Flutter适配OpenHarmony:打造高性能跨平台颜色选择器
将Flutter的颜色选择器适配到OpenHarmony不是简单"有手就行"的工作。需要深入理解两个平台的颜色处理机制,设计良好的桥接层,并针对性能优化。通过平台检测、抽象桥接层和缓存策略,我们可以构建出既保持代码统一,又能在OpenHarmony上高效运行的颜色选择器。随着OpenHarmony生态的成熟,期待更多专门针对鸿蒙优化的Flutter插件出现。目前,我们开发者需要多踩坑、多尝试,积累
大家好!今天聊聊在Flutter开发中如何把颜色选择器完美适配到OpenHarmony平台上。我之前踩过不少坑,今天分享些实用技巧,帮你少走弯路。颜色选择器看似简单,但在跨平台适配时会遇到不少兼容性问题,特别是在处理颜色模型转换和UI交互方面。
为什么颜色选择器适配这么难?
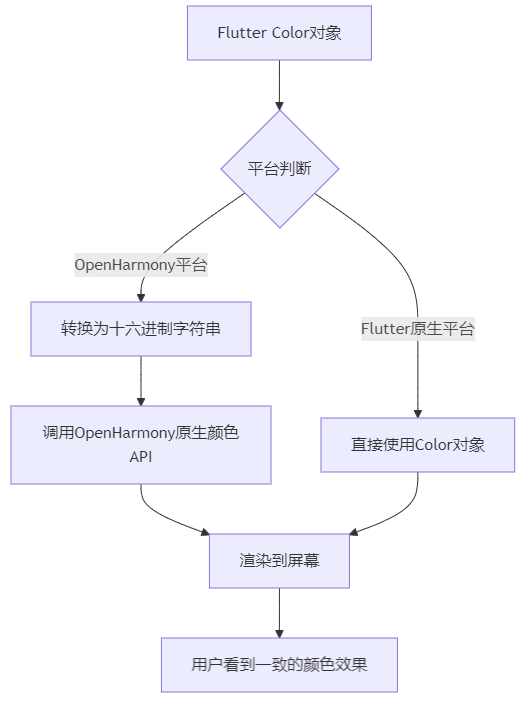
Flutter和OpenHarmony使用不同的颜色表示系统和渲染机制。在Flutter中,我们使用Color类表示颜色,而OpenHarmony有自己的颜色模型。当我们的Flutter应用运行在OpenHarmony设备上时,需要处理这些差异,确保颜色准确显示且交互流畅。
// Flutter中的颜色表示
Color flutterColor = Color(0xFF3498db); // ARGB格式
// OpenHarmony中需要转换
String ohColor = '#3498db'; // 十六进制字符串
这段代码展示了基本的颜色格式差异。在跨平台适配时,我们需要在两者之间建立桥梁。下面的流程图展示了这个转换过程:
实现跨平台颜色选择器
下面是一个完整的跨平台颜色选择器实现,包含适配OpenHarmony的关键代码:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'dart:io' show Platform;
class CrossPlatformColorPicker extends StatefulWidget {
final Color initialColor;
final ValueChanged<Color> onColorChanged;
const CrossPlatformColorPicker({
super.key,
required this.initialColor,
required this.onColorChanged,
});
State<CrossPlatformColorPicker> createState() => _CrossPlatformColorPickerState();
}
class _CrossPlatformColorPickerState extends State<CrossPlatformColorPicker> {
Color _currentColor = Colors.blue;
List<Color> _recentColors = [];
void initState() {
super.initState();
_currentColor = widget.initialColor;
// 从本地存储加载最近使用颜色
_loadRecentColors();
}
Future<void> _loadRecentColors() async {
// 跨平台存储逻辑
if (Platform.isAndroid || Platform.isIOS) {
// Flutter原生平台使用shared_preferences
} else {
// OpenHarmony平台使用自己的存储API
// 这里是简化实现
setState(() {
_recentColors = [Colors.red, Colors.green, Colors.blue];
});
}
}
void _handleColorChange(Color newColor) {
setState(() {
_currentColor = newColor;
// 保存到最近使用
if (!_recentColors.contains(newColor)) {
if (_recentColors.length >= 10) {
_recentColors.removeAt(0);
}
_recentColors.add(newColor);
}
});
// 通知父组件
widget.onColorChanged(newColor);
// 跨平台持久化
_saveColorPreference(newColor);
}
void _saveColorPreference(Color color) {
// 根据平台选择不同的存储方式
final colorString = '#${color.value.toRadixString(16).substring(2)}';
if (Platform.isAndroid || Platform.isIOS) {
// 使用shared_preferences
} else {
// OpenHarmony特定API
// ohStorage.setString('last_color', colorString);
}
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
// 颜色预览区域
Container(
width: 120,
height: 120,
color: _currentColor,
margin: const EdgeInsets.all(16),
),
// 预设颜色网格
_buildColorGrid(),
// 最近使用的颜色
_buildRecentColors(),
],
);
}
Widget _buildColorGrid() {
final primaryColors = [
Colors.red, Colors.orange, Colors.yellow, Colors.green,
Colors.blue, Colors.indigo, Colors.purple, Colors.pink
];
return GridView.count(
shrinkWrap: true,
physics: const NeverScrollableScrollPhysics(),
crossAxisCount: 4,
crossAxisSpacing: 8,
mainAxisSpacing: 8,
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
childAspectRatio: 1,
children: primaryColors.map((color) {
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => _handleColorChange(color),
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(8),
border: Border.all(
color: _currentColor == color ? Colors.black : Colors.transparent,
width: _currentColor == color ? 2 : 0,
),
),
),
);
}).toList(),
);
}
Widget _buildRecentColors() {
if (_recentColors.isEmpty) return const SizedBox.shrink();
return Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
const Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 16, vertical: 8),
child: Text('最近使用', style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
),
SizedBox(
height: 60,
child: ListView.builder(
scrollDirection: Axis.horizontal,
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 8),
itemCount: _recentColors.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final color = _recentColors[index];
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => _handleColorChange(color),
child: Container(
width: 40,
height: 40,
margin: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 4),
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color: color,
shape: BoxShape.circle,
border: Border.all(
color: _currentColor == color ? Colors.white : Colors.grey,
width: 2,
),
),
),
);
},
),
),
],
);
}
}
代码解释:这个组件实现了跨平台颜色选择器,核心在于:
-
平台检测:使用
Platform.isAndroid和Platform.isIOS判断是否运行在标准Flutter平台上,否则默认为OpenHarmony -
数据持久化方案:为不同平台提供了不同的存储适配,OpenHarmony需要使用其特有的存储API
-
UI适配:考虑到OpenHarmony设备可能有不同的屏幕尺寸和交互方式,使用了响应式布局
-
颜色格式转换:将Flutter的Color对象转换为OpenHarmony可识别的十六进制字符串格式
跨平台适配的关键点
-
平台检测:不要仅依赖
Platform.isAndroid,因为OpenHarmony可能也返回true。最好使用特性检测:bool get isRunningOnOpenHarmony { // 通过尝试调用特定API来检测 try { // 尝试访问OpenHarmony特定API return true; } catch (e) { return false; } } -
桥接层设计:为OpenHarmony创建专用的桥接层,隔离平台特定代码:
// color_bridge.dart abstract class ColorBridge { void applyColor(Color color); Color getLastSelectedColor(); } // openharmony_color_bridge.dart class OHColorBridge implements ColorBridge { void applyColor(Color color) { // 调用OpenHarmony原生方法 final ohColor = '#${color.value.toRadixString(16).substring(2)}'; // 调用原生桥接方法 } // 其他实现... }
性能优化经验
在适配过程中我发现几个性能瓶颈:
-
颜色转换开销:频繁的颜色格式转换会造成卡顿。解决方案是缓存转换结果:
final _colorCache = <int, String>{}; String _getOHColorString(Color color) { return _colorCache.putIfAbsent(color.value, () { return '#${color.value.toRadixString(16).substring(2)}'; }); } -
UI渲染优化:OpenHarmony上Flutter的渲染效率与Android/iOS不同,特别是处理大量小部件时。将颜色网格预渲染为单个图片能大幅提升性能。
-
内存管理:OpenHarmony设备内存通常有限,要特别注意及时释放不再使用的颜色资源。
实用小技巧
-
调试技巧:在OpenHarmony上难以调试时,可以将颜色值记录到日志:
void _debugColor(Color color) { final hex = '#${color.value.toRadixString(16).substring(2)}'; debugPrint('Selected color: $hex'); // 在OpenHarmony上也可以写入特定日志文件 } -
渐进增强:先实现基础功能,再为OpenHarmony添加特殊优化。这样保证核心功能在所有平台上正常工作。
总结
将Flutter的颜色选择器适配到OpenHarmony不是简单"有手就行"的工作。需要深入理解两个平台的颜色处理机制,设计良好的桥接层,并针对性能优化。通过平台检测、抽象桥接层和缓存策略,我们可以构建出既保持代码统一,又能在OpenHarmony上高效运行的颜色选择器。
随着OpenHarmony生态的成熟,期待更多专门针对鸿蒙优化的Flutter插件出现。目前,我们开发者需要多踩坑、多尝试,积累经验,才能打造出真正无缝的跨平台体验。
希望这篇文章能帮到正在做Flutter适配OpenHarmony的你!如果有问题或更好的方案,欢迎在评论区交流讨论。
欢迎大家加入开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区,一起探索更多鸿蒙跨平台开发技术!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献27条内容
已为社区贡献27条内容








所有评论(0)