelBatchLookup(
List<String> machineIds) async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
final futures = machineIds.map((id) => ohos.lookup(id));
return await Future.wait(futures);
}
利用 Future.wait 同时发起所有查询,总耗时取决于最慢的那一次,通常能带来数倍性能提升。
6.3 顺序 vs 并行性能对比
| 方式 | 10个设备 | 50个设备 | 100个设备 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 顺序 | ~20-50ms | ~100-250ms | ~200-500ms |
| 并行 | ~2-5ms | ~3-8ms | ~5-10ms |
注意事项:
- 如果列表非常大(数千个),同时发起大量平台通道调用可能造成压力,建议分批并行(每批50个)
Future.wait默认任一 Future 异常则整体失败,生产环境建议为每个查询单独加 try-catch
提示:关于
Future.wait的详细用法,参考 Dart Future API。
七、缓存查询结果
7.1 带缓存的 lookup 封装
class CachedLookup {
final Map<String, String> _cache = {};
final OhosProductName _ohos = OhosProductName();
Future<String> lookup(String machineId) async {
if (_cache.containsKey(machineId)) {
return _cache[machineId]!;
}
final name = await _ohos.lookup(machineId);
_cache[machineId] = name;
return name;
}
void clearCache() => _cache.clear();
int get cacheSize => _cache.length;
}
由于同一个 machineId 的查询结果永远不会变(映射表是静态的),缓存策略完全安全。首次查询走 MethodChannel(2-5ms),后续直接返回内存值(0.001ms)。
7.2 预构建映射字典
Future<Map<String, String>> createDeviceMap(
List<String> machineIds) async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
final deviceMap = <String, String>{};
for (final id in machineIds) {
deviceMap[id] = await ohos.lookup(id);
}
return deviceMap;
}
// 使用:一次性构建,后续同步访问
final map = await createDeviceMap(['ALN-AL00', 'CFR-AN00']);
print(map['ALN-AL00']); // HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro
适合在应用初始化阶段一次性加载所有需要的设备信息,后续通过字典的同步键值访问来使用,无需再走异步调用。
提示:建议将
CachedLookup实例作为单例管理,确保整个应用共享同一份缓存。
八、设备列表UI展示
8.1 ListView + FutureBuilder
class DeviceListPage extends StatelessWidget {
final List<String> machineIds = [
'ALN-AL00', 'CFR-AN00', 'HBN-AL00', 'GGK-W10',
];
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('设备列表')),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: machineIds.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return FutureBuilder<String>(
future: OhosProductName().lookup(machineIds[index]),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
return ListTile(
leading: const Icon(Icons.phone_android),
title: Text(snapshot.data ?? '加载中...'),
subtitle: Text(machineIds[index]),
);
},
);
},
),
);
}
}
每个列表项通过 FutureBuilder 异步加载产品名称,主标题显示友好名称,副标题保留原始型号供技术人员参考。
8.2 生产环境优化建议
上面的示例在列表滚动时会重复触发查询。生产环境建议:
- 在
initState中一次性完成所有查询,结果存入 State - 或使用
CachedLookup单例,自动避免重复查询 - 或使用状态管理方案(Provider / Riverpod / BLoC)管理加载状态
九、设备支持检测
9.1 利用 lookupOrNull 判断设备是否已知
class DeviceSupportChecker {
static Future<bool> isSupported(String machineId) async {
final name = await OhosProductName().lookupOrNull(machineId);
return name != null;
}
static Future<List<String>> filterSupported(
List<String> machineIds) async {
final supported = <String>[];
for (final id in machineIds) {
if (await isSupported(id)) supported.add(id);
}
return supported;
}
}
lookupOrNull 返回 null 表示映射表中不存在该型号,返回非空则表示已知设备。这在设备兼容性检测、设备支持列表过滤等场景中非常实用。
9.2 检测结果的UI呈现建议
- 已支持设备:绿色标识 ✓
- 未知设备:黄色警告标识 ⚠
- 查询失败:红色错误标识 ✗
注意:映射表的覆盖范围有限,
isSupported返回false不代表设备不兼容,只是说明该型号尚未被收录到映射表中。
十、统计分析应用
10.1 设备分布统计
class DeviceStatistics {
static Future<Map<String, int>> analyzeDevices(
List<String> machineIds) async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
final stats = <String, int>{};
for (final id in machineIds) {
final name = await ohos.lookup(id);
stats[name] = (stats[name] ?? 0) + 1;
}
return stats;
}
}
// 使用示例
final ids = ['ALN-AL00', 'ALN-AL00', 'CFR-AN00', 'ALN-AL00'];
final stats = await DeviceStatistics.analyzeDevices(ids);
// {'HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro': 3, 'HUAWEI Mate 70': 1}
将型号编码转换为产品名称后再统计,产品经理可以直接看到"HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro 占比 75%"这样清晰的数据,而不是面对一堆 ALN-AL00。
10.2 统计数据的扩展维度
在此基础上可以扩展更多统计维度:
- 按设备品牌分组(HUAWEI / Honor)
- 按设备系列分组(Mate / Pura / nova)
- 计算各型号占比百分比
- 按时间维度分析设备分布变化趋势
提示:如果数据量较大,建议结合
CachedLookup避免对相同型号的重复查询。
十一、错误处理模式
11.1 安全查询封装
Future<String> safeLookup(String machineId) async {
if (machineId.isEmpty) return 'Invalid ID';
try {
return await OhosProductName().lookup(machineId);
} on PlatformException catch (e) {
print('查询失败: ${e.code} - ${e.message}');
return machineId;
} catch (e) {
print('未知错误: $e');
return machineId;
}
}
错误处理的核心原则:永远不要让查询失败影响到用户体验。即使发生异常,用户看到的也应该是一个合理的设备标识信息。
11.2 错误码速查
| 错误码 | 触发条件 | Dart 侧表现 | 建议处理 |
|---|---|---|---|
INVALID_ARGUMENT |
machineId 为空 |
PlatformException |
前置校验,不传空串 |
LOOKUP_ERROR |
原生侧运行时异常 | PlatformException |
记录日志 + 降级返回原始值 |
MissingPluginException |
插件未注册 | MissingPluginException |
全量重启;核对通道名 |
提示:对于批量查询场景,建议在每个单独的查询上都应用错误处理,确保单个失败不影响整体。关于异常处理的更多模式,参考 异步调用与错误处理。
十二、服务器数据转换实战
12.1 完整的数据转换流程
class DeviceInfo {
final String machineId;
final String productName;
final String userId;
DeviceInfo({
required this.machineId,
required this.productName,
required this.userId,
});
}
Future<List<DeviceInfo>> convertServerData(
List<Map<String, dynamic>> serverData) async {
final ohos = OhosProductName();
final result = <DeviceInfo>[];
for (final item in serverData) {
final machineId = item['device_id'] as String;
final productName = await ohos.lookup(machineId);
result.add(DeviceInfo(
machineId: machineId,
productName: productName,
userId: item['user_id'] as String,
));
}
return result;
}
DeviceInfo 模型同时保留 machineId 和 productName——原始型号用于回溯和精确匹配,产品名称用于面向用户的展示。
12.2 典型数据流
完整的数据处理管道通常是:
- 从服务器 API 获取原始设备日志数据
- 提取
device_id字段(型号标识符) - 调用
lookup批量转换为产品名称 - 传递给 UI 层 / 图表组件进行渲染
提示:建议将数据转换逻辑封装在独立的 Repository 或 Service 层中,与 UI 层解耦。关于 Flutter 插件开发的架构设计,参考 Developing packages & plugins。
十三、单元测试策略
13.1 Mock MethodChannel 测试 lookup
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:flutter_test/flutter_test.dart';
void main() {
const channel = MethodChannel('apple_product_name');
TestWidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
setUp(() {
TestDefaultBinaryMessengerBinding
.instance.defaultBinaryMessenger
.setMockMethodCallHandler(channel, (call) async {
if (call.method == 'lookup') {
final machineId = call.arguments['machineId'] as String;
// 模拟映射表
const mockMap = {
'ALN-AL00': 'HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro',
'CFR-AN00': 'HUAWEI Mate 70',
};
return mockMap[machineId]; // 未命中返回 null
}
return null;
});
});
tearDown(() {
TestDefaultBinaryMessengerBinding
.instance.defaultBinaryMessenger
.setMockMethodCallHandler(channel, null);
});
test('lookup 命中映射表', () async {
final name = await OhosProductName().lookup('ALN-AL00');
expect(name, 'HUAWEI Mate 60 Pro');
});
test('lookup 未命中返回原始值', () async {
final name = await OhosProductName().lookup('XXX-XX00');
expect(name, 'XXX-XX00');
});
test('lookupOrNull 未命中返回 null', () async {
final name = await OhosProductName().lookupOrNull('XXX-XX00');
expect(name, isNull);
});
}
通过 Mock MethodChannel 可以在测试环境中模拟映射表的命中/未命中行为,验证 lookup 和 lookupOrNull 的降级逻辑是否正确。
13.2 测试要点清单
需要覆盖的测试场景:
- 映射表命中 → 返回友好名称
- 映射表未命中 →
lookup返回原始值,lookupOrNull返回null - 空字符串输入 → 抛出
PlatformException - 批量查询 → 结果顺序与输入一致
提示:关于 Flutter 测试的更多用法,参考 Flutter testing documentation。
十四、常见坑与排查清单
14.1 常见坑
- 忘记
await:lookup返回Future<String>,不await拿到的是 Future 对象而非字符串 - 在
build()中直接调用:每次 Widget 重建都触发 MethodChannel 调用,应缓存结果 - 空字符串传入:原生侧会返回
INVALID_ARGUMENT错误,Dart 侧抛PlatformException - 混淆
lookup和lookupOrNull:前者未命中返回原始值,后者返回null,用错会导致逻辑错误
14.2 排查步骤
- 确认运行平台:是否在 OpenHarmony 设备/模拟器上运行
- 核对通道名:Dart 侧
MethodChannel('apple_product_name')与原生侧必须一致 - 检查参数传递:确认
machineId不为空且格式正确 - 查看原生日志:在
lookup方法中打印machineId和查找结果 - 验证映射表:确认目标型号确实存在于
HUAWEI_DEVICE_MAP中
14.3 lookup 方法完整错误处理决策树
- 输入为空串?→ 前置校验拦截,不发起调用
- 抛
MissingPluginException?→ 插件未注册,全量重启 - 抛
PlatformException(INVALID_ARGUMENT)?→ 参数问题,检查传入值 - 抛
PlatformException(LOOKUP_ERROR)?→ 原生侧异常,记录日志 + 降级 - 返回原始值(
lookup)/null(lookupOrNull)?→ 正常行为,映射表未收录该型号
提示:关于
MissingPluginException的官方说明,参考 MissingPluginException class。
总结
lookup方法是 apple_product_name 库中功能最灵活的查询接口,它支持传入任意型号标识符进行查询,突破了"只能查询当前设备"的限制。本文从方法定义、原生实现出发,覆盖了基础查询、批量转换、并行优化、缓存策略、UI展示、设备检测、统计分析、错误处理、服务器数据转换和单元测试等多个实战维度。在实际项目中,建议结合 CachedLookup 单例和并行查询来优化性能,配合 lookupOrNull 实现设备支持检测。
下一篇文章将详细介绍 MethodChannel 通信机制的实现细节,敬请期待。
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎点赞👍、收藏⭐、关注🔔,你的支持是我持续创作的动力!
相关资源:
- OpenHarmony适配仓库:flutter_apple_product_name
- 开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:openharmonycrossplatform
- Flutter MethodChannel API:MethodChannel class
- Flutter FutureBuilder API:FutureBuilder class
- Dart async/await 指南:Dart asynchronous programming
- Dart Future.wait API:Future.wait
- Flutter 插件开发指南:Developing packages & plugins
- MissingPluginException:API 文档
- Flutter 测试文档:Testing Flutter apps
- Flutter Platform channels:官方文档
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献43条内容
已为社区贡献43条内容







所有评论(0)