Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战 文件存储与数据库操作完全指南
Flutter数据存储完全指南:从文件操作到SQLite数据库 本文详细介绍了Flutter应用开发中的数据存储方案。首先讲解文件系统操作,包括使用path_provider获取各类目录路径,以及文件的读写、删除等基本操作。然后重点介绍了SQLite数据库的使用,包括数据库初始化、表创建、版本升级等核心配置,以及完整的CRUD操作实现。文章提供了可直接使用的工具类代码,涵盖文件读写辅助类、目录操作
·
【Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战】Flutter文件存储与数据库操作完全指南
前言
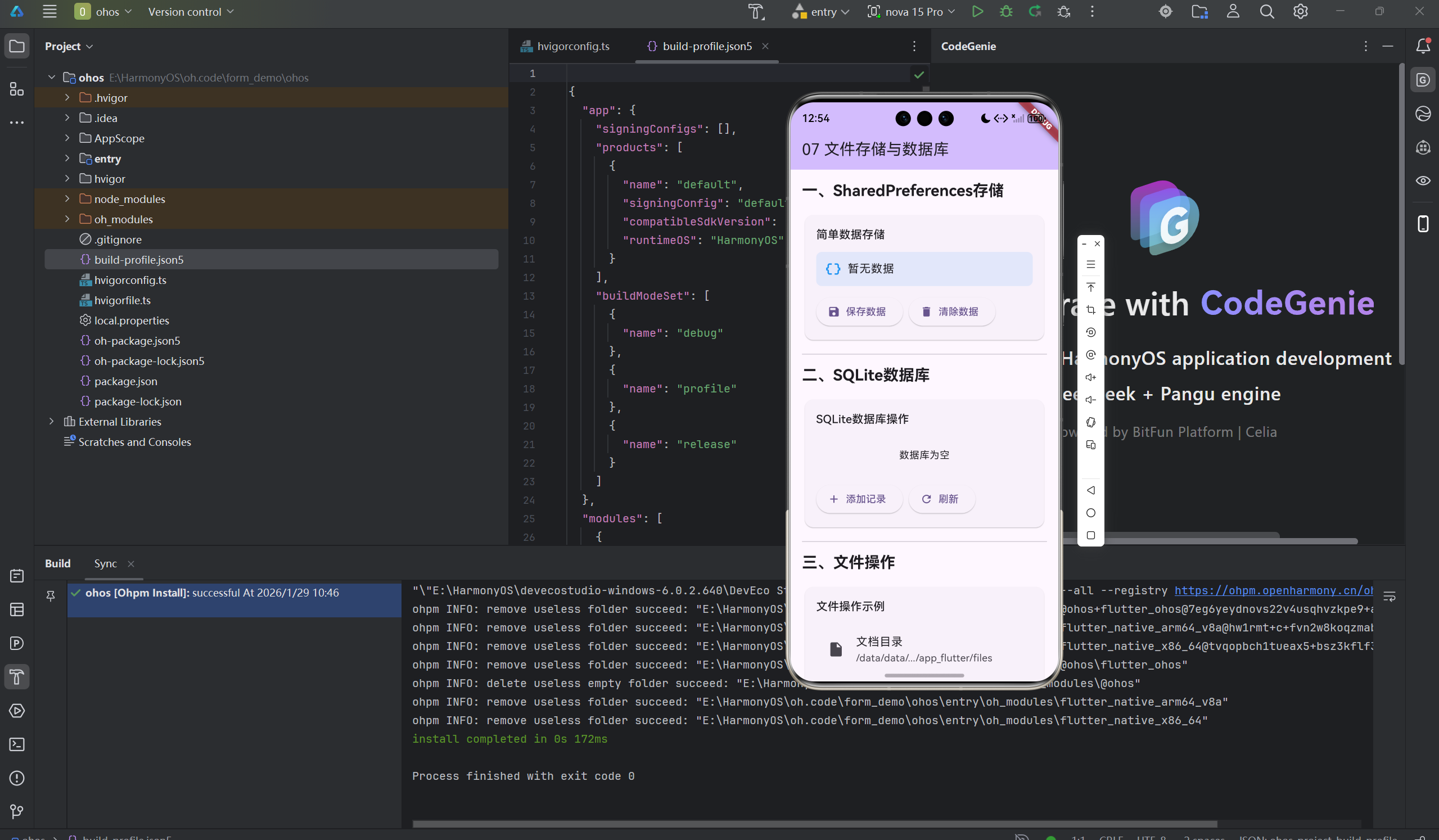
做应用开发,数据存储是绕不开的话题。简单的配置用SharedPreferences就够了,但复杂的业务数据就需要数据库。
Flutter中用sqflite操作SQLite很方便,但也有一些坑需要避开。这篇文章我想分享数据存储的实践经验。
一、文件系统操作
1.1 路径获取
dependencies:
path_provider: ^2.1.1
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
Future<void> getPaths() async {
// 临时目录
final tempDir = await getTemporaryDirectory();
// 应用文档目录
final appDocDir = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
// 应用支持目录
final appSupportDir = await getApplicationSupportDirectory();
// 外部存储目录
final externalDir = await getExternalStorageDirectory();
}
1.2 文件读写
import 'dart:io';
class FileHelper {
static Future<void> writeString(String path, String content) async {
final file = File(path);
await file.writeAsString(content);
}
static Future<String> readString(String path) async {
final file = File(path);
return await file.readAsString();
}
static Future<void> writeBytes(String path, List<int> bytes) async {
final file = File(path);
await file.writeAsBytes(bytes);
}
static Future<List<int>> readBytes(String path) async {
final file = File(path);
return await file.readAsBytes();
}
static Future<bool> exists(String path) async {
return await File(path).exists();
}
static Future<void> delete(String path) async {
final file = File(path);
if (await file.exists()) {
await file.delete();
}
}
}
1.3 目录操作
class DirectoryHelper {
static Future<void> createDirectory(String path) async {
final dir = Directory(path);
if (!await dir.exists()) {
await dir.create(recursive: true);
}
}
static Future<List<FileSystemEntity>> listFiles(String path) async {
final dir = Directory(path);
return dir.listSync();
}
static Future<void> deleteDirectory(String path) async {
final dir = Directory(path);
if (await dir.exists()) {
await dir.delete(recursive: true);
}
}
}
二、SQLite数据库
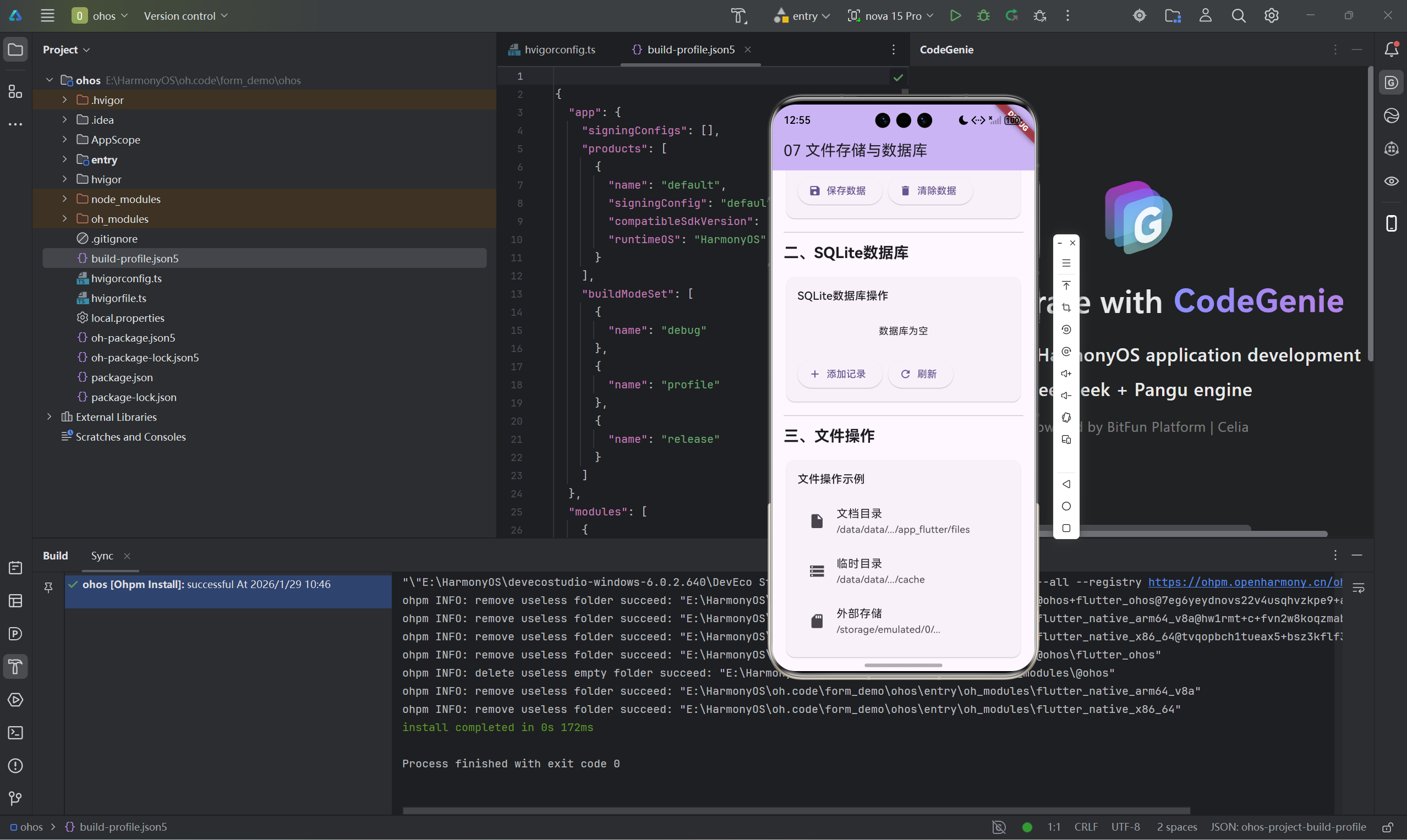
2.1 数据库辅助类
dependencies:
sqflite: ^2.3.0
path: ^1.8.0
import 'package:sqflite/sqflite.dart';
import 'package:path/path.dart';
class DatabaseHelper {
static final DatabaseHelper _instance = DatabaseHelper._internal();
static Database? _database;
factory DatabaseHelper() => _instance;
DatabaseHelper._internal();
Future<Database> get database async {
if (_database != null) return _database!;
_database = await _initDatabase();
return _database!;
}
Future<Database> _initDatabase() async {
final dbPath = await getDatabasesPath();
final path = join(dbPath, 'app.db');
return await openDatabase(
path,
version: 1,
onCreate: _onCreate,
onUpgrade: _onUpgrade,
);
}
Future<void> _onCreate(Database db, int version) async {
await db.execute('''
CREATE TABLE users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
created_at INTEGER NOT NULL
)
''');
await db.execute('''
CREATE TABLE todos (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
title TEXT NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
is_completed INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
user_id INTEGER,
created_at INTEGER NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users (id)
)
''');
}
Future<void> _onUpgrade(Database db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) async {
if (oldVersion < 2) {
await db.execute('ALTER TABLE users ADD COLUMN avatar TEXT');
}
}
}
2.2 CRUD操作
class UserDao {
final DatabaseHelper _dbHelper = DatabaseHelper();
Future<int> insert(User user) async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
return await db.insert('users', user.toMap());
}
Future<List<User>> queryAll() async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> maps = await db.query('users');
return maps.map((map) => User.fromMap(map)).toList();
}
Future<User?> queryById(int id) async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
final List<Map<String, dynamic>> maps = await db.query(
'users',
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [id],
);
if (maps.isEmpty) return null;
return User.fromMap(maps.first);
}
Future<int> update(User user) async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
return await db.update(
'users',
user.toMap(),
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [user.id],
);
}
Future<int> delete(int id) async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
return await db.delete(
'users',
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [id],
);
}
}
2.3 事务处理
class TransactionExample {
final DatabaseHelper _dbHelper = DatabaseHelper();
Future<void> transferData(int fromId, int toId) async {
final db = await _dbHelper.database;
await db.transaction((txn) async {
await txn.update(
'users',
{'balance': 100},
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [fromId],
);
await txn.update(
'users',
{'balance': 200},
where: 'id = ?',
whereArgs: [toId],
);
});
}
}
三、数据持久化方案对比
3.1 方案对比
| 方案 | 适用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SharedPreferences | 简单配置 | 简单易用 | 不适合复杂数据 |
| SQLite | 结构化数据 | 功能强大、支持查询 | 相对复杂 |
| 文件存储 | 大文件、图片 | 灵活 | 需要手动管理 |
| ObjectBox | 高性能需求 | 快速、易用 | 需要代码生成 |
3.2 选择建议
class StorageFactory {
static StorageService create(StorageType type) {
switch (type) {
case StorageType.preferences:
return PreferencesStorageService();
case StorageType.database:
return DatabaseStorageService();
case StorageType.file:
return FileStorageService();
}
}
}
enum StorageType {
preferences,
database,
file,
}
四、数据库最佳实践
4.1 单例模式
class DatabaseHelper {
static final DatabaseHelper _instance = DatabaseHelper._internal();
factory DatabaseHelper() => _instance;
DatabaseHelper._internal();
}
4.2 数据库版本管理
class Migration {
final int fromVersion;
final int toVersion;
final String migrationSql;
const Migration({
required this.fromVersion,
required this.toVersion,
required this.migrationSql,
});
}
class MigrationManager {
static const List<Migration> migrations = [
Migration(
fromVersion: 1,
toVersion: 2,
migrationSql: 'ALTER TABLE users ADD COLUMN avatar TEXT',
),
Migration(
fromVersion: 2,
toVersion: 3,
migrationSql: 'CREATE INDEX idx_user_email ON users(email)',
),
];
static Future<void> migrate(Database db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) async {
for (final migration in migrations) {
if (oldVersion >= migration.fromVersion && newVersion >= migration.toVersion) {
await db.execute(migration.migrationSql);
}
}
}
}
4.3 性能优化
class PerformanceOptimizations {
// 批量插入
static Future<void> batchInsert(Database db, List<User> users) async {
final batch = db.batch();
for (final user in users) {
batch.insert('users', user.toMap());
}
await batch.commit(noResult: true);
}
// 使用索引
static Future<void> createIndex(Database db) async {
await db.execute('CREATE INDEX idx_user_email ON users(email)');
}
// 查询优化
static Future<List<User>> queryWithLimit(Database db, int limit, int offset) async {
final maps = await db.query(
'users',
limit: limit,
offset: offset,
);
return maps.map((map) => User.fromMap(map)).toList();
}
}
总结
数据存储是应用的基础功能。
核心要点:
- 根据数据类型选择合适的存储方案
- SQLite适合结构化数据存储
- 使用事务保证数据一致性
- 注意数据库版本管理和迁移
- 合理使用索引和批量操作优化性能
选择建议:
- 简单配置:SharedPreferences
- 复杂数据:SQLite
- 大文件:文件存储
- 高性能:ObjectBox
好的数据存储设计让应用更可靠。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献27条内容
已为社区贡献27条内容








所有评论(0)