Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:扫雷游戏算法深度解析与优化
扫雷游戏看似简单,但其背后蕴含了丰富的算法设计与优化技巧。本文深入探讨扫雷游戏的核心算法实现,包括洪水填充算法的递归与迭代实现对比、地雷生成的优化策略、游戏可解性保证、自动求解算法等高级主题。通过本文学习,读者将掌握如何在实际项目中应用算法优化技巧,提升游戏性能和用户体验。洪水填充算法:递归vs迭代,BFS vs DFS地雷生成优化:避免首次踩雷、洗牌算法、可解性保证高级功能:双键点击、计时器、最
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:扫雷游戏算法深度解析与优化
文章目录
摘要
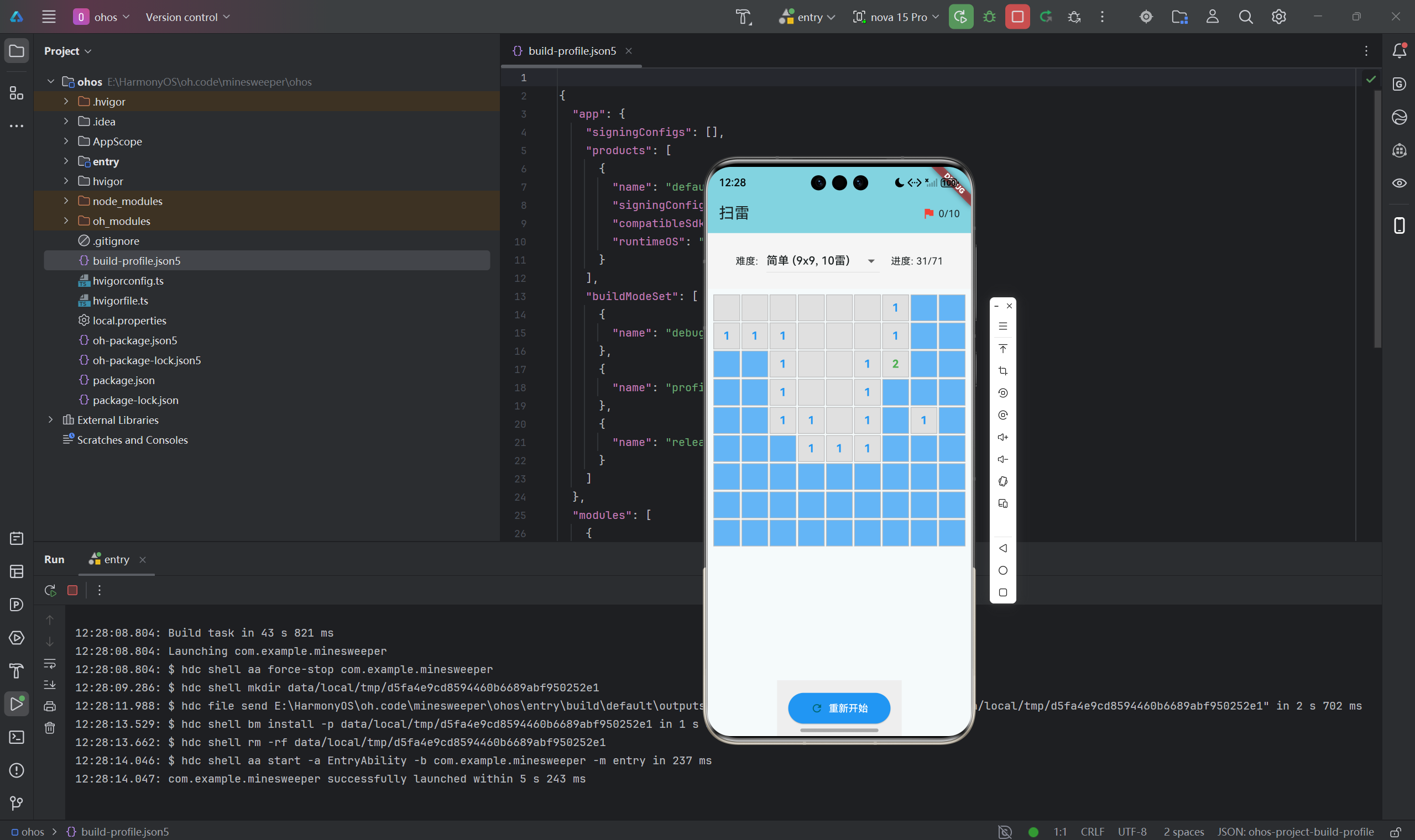
扫雷游戏看似简单,但其背后蕴含了丰富的算法设计与优化技巧。本文深入探讨扫雷游戏的核心算法实现,包括洪水填充算法的递归与迭代实现对比、地雷生成的优化策略、游戏可解性保证、自动求解算法等高级主题。通过本文学习,读者将掌握如何在实际项目中应用算法优化技巧,提升游戏性能和用户体验。
一、洪水填充算法深度解析
1.1 算法原理
洪水填充(Flood Fill)算法用于揭开连续的空白区域。当玩家点击一个相邻地雷数为0的格子时,需要递归揭开周围所有相连的空白格子。
核心思想:
- 从起始格子开始
- 如果是空白格子(adjacentMines == 0),揭开它
- 递归处理周围8个方向
- 遇到数字格子或已揭开格子则停止
1.2 递归实现分析
void _revealCell(int x, int y) {
// 边界检查
if (x < 0 || x >= _cols || y < 0 || y >= _rows) return;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
// 只处理未揭开的格子
if (cell.state != CellState.hidden) return;
// 踩到地雷
if (cell.isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_gameOver = true;
_revealAllMines();
return;
}
// 揭开当前格子
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_revealedCount++;
// 如果是空白格子,递归揭开周围
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
_revealCell(x + dx, y + dy);
}
}
}
}
时间复杂度:O(rows × cols)
空间复杂度:O(rows × cols) - 最坏情况下递归深度
优点:
- 代码简洁易懂
- 自然表达算法逻辑
缺点:
- 可能栈溢出(大地图)
- 重复访问检查不够高效
1.3 迭代实现优化
使用BFS(广度优先搜索)的迭代实现:
void _revealCellIterative(int startX, int startY) {
final queue = <Point>[];
final visited = <Point>{};
queue.add(Point(startX, startY));
while (queue.isNotEmpty) {
final point = queue.removeAt(0);
if (visited.contains(point)) continue;
visited.add(point);
final x = point.x;
final y = point.y;
// 边界检查
if (x < 0 || x >= _cols || y < 0 || y >= _rows) continue;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
// 只处理未揭开的格子
if (cell.state != CellState.hidden) continue;
// 踩到地雷
if (cell.isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_gameOver = true;
_revealAllMines();
return;
}
// 揭开当前格子
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_revealedCount++;
// 如果是空白格子,将周围格子加入队列
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final neighbor = Point(x + dx, y + dy);
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
}
优化点:
- 使用队列而非调用栈
- 使用Set记录已访问节点
- 避免递归深度限制
性能对比:
| 实现方式 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 栈溢出风险 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 递归 | O(n) | O(n) | 高 |
| 迭代BFS | O(n) | O(n) | 无 |
1.4 DFS深度优先实现
void _revealCellDFS(int startX, int startY) {
final stack = <Point>[];
final visited = <Point>{};
stack.add(Point(startX, startY));
while (stack.isNotEmpty) {
final point = stack.removeLast();
if (visited.contains(point)) continue;
visited.add(point);
final x = point.x;
final y = point.y;
if (x < 0 || x >= _cols || y < 0 || y >= _rows) continue;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
if (cell.state != CellState.hidden) continue;
if (cell.isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_gameOver = true;
_revealAllMines();
return;
}
_grid[y][x] = cell.copyWith(state: CellState.revealed);
_revealedCount++;
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) {
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final neighbor = Point(x + dx, y + dy);
if (!visited.contains(neighbor)) {
stack.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
}
}
BFS vs DFS:
- BFS:按层级展开,视觉效果更自然
- DFS:可能更快揭开更多格子,内存访问更局部
二、地雷生成算法优化
2.1 基础随机放置
void _placeMines() {
int placed = 0;
while (placed < _totalMines) {
final x = _random.nextInt(_cols);
final y = _random.nextInt(_rows);
if (!_grid[y][x].isMine) {
_grid[y][x] = Cell(
x: x,
y: y,
isMine: true,
adjacentMines: _grid[y][x].adjacentMines,
);
placed++;
}
}
}
问题:
- 可能无限循环(地雷数超过格子数)
- 首次点击可能踩雷
- 游戏可能无解
2.2 避免首次踩雷算法
Point? _firstClick;
void _revealCell(int x, int y) {
// 如果是第一次点击,先放置地雷
if (_firstClick == null) {
_firstClick = Point(x, y);
_placeMinesAvoiding(x, y);
_calculateAdjacentMines();
}
// 正常揭开逻辑...
}
void _placeMinesAvoiding(int safeX, int safeY) {
final safeZone = <Point>[];
// 构建安全区域(首次点击及其周围8格)
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
final nx = safeX + dx;
final ny = safeY + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < _cols && ny >= 0 && ny < _rows) {
safeZone.add(Point(nx, ny));
}
}
}
// 获取所有非安全区域
final available = <Point>[];
for (int y = 0; y < _rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < _cols; x++) {
if (!safeZone.contains(Point(x, y))) {
available.add(Point(x, y));
}
}
}
// 洗牌算法
available.shuffle(_random);
// 放置地雷
for (int i = 0; i < _totalMines && i < available.length; i++) {
final point = available[i];
_grid[point.y][point.x] = Cell(
x: point.x,
y: point.y,
isMine: true,
adjacentMines: 0,
);
}
}
优点:
- 保证首次点击安全
- 首次点击必定揭开一片区域
- O(n) 时间复杂度
2.3 洗牌算法优化
使用Fisher-Yates洗牌算法:
void _placeMinesShuffle() {
// 创建所有位置列表
final positions = <Point>[];
for (int y = 0; y < _rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < _cols; x++) {
positions.add(Point(x, y));
}
}
// Fisher-Yates洗牌
for (int i = positions.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
final j = _random.nextInt(i + 1);
final temp = positions[i];
positions[i] = positions[j];
positions[j] = temp;
}
// 取前n个作为地雷
for (int i = 0; i < _totalMines; i++) {
final point = positions[i];
_grid[point.y][point.x] = Cell(
x: point.x,
y: point.y,
isMine: true,
adjacentMines: 0,
);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
2.4 可解性保证算法
bool _isSolvable() {
// 使用求解器检查是否可解
final solver = MinesweeperSolver(_grid, _rows, _cols, _totalMines);
return solver.canSolve();
}
class MinesweeperSolver {
final List<List<Cell>> grid;
final int rows;
final int cols;
final int totalMines;
MinesweeperSolver(this.grid, this.rows, this.cols, this.totalMines);
bool canSolve() {
// 复制游戏状态
final workGrid = _copyGrid();
int revealedCount = 0;
int flagCount = 0;
bool changed = true;
while (changed) {
changed = false;
// 应用基本规则
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
final cell = workGrid[y][x];
if (cell.state != CellState.revealed) continue;
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) continue;
final hidden = _getHiddenNeighbors(x, y, workGrid);
final flagged = _getFlaggedNeighbors(x, y, workGrid);
// 规则1:如果相邻未揭开数 == 剩余地雷数,全部标记
if (hidden.length == cell.adjacentMines - flagged.length) {
for (final point in hidden) {
if (workGrid[point.y][point.x].state == CellState.hidden) {
workGrid[point.y][point.x].state = CellState.flagged;
flagCount++;
changed = true;
}
}
}
// 规则2:如果已标记数 == 相邻地雷数,全部揭开
if (flagged.length == cell.adjacentMines) {
for (final point in hidden) {
if (workGrid[point.y][point.x].state == CellState.hidden) {
if (workGrid[point.y][point.x].isMine) {
return false; // 踩雷,无解
}
workGrid[point.y][point.x].state = CellState.revealed;
revealedCount++;
changed = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 检查是否胜利
final safeCells = rows * cols - totalMines;
return revealedCount == safeCells;
}
List<Point> _getHiddenNeighbors(int x, int y, List<List<Cell>> grid) {
final result = <Point>[];
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final nx = x + dx;
final ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < cols && ny >= 0 && ny < rows) {
if (grid[ny][nx].state == CellState.hidden) {
result.add(Point(nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
List<Point> _getFlaggedNeighbors(int x, int y, List<List<Cell>> grid) {
final result = <Point>[];
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final nx = x + dx;
final ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < cols && ny >= 0 && ny < rows) {
if (grid[ny][nx].state == CellState.flagged) {
result.add(Point(nx, ny));
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
List<List<Cell>> _copyGrid() {
return grid.map((row) {
return row.map((cell) => Cell(
x: cell.x,
y: cell.y,
isMine: cell.isMine,
adjacentMines: cell.adjacentMines,
state: cell.state,
)).toList();
}).toList();
}
}
三、高级游戏功能
3.1 双键点击(Chord)
当周围标记数等于数字时,点击数字可揭开所有未标记的周围格子:
void _onCellChord(int x, int y) {
if (_gameOver || _gameWon) return;
final cell = _grid[y][x];
if (cell.state != CellState.revealed) return;
if (cell.adjacentMines == 0) return;
final neighbors = _getNeighbors(x, y);
final flagged = neighbors.where((p) =>
_grid[p.y][p.x].state == CellState.flagged
).length;
if (flagged == cell.adjacentMines) {
for (final point in neighbors) {
if (_grid[point.y][point.x].state == CellState.hidden) {
_revealCell(point.x, point.y);
}
}
setState(() {});
_checkGameState();
}
}
List<Point> _getNeighbors(int x, int y) {
final result = <Point>[];
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final nx = x + dx;
final ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < _cols && ny >= 0 && ny < _rows) {
result.add(Point(nx, ny));
}
}
}
return result;
}
3.2 计时器实现
int _elapsedSeconds = 0;
Timer? _timer;
void _startTimer() {
_stopTimer();
_elapsedSeconds = 0;
_timer = Timer.periodic(const Duration(seconds: 1), (timer) {
setState(() {
_elapsedSeconds++;
});
});
}
void _stopTimer() {
_timer?.cancel();
_timer = null;
}
void dispose() {
_stopTimer();
super.dispose();
}
3.3 最佳成绩记录
class BestTimes {
final int easy;
final int medium;
final int hard;
BestTimes({required this.easy, required this.medium, required this.hard});
factory BestTimes.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return BestTimes(
easy: json['easy'] ?? 999,
medium: json['medium'] ?? 999,
hard: json['hard'] ?? 999,
);
}
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() {
return {
'easy': easy,
'medium': medium,
'hard': hard,
};
}
}
// 使用SharedPreferences保存
Future<void> _saveBestTime(Difficulty difficulty, int seconds) async {
final prefs = await SharedPreferences.getInstance();
final key = 'best_time_${difficulty.name}';
final current = prefs.getInt(key) ?? 999;
if (seconds < current) {
await prefs.setInt(key, seconds);
_showNewRecordDialog(difficulty, seconds);
}
}
四、性能优化技巧
4.1 惰性计算
只在需要时计算相邻地雷数:
int? _adjacentMinesCache;
int getAdjacentMines(int x, int y) {
if (_adjacentMinesCache != null) {
return _adjacentMinesCache!;
}
int count = 0;
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
if (dx == 0 && dy == 0) continue;
final nx = x + dx;
final ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < _cols && ny >= 0 && ny < _rows) {
if (_grid[ny][nx].isMine) {
count++;
}
}
}
}
_adjacentMinesCache = count;
return count;
}
4.2 局部刷新优化
只刷新变化的格子:
final Set<Point> _changedCells = {};
void _revealCell(int x, int y) {
// ... 揭开逻辑 ...
_changedCells.add(Point(x, y));
// 只刷新变化的区域
setState(() {
// 触发重建
});
_changedCells.clear();
}
4.3 位运算优化
使用位运算存储格子状态:
class CellData {
final int data; // 位掩码
// 位定义
static const int MINE_BIT = 1 << 0;
static const int REVEALED_BIT = 1 << 1;
static const int FLAGGED_BIT = 1 << 2;
static const int ADJACENT_SHIFT = 3;
CellData({required bool isMine, required bool revealed,
required bool flagged, required int adjacentMines})
: data = (isMine ? MINE_BIT : 0) |
(revealed ? REVEALED_BIT : 0) |
(flagged ? FLAGGED_BIT : 0) |
(adjacentMines << ADJACENT_SHIFT);
bool get isMine => (data & MINE_BIT) != 0;
bool get revealed => (data & REVEALED_BIT) != 0;
bool get flagged => (data & FLAGGED_BIT) != 0;
int get adjacentMines => (data >> ADJACENT_SHIFT) & 0x0F;
}
五、测试与调试
5.1 单元测试
test('Mine placement should avoid first click', () {
final game = MinesweeperGame(difficulty: Difficulty.easy);
// 模拟第一次点击
game.revealCell(5, 5);
expect(game.isGameOver, isFalse);
expect(game.grid[5][5].isMine, isFalse);
});
test('Flood fill should reveal all connected cells', () {
final game = MinesweeperGame(difficulty: Difficulty.easy);
// 创建测试场景
game.grid[1][1] = Cell(x: 1, y: 1, isMine: false, adjacentMines: 0);
game.grid[1][2] = Cell(x: 1, y: 2, isMine: false, adjacentMines: 0);
game.grid[2][1] = Cell(x: 2, y: 1, isMine: false, adjacentMines: 0);
game.revealCell(1, 1);
expect(game.grid[1][1].state, CellState.revealed);
expect(game.grid[1][2].state, CellState.revealed);
expect(game.grid[2][1].state, CellState.revealed);
});
5.2 可视化调试
void _printGridDebug() {
for (int y = 0; y < _rows; y++) {
final row = StringBuffer();
for (int x = 0; x < _cols; x++) {
final cell = _grid[y][x];
if (cell.isMine) {
row.write('* ');
} else if (cell.state == CellState.revealed) {
row.write('${cell.adjacentMines} ');
} else if (cell.state == CellState.flagged) {
row.write('F ');
} else {
row.write('? ');
}
}
print(row.toString());
}
}
六、总结
本文深入探讨了扫雷游戏的算法实现与优化:
- 洪水填充算法:递归vs迭代,BFS vs DFS
- 地雷生成优化:避免首次踩雷、洗牌算法、可解性保证
- 高级功能:双键点击、计时器、最佳成绩
- 性能优化:惰性计算、局部刷新、位运算
- 测试调试:单元测试、可视化调试
这些算法优化技巧不仅适用于扫雷游戏,也可以应用到其他网格类游戏和图算法问题中。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区: 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献64条内容
已为社区贡献64条内容








所有评论(0)