Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:记账应用数据统计与可视化
本文介绍了在Flutter for OpenHarmony平台上实现记账应用数据统计与可视化的关键技术。重点讲解了基础统计算法、分类汇总统计等核心功能实现,包括总余额计算、收支分类和时间维度分析。通过优化算法和空值处理确保统计准确性,并展示了如何将抽象数据转化为直观的图表展示。文章提供了完整的Dart代码示例,帮助开发者快速掌握记账应用的数据统计功能实现方法。
·
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:记账应用数据统计与可视化
文章目录
摘要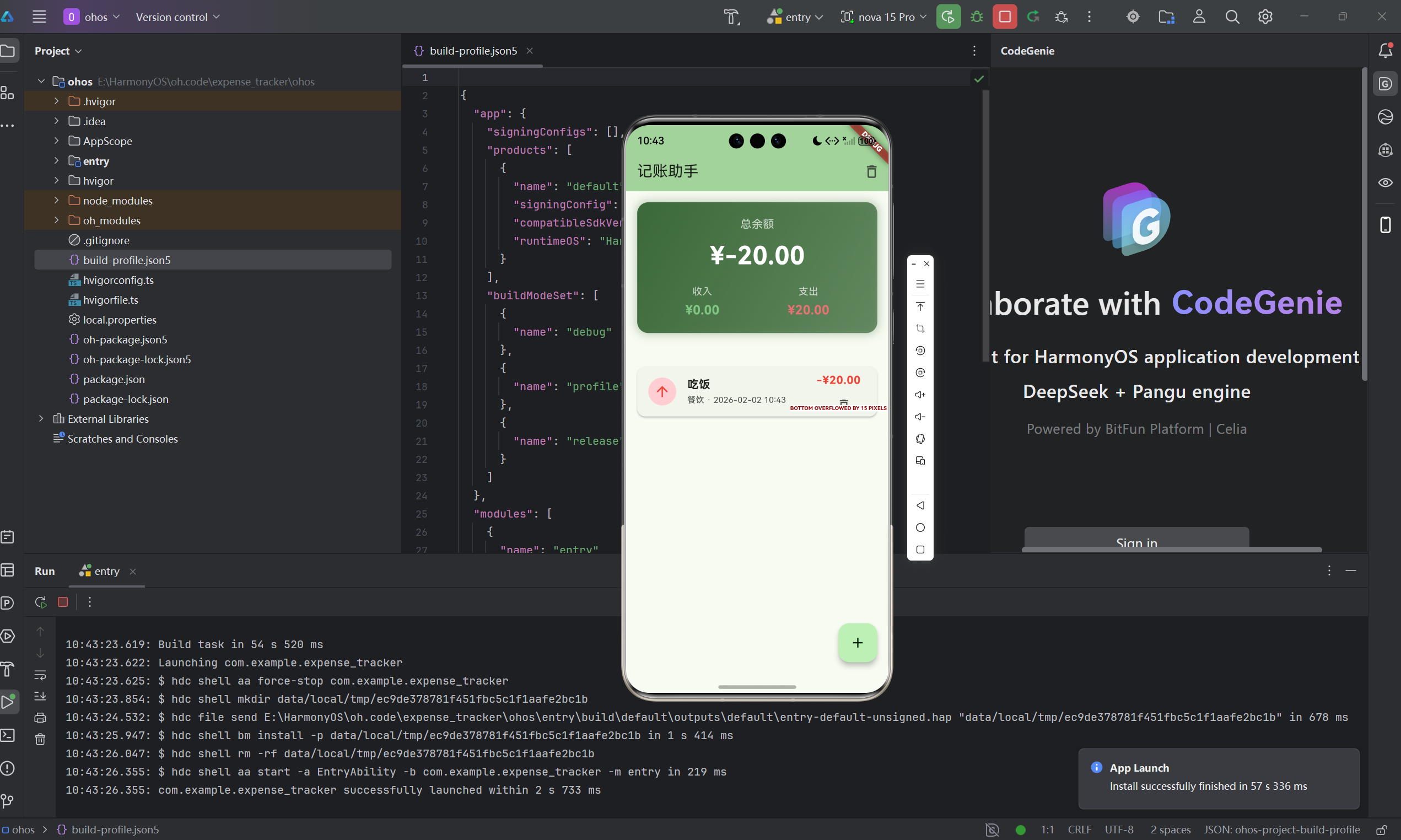
数据统计与可视化是记账应用的核心价值体现。本文将详细介绍如何在Flutter for OpenHarmony平台上实现记账应用的数据统计功能,包括收支计算、分类汇总、时间维度分析等核心技术点。通过本文学习,读者将掌握Dart语言的数据处理技巧,了解如何将抽象的数据转化为直观的图表展示。
一、数据可视化的重要性
1.1 为什么需要数据可视化
记账应用的核心价值不仅仅是记录收支,更重要的是通过数据分析帮助用户了解财务状况。
可视化的价值
- 快速了解收支情况
- 发现消费规律
- 辅助财务决策
- 增强用户体验
1.2 常见的统计维度
时间维度
- 日统计:当天的收支情况
- 周统计:本周的收支汇总
- 月统计:每月的收支对比
- 年统计:年度财务总览
分类维度
- 支出分类:各类支出占比
- 收入分类:各类收入来源
- 分类趋势:各分类的时间变化
金额维度
- 总余额:资产净值
- 收入总额:总收入统计
- 支出总额:总支出统计
- 收支比:收入支出比例
1.3 本项目实现的统计功能
| 统计类型 | 实现方式 | 展示形式 |
|---|---|---|
| 总余额 | 收入减支出 | 数字卡片 |
| 总收入 | 遍历累加 | 数字卡片 |
| 总支出 | 遍历累加 | 数字卡片 |
| 日收支统计 | 按日期分组 | 列表展示 |
二、数据统计算法实现
2.1 基础统计算法
最基础的统计是计算总余额、总收入和总支出:
void _calculateTotals() {
// 初始化统计变量
_totalIncome = 0;
_totalExpense = 0;
// 遍历所有交易记录
for (var transaction in _transactions) {
if (transaction.isExpense) {
// 累加支出
_totalExpense += transaction.amount;
} else {
// 累加收入
_totalIncome += transaction.amount;
}
}
// 计算余额
_totalBalance = _totalIncome - _totalExpense;
}
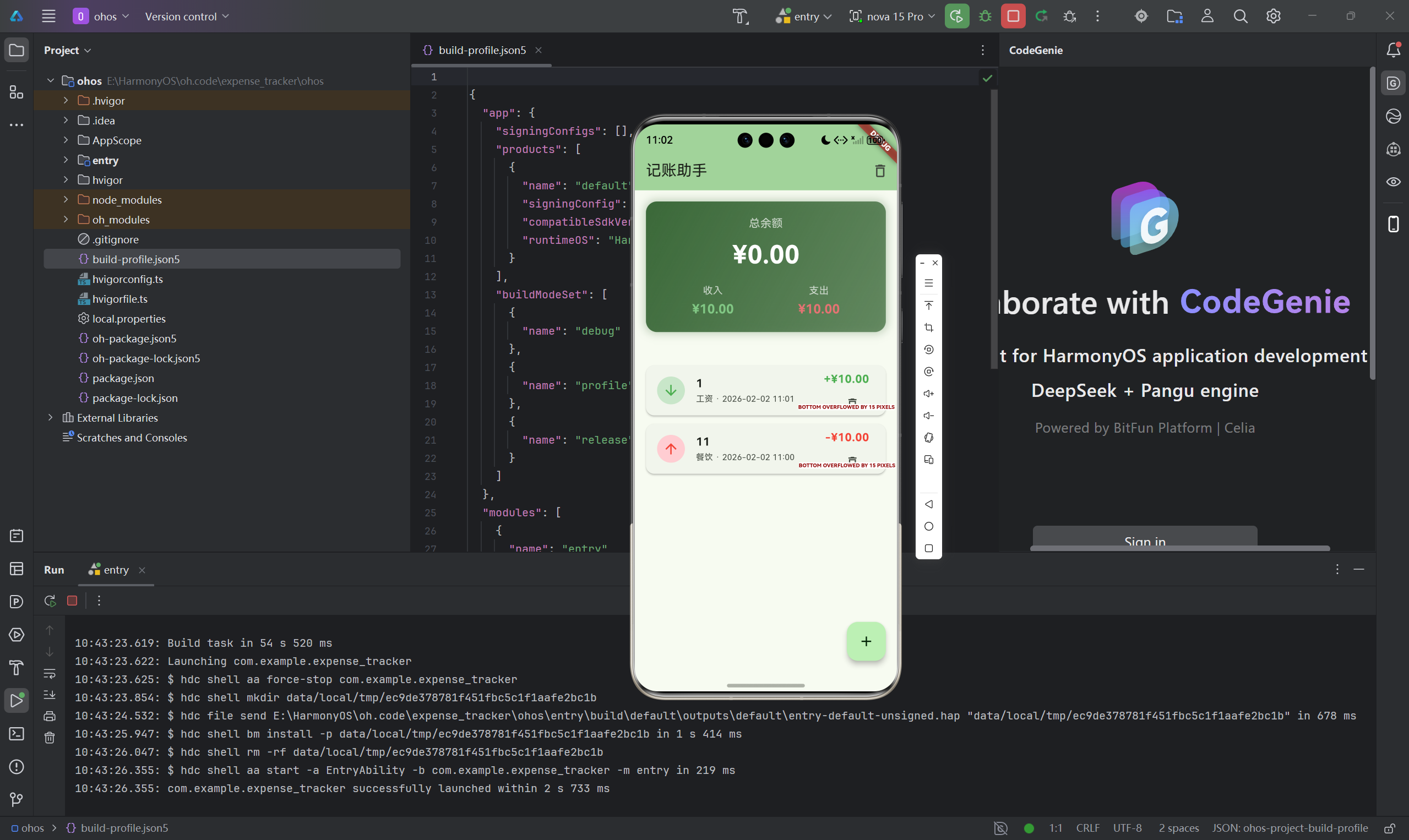
算法分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),n为交易记录数
- 空间复杂度:O(1),只使用固定数量的变量
- 适用场景:每次数据变化后重新计算
2.2 优化统计计算
使用reduce方法简化计算:
void _calculateTotalsOptimized() {
// 使用reduce一次性计算
final totals = _transactions.fold(
{'income': 0.0, 'expense': 0.0},
(Map<String, double> totals, transaction) {
if (transaction.isExpense) {
totals['expense'] = totals['expense']! + transaction.amount;
} else {
totals['income'] = totals['income']! + transaction.amount;
}
return totals;
},
);
_totalIncome = totals['income']!;
_totalExpense = totals['expense']!;
_totalBalance = _totalIncome - _totalExpense;
}
2.3 空值处理
确保计算结果的准确性:
void _calculateTotals() {
_totalIncome = 0;
_totalExpense = 0;
for (var transaction in _transactions) {
// 确保金额不为空
final amount = transaction.amount;
if (amount <= 0) continue; // 跳过无效金额
if (transaction.isExpense) {
_totalExpense += amount;
} else {
_totalIncome += amount;
}
}
// 处理精度问题
_totalBalance = double.parse(
(_totalIncome - _totalExpense).toStringAsFixed(2)
);
}
三、分类统计功能
3.1 分类数据结构
设计分类统计的数据模型:
class CategorySummary {
final String category; // 分类名称
final double total; // 总金额
final int count; // 交易笔数
final double percentage; // 占比
CategorySummary({
required this.category,
required this.total,
required this.count,
required this.percentage,
});
}
3.2 按分类汇总
实现按分类汇总的统计方法:
List<CategorySummary> _calculateCategorySummary(bool isExpense) {
final Map<String, double> categoryTotals = {};
final Map<String, int> categoryCounts = {};
double grandTotal = 0;
// 统计每个分类的总金额和笔数
for (var transaction in _transactions) {
if (transaction.isExpense == isExpense) {
final category = transaction.category;
categoryTotals[category] =
(categoryTotals[category] ?? 0) + transaction.amount;
categoryCounts[category] =
(categoryCounts[category] ?? 0) + 1;
grandTotal += transaction.amount;
}
}
// 生成分类汇总列表
final summaries = categoryTotals.entries.map((entry) {
return CategorySummary(
category: entry.key,
total: entry.value,
count: categoryCounts[entry.key] ?? 0,
percentage: grandTotal > 0
? (entry.value / grandTotal * 100)
: 0,
);
}).toList();
// 按金额降序排序
summaries.sort((a, b) => b.total.compareTo(a.total));
return summaries;
}
3.3 分类统计UI展示
展示分类统计结果:
Widget _buildCategorySummary(List<CategorySummary> summaries) {
if (summaries.isEmpty) {
return const Center(
child: Text('暂无数据'),
);
}
return Column(
children: summaries.map((summary) {
return Card(
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 4, horizontal: 16),
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
// 分类名称
Text(
summary.category,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
// 金额和笔数
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
Text(
'¥${summary.total.toStringAsFixed(2)}',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
Text(
'${summary.count}笔',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.grey[600],
),
),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
// 占比进度条
LinearProgressIndicator(
value: summary.percentage / 100,
backgroundColor: Colors.grey[200],
),
const SizedBox(height: 4),
// 占比文字
Text(
'占比: ${summary.percentage.toStringAsFixed(1)}%',
style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 12),
),
],
),
),
);
}).toList(),
);
}
四、时间维度数据分析
4.1 按日期分组统计
实现按日期分组的统计算法:
Map<String, CategorySummary> _calculateDailySummary() {
final Map<String, double> dailyTotals = {};
final Map<String, bool> dailyTypes = {};
for (var transaction in _transactions) {
// 提取日期部分作为key
final dateKey = DateFormat('yyyy-MM-dd').format(transaction.date);
dailyTotals[dateKey] =
(dailyTotals[dateKey] ?? 0) + transaction.amount;
dailyTypes[dateKey] = transaction.isExpense;
}
return dailyTotals;
}
4.2 按月分组统计
实现按月份分组的统计:
Map<String, Map<String, double>> _calculateMonthlySummary() {
final Map<String, Map<String, double>> monthlyData = {};
for (var transaction in _transactions) {
// 提取年月作为key
final monthKey = DateFormat('yyyy-MM').format(transaction.date);
monthlyData.putIfAbsent(monthKey, () => {
'income': 0.0,
'expense': 0.0,
});
if (transaction.isExpense) {
monthlyData[monthKey]!['expense'] =
monthlyData[monthKey]!['expense']! + transaction.amount;
} else {
monthlyData[monthKey]!['income'] =
monthlyData[monthKey]!['income']! + transaction.amount;
}
}
return monthlyData;
}
4.3 日期范围筛选
实现按日期范围筛选的功能:
List<Transaction> _filterByDateRange(DateTime start, DateTime end) {
return _transactions.where((transaction) {
return transaction.date.isAfter(start.subtract(const Duration(days: 1))) &&
transaction.date.isBefore(end.add(const Duration(days: 1)));
}).toList();
}
// 使用示例
final now = DateTime.now();
final startOfMonth = DateTime(now.year, now.month, 1);
final endOfMonth = DateTime(now.year, now.month + 1, 0);
final monthlyTransactions = _filterByDateRange(startOfMonth, endOfMonth);
五、UI可视化展示
5.1 余额卡片设计
余额卡片是最直观的数据展示:
Widget _buildBalanceCard() {
return Container(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
gradient: LinearGradient(
begin: Alignment.topLeft,
end: Alignment.bottomRight,
colors: [
Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary,
Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary.withAlpha(179),
],
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16),
boxShadow: [
BoxShadow(
color: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.primary.withAlpha(77),
blurRadius: 10,
spreadRadius: 2,
),
],
),
child: Column(
children: [
const Text(
'总余额',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
// 余额显示
Text(
'¥${_totalBalance.toStringAsFixed(2)}',
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 36,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 收支对比
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceAround,
children: [
_buildSummaryItem(
'收入',
'¥${_totalIncome.toStringAsFixed(2)}',
Colors.green[300]!,
),
_buildSummaryItem(
'支出',
'¥${_totalExpense.toStringAsFixed(2)}',
Colors.red[300]!,
),
],
),
],
),
);
}
Widget _buildSummaryItem(String label, String value, Color color) {
return Column(
children: [
Text(
label,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
color: Colors.white70,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 4),
Text(
value,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: color,
),
),
],
);
}
5.2 收支比例展示
使用圆形进度条展示收支比例:
Widget _buildIncomeExpenseRatio() {
final total = _totalIncome + _totalExpense;
if (total == 0) return const SizedBox();
final incomeRatio = _totalIncome / total;
final expenseRatio = _totalExpense / total;
return Card(
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Text(
'收支比例',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 收入比例
_buildRatioBar('收入', incomeRatio, Colors.green),
const SizedBox(height: 12),
// 支出比例
_buildRatioBar('支出', expenseRatio, Colors.red),
],
),
),
);
}
Widget _buildRatioBar(String label, double ratio, Color color) {
return Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween,
children: [
Text(label),
Text('${(ratio * 100).toStringAsFixed(1)}%'),
],
),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
LinearProgressIndicator(
value: ratio,
backgroundColor: Colors.grey[200],
valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(color),
),
],
);
}
5.3 列表排序展示
支持多种排序方式:
enum SortType {
dateDesc, // 按日期降序
dateAsc, // 按日期升序
amountDesc, // 按金额降序
amountAsc, // 按金额升序
}
List<Transaction> _sortTransactions(List<Transaction> transactions, SortType sortType) {
final sorted = List<Transaction>.from(transactions);
switch (sortType) {
case SortType.dateDesc:
sorted.sort((a, b) => b.date.compareTo(a.date));
break;
case SortType.dateAsc:
sorted.sort((a, b) => a.date.compareTo(b.date));
break;
case SortType.amountDesc:
sorted.sort((a, b) => b.amount.compareTo(a.amount));
break;
case SortType.amountAsc:
sorted.sort((a, b) => a.amount.compareTo(b.amount));
break;
}
return sorted;
}
六、高级统计功能
6.1 月度对比分析
实现不同月份的收支对比:
Map<String, Map<String, double>> _getMonthlyComparison() {
final now = DateTime.now();
final thisMonth = DateFormat('yyyy-MM').format(now);
final lastMonth = DateFormat('yyyy-MM').format(
DateTime(now.year, now.month - 1, 1)
);
final monthlyData = _calculateMonthlySummary();
return {
'本月': monthlyData[thisMonth] ?? {'income': 0.0, 'expense': 0.0},
'上月': monthlyData[lastMonth] ?? {'income': 0.0, 'expense': 0.0},
};
}
6.2 平均消费计算
计算平均每日支出:
double _calculateAverageDailyExpense() {
if (_transactions.isEmpty) return 0;
// 获取最早的交易日期
final firstDate = _transactions
.map((t) => t.date)
.reduce((a, b) => a.isBefore(b) ? a : b);
final days = DateTime.now().difference(firstDate).inDays + 1;
return _totalExpense / days;
}
6.3 最大支出记录
查找单笔最大支出:
Transaction? _getLargestExpense() {
final expenses = _transactions.where((t) => t.isExpense).toList();
if (expenses.isEmpty) return null;
expenses.sort((a, b) => b.amount.compareTo(a.amount));
return expenses.first;
}
七、总结
本文详细介绍了记账应用的数据统计与可视化实现,主要内容包括:
- 基础统计:实现收入、支出、余额的计算
- 分类统计:按分类汇总和占比分析
- 时间统计:按日期、月份分组统计
- UI展示:直观的数据可视化界面
- 高级功能:月度对比、平均值计算等
数据统计是记账应用的核心价值,通过合理的数据处理和可视化展示,可以帮助用户更好地了解财务状况,做出明智的消费决策。这些统计技巧同样适用于其他类型的数据分析应用。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区: 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献44条内容
已为社区贡献44条内容








所有评论(0)