RN for OpenHarmony 实战 TodoList 项目:任务截止日期显示
这篇文章探讨了任务管理应用中截止日期的重要性及实现方式。摘要如下: 核心观点:截止日期是任务管理的关键维度,能有效提高任务完成率 技术实现要点: 使用字符串存储日期(ISO 8601格式),便于序列化和比较 日期与分类标签在同一行显示,形成清晰的元信息区域 采用emoji替代图标,实现轻量化的跨平台显示 设计考量: 通过字体大小(11px)和颜色(#666/#888)区分主次信息 日期与创建时间采
案例开源地址:https://gitcode.com/lqjmac/rn_openharmony_todolist
时间,任务管理的隐形维度
做过项目管理的人都知道,一个任务如果没有截止日期,它就永远不会被完成。
“这个功能什么时候做?”
“有空就做。”
结果呢?永远没空。
截止日期给任务赋予了紧迫感。它把模糊的"以后"变成了具体的"12月30日"。当你看到日期一天天逼近,你就不得不行动起来。
在我们的 TodoList 应用中,每个任务都有一个截止日期,显示在任务卡片的元信息区域。今天我们就来看看这个功能是怎么实现的。
数据结构中的日期字段
先看任务的类型定义:
interface Task {
id: string;
title: string;
completed: boolean;
priority: 'high' | 'medium' | 'low';
category: string;
dueDate: string;
note: string;
createdAt: number;
}
dueDate 字段存储截止日期,类型是 string。
为什么用字符串而不是 Date 对象或时间戳?
几个实际的考虑:
1. 序列化友好
如果要把任务数据存到本地存储或发送到服务器,字符串可以直接使用,不需要额外的转换。Date 对象需要先转成字符串,取出来再转回 Date,多了两步操作。
2. 显示方便
我们只需要显示日期,不需要精确到时分秒。'2024-12-30' 这样的格式直接就能用,不需要格式化。
3. 比较简单
字符串格式的日期(ISO 格式)可以直接用字符串比较来判断先后顺序。'2024-12-30' > '2024-12-25' 返回 true,因为字符串比较是按字典序的,而 ISO 日期格式正好符合这个规律。
初始数据中的日期
看看初始任务数据是怎么设置日期的:
const [tasks, setTasks] = useState<Task[]>([
{id: '1', title: '学习 React Native', completed: false, priority: 'high', category: '学习', dueDate: '2024-12-30', note: '完成基础教程', createdAt: Date.now()},
{id: '2', title: '完成项目文档', completed: true, priority: 'medium', category: '工作', dueDate: '2024-12-28', note: '', createdAt: Date.now()},
{id: '3', title: '健身运动', completed: false, priority: 'low', category: '生活', dueDate: '2024-12-27', note: '跑步30分钟', createdAt: Date.now()},
{id: '4', title: '阅读技术书籍', completed: false, priority: 'medium', category: '学习', dueDate: '2024-12-29', note: '', createdAt: Date.now()},
{id: '5', title: '整理代码仓库', completed: true, priority: 'low', category: '工作', dueDate: '2024-12-26', note: '清理无用分支', createdAt: Date.now()},
]);
日期格式是 YYYY-MM-DD,这是 ISO 8601 标准的日期格式。选择这个格式有几个好处:
- 国际通用,没有歧义(不像
12/30/2024和30/12/2024的争议) - 排序友好,字符串排序就是时间排序
- JavaScript 的
Date对象可以直接解析
注意 createdAt 用的是时间戳 Date.now(),而 dueDate 用的是日期字符串。这是因为创建时间需要精确到毫秒(用于排序和唯一性),而截止日期只需要精确到天。
在任务卡片中显示日期
日期显示在任务卡片的元信息区域:
const TaskItem = ({item, index}: {item: Task; index: number}) => {
const itemAnim = useRef(new Animated.Value(0)).current;
useEffect(() => {
Animated.timing(itemAnim, {toValue: 1, duration: 300, delay: index * 50, useNativeDriver: true}).start();
}, []);
return (
<Animated.View style={[styles.taskCard, {backgroundColor: theme.card, borderColor: theme.border, opacity: itemAnim,
transform: [{translateX: itemAnim.interpolate({inputRange: [0, 1], outputRange: [-50, 0]})}],
shadowColor: '#000', shadowOffset: {width: 0, height: 2}, shadowOpacity: darkMode ? 0.3 : 0.1, shadowRadius: 4, elevation: 3}]}>
<View style={[styles.priorityBar, {backgroundColor: priorityColors[item.priority]}]} />
<View style={styles.taskContent}>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => toggleTask(item.id)} style={styles.checkbox}>
<View style={[styles.checkboxInner, {borderColor: theme.accent}, item.completed && {backgroundColor: theme.accent}]}>
{item.completed && <Text style={styles.checkmark}>✓</Text>}
</View>
</TouchableOpacity>
<View style={styles.taskInfo}>
<Text style={[styles.taskTitle, {color: theme.text}, item.completed && styles.completedText]}>{item.title}</Text>
<View style={styles.taskMeta}>
<View style={[styles.categoryTag, {backgroundColor: theme.accent + '30'}]}>
<Text style={[styles.categoryText, {color: theme.accent}]}>{item.category}</Text>
</View>
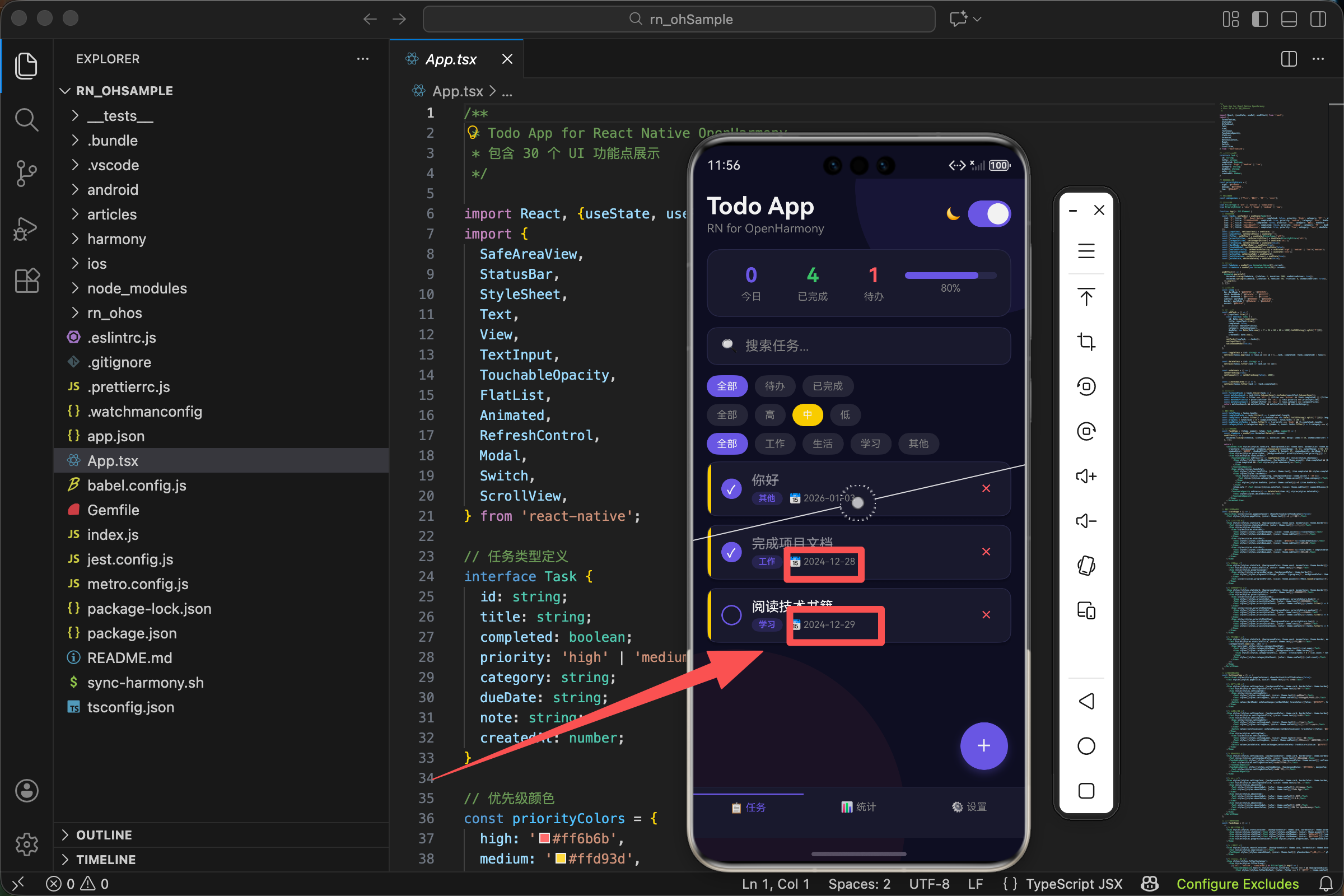
<Text style={[styles.dueDate, {color: theme.subText}]}>📅 {item.dueDate}</Text>
</View>
{item.note ? <Text style={[styles.noteText, {color: theme.subText}]} numberOfLines={1}>💬 {item.note}</Text> : null}
</View>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => deleteTask(item.id)} style={styles.deleteBtn}>
<Text style={styles.deleteBtnText}>×</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
</Animated.View>
);
};
日期显示的关键代码就这一行:
<Text style={[styles.dueDate, {color: theme.subText}]}>📅 {item.dueDate}</Text>
简单直接。一个日历 emoji 加上日期字符串。
emoji 的使用是一个设计选择。它比文字图标更生动,比图片图标更轻量。在跨平台应用中,emoji 是一个很好的图标方案——不需要额外的图标库,所有平台都支持。
日期显示的样式
dueDate: {fontSize: 11},
样式很简单,只定义了字体大小。颜色通过内联样式动态设置:
{color: theme.subText}
theme.subText 是次要文字颜色,在深色模式下是 #888888,在浅色模式下是 #666666。这个颜色比主文字颜色浅,表示这是辅助信息,不是最重要的内容。
11 像素的字体大小也是刻意的选择。它比任务标题(16 像素)小很多,形成明显的视觉层次。用户的视线会先被标题吸引,然后才注意到下面的元信息。
元信息区域的布局
日期和分类标签放在同一行:
<View style={styles.taskMeta}>
<View style={[styles.categoryTag, {backgroundColor: theme.accent + '30'}]}>
<Text style={[styles.categoryText, {color: theme.accent}]}>{item.category}</Text>
</View>
<Text style={[styles.dueDate, {color: theme.subText}]}>📅 {item.dueDate}</Text>
</View>
taskMeta 的样式:
taskMeta: {flexDirection: 'row', alignItems: 'center', gap: 8},
flexDirection: 'row'- 水平排列alignItems: 'center'- 垂直居中对齐gap: 8- 元素之间的间距
分类标签在左边,日期在右边。这个顺序是有讲究的——分类是一个"标签",视觉上更突出(有背景色),放在前面;日期是纯文字,相对低调,放在后面。
添加任务时设置日期
当用户添加新任务时,我们自动设置一个默认的截止日期:
const addTask = () => {
if (inputText.trim()) {
const newTask: Task = {
id: Date.now().toString(),
title: inputText.trim(),
completed: false,
priority: newTaskPriority,
category: newTaskCategory,
dueDate: new Date(Date.now() + 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000).toISOString().split('T')[0],
note: '',
createdAt: Date.now(),
};
setTasks([newTask, ...tasks]);
setInputText('');
setShowAddModal(false);
}
};
重点看这一行:
dueDate: new Date(Date.now() + 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000).toISOString().split('T')[0],
这行代码做了什么?
1. 计算 7 天后的时间戳
Date.now() + 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000
Date.now() 返回当前时间的毫秒时间戳。加上 7 天的毫秒数(7天 × 24小时 × 60分钟 × 60秒 × 1000毫秒),得到 7 天后的时间戳。
2. 创建 Date 对象
new Date(...)
用时间戳创建一个 Date 对象。
3. 转换为 ISO 字符串
.toISOString()
得到类似 '2024-12-30T08:30:00.000Z' 的字符串。
4. 提取日期部分
.split('T')[0]
用 'T' 分割字符串,取第一部分,得到 '2024-12-30'。
为什么默认是 7 天后?这是一个产品决策。大多数任务不会是当天要完成的,给一周的缓冲时间比较合理。当然,在实际产品中,这个日期应该是可以修改的。
今日任务的统计
在统计区域,我们显示了今日到期的任务数量:
const todayTasks = tasks.filter(t => t.dueDate === new Date().toISOString().split('T')[0]).length;
这行代码筛选出截止日期是今天的任务。
new Date().toISOString().split('T')[0] 获取今天的日期字符串,然后与每个任务的 dueDate 比较。
显示在界面上:
<View style={styles.statItem}>
<Text style={[styles.statNumber, {color: theme.accent}]}>{todayTasks}</Text>
<Text style={[styles.statLabel, {color: theme.subText}]}>今日</Text>
</View>
"今日"这个统计项很重要。它告诉用户:今天有多少任务需要完成。如果数字是 0,用户可以放松一下;如果数字很大,用户就知道今天要忙了。
统计区域的完整布局
<View style={[styles.statsContainer, {backgroundColor: theme.card, borderColor: theme.border}]}>
<View style={styles.statItem}>
<Text style={[styles.statNumber, {color: theme.accent}]}>{todayTasks}</Text>
<Text style={[styles.statLabel, {color: theme.subText}]}>今日</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.statItem}>
<Text style={[styles.statNumber, {color: '#6bcb77'}]}>{completedTasks}</Text>
<Text style={[styles.statLabel, {color: theme.subText}]}>已完成</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.statItem}>
<Text style={[styles.statNumber, {color: '#ff6b6b'}]}>{totalTasks - completedTasks}</Text>
<Text style={[styles.statLabel, {color: theme.subText}]}>待办</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.progressContainer}>
<View style={[styles.progressBar, {backgroundColor: theme.border}]}>
<View style={[styles.progressFill, {width: `${progress}%`, backgroundColor: theme.accent}]} />
</View>
<Text style={[styles.progressText, {color: theme.subText}]}>{Math.round(progress)}%</Text>
</View>
</View>
四个统计项并排显示:今日任务、已完成、待办、完成进度。
样式定义:
statsContainer: {flexDirection: 'row', alignItems: 'center', padding: 16, borderRadius: 16, borderWidth: 1, marginBottom: 12},
statItem: {alignItems: 'center', flex: 1},
statNumber: {fontSize: 24, fontWeight: 'bold'},
statLabel: {fontSize: 12, marginTop: 4},
每个 statItem 设置了 flex: 1,所以它们会平分可用空间。alignItems: 'center' 让数字和标签水平居中。
数字用 24 像素的粗体,非常醒目。标签用 12 像素的普通字体,作为数字的说明。
日期相关的潜在优化
当前的实现比较基础,在实际产品中可能需要更多功能:
1. 日期选择器
目前添加任务时日期是自动设置的,用户无法修改。可以加一个日期选择器组件,让用户自己选择截止日期。
React Native 社区有很多日期选择器库,比如 @react-native-community/datetimepicker。
2. 过期提醒
如果任务已经过期(截止日期早于今天),可以用红色显示日期,或者加一个"已过期"的标签。
const isOverdue = item.dueDate < new Date().toISOString().split('T')[0] && !item.completed;
<Text style={[styles.dueDate, {color: isOverdue ? '#ff6b6b' : theme.subText}]}>
📅 {item.dueDate} {isOverdue && '(已过期)'}
</Text>
3. 相对日期显示
把 '2024-12-30' 显示成"3天后"或"明天",更直观。
function formatRelativeDate(dateStr: string): string {
const today = new Date();
const date = new Date(dateStr);
const diffDays = Math.ceil((date.getTime() - today.getTime()) / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));
if (diffDays === 0) return '今天';
if (diffDays === 1) return '明天';
if (diffDays === -1) return '昨天';
if (diffDays > 0) return `${diffDays}天后`;
return `${Math.abs(diffDays)}天前`;
}
4. 按日期排序
让用户可以按截止日期排序任务,把最紧急的任务排在前面。
const sortedTasks = [...filteredTasks].sort((a, b) => a.dueDate.localeCompare(b.dueDate));
时区问题
使用日期字符串有一个潜在的问题:时区。
new Date().toISOString() 返回的是 UTC 时间。如果用户在北京(UTC+8),当地时间是 2024-12-30 早上 6 点,toISOString() 返回的日期部分是 '2024-12-29',因为 UTC 时间还是 29 号晚上 10 点。
这可能导致"今日任务"的统计不准确。
解决方案是使用本地时间:
function getLocalDateString(): string {
const now = new Date();
const year = now.getFullYear();
const month = String(now.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0');
const day = String(now.getDate()).padStart(2, '0');
return `${year}-${month}-${day}`;
}
这个函数返回本地时区的日期字符串,避免了时区问题。
日期格式的本地化
'2024-12-30' 是程序员友好的格式,但对普通用户来说可能不够友好。不同地区的用户习惯不同的日期格式:
- 中国:2024年12月30日 或 2024/12/30
- 美国:12/30/2024
- 欧洲:30/12/2024
可以用 Intl.DateTimeFormat 来格式化:
function formatDate(dateStr: string): string {
const date = new Date(dateStr);
return new Intl.DateTimeFormat('zh-CN', {
year: 'numeric',
month: 'long',
day: 'numeric',
}).format(date);
}
// '2024-12-30' -> '2024年12月30日'
或者更简短的格式:
function formatDateShort(dateStr: string): string {
const date = new Date(dateStr);
return new Intl.DateTimeFormat('zh-CN', {
month: 'short',
day: 'numeric',
}).format(date);
}
// '2024-12-30' -> '12月30日'
小结
日期显示看起来简单,但涉及的细节不少:
- 数据格式的选择(字符串 vs Date vs 时间戳)
- 默认值的设置(7天后)
- 显示格式(ISO格式 vs 本地化格式)
- 时区处理
- 与其他功能的联动(统计、筛选、排序)
在我们的实现中,选择了最简单的方案:ISO 格式的日期字符串,直接显示。这对于一个演示项目来说足够了。
但如果要做成一个真正的产品,上面提到的那些优化点都值得考虑。特别是日期选择器和过期提醒,这两个功能对用户体验的提升是很明显的。
时间管理的本质是优先级管理。截止日期帮助用户判断任务的紧迫程度,从而做出更好的决策。一个好的待办应用,应该让用户一眼就能看出哪些任务需要立即处理,哪些可以稍后再说。
深入理解日期在任务卡片中的视觉层次
回到任务卡片的完整结构,我们来分析日期在整个视觉层次中的位置:
<View style={styles.taskInfo}>
<Text style={[styles.taskTitle, {color: theme.text}, item.completed && styles.completedText]}>{item.title}</Text>
<View style={styles.taskMeta}>
<View style={[styles.categoryTag, {backgroundColor: theme.accent + '30'}]}>
<Text style={[styles.categoryText, {color: theme.accent}]}>{item.category}</Text>
</View>
<Text style={[styles.dueDate, {color: theme.subText}]}>📅 {item.dueDate}</Text>
</View>
{item.note ? <Text style={[styles.noteText, {color: theme.subText}]} numberOfLines={1}>💬 {item.note}</Text> : null}
</View>
taskInfo 容器内有三层信息:
第一层:任务标题
最重要的信息,字体最大(16像素),颜色最深(主文字色)。用户的视线首先会落在这里。
第二层:元信息(分类 + 日期)
次要信息,字体较小(10-11像素),颜色较浅。分类有背景色,日期是纯文字。
第三层:备注
可选信息,只有在有备注时才显示。字体小,颜色浅,最多显示一行。
这种层次设计遵循了信息架构的基本原则:重要的信息要突出,次要的信息要弱化。用户可以快速扫描列表,只看标题就能了解任务内容;如果需要更多细节,再看下面的元信息。
日期与主题系统的配合
我们的应用支持深色和浅色两种主题。日期的颜色需要根据主题动态变化:
const theme = {
bg: darkMode ? '#0f0f23' : '#f5f5f5',
card: darkMode ? '#1a1a2e' : '#ffffff',
text: darkMode ? '#ffffff' : '#333333',
subText: darkMode ? '#888888' : '#666666',
border: darkMode ? '#2a2a4a' : '#e0e0e0',
accent: '#6c5ce7',
};
日期使用 theme.subText 颜色:
- 深色模式:
#888888(中灰色) - 浅色模式:
#666666(深灰色)
这两个颜色都比主文字色浅,但又不会浅到看不清。它们在各自的背景上都有足够的对比度,符合可访问性标准。
为什么不用固定颜色?因为同一个灰色在深色背景和浅色背景上的视觉效果是不同的。#888888 在深色背景上看起来刚好,但在浅色背景上会显得太浅。反过来,#666666 在浅色背景上合适,但在深色背景上会显得太深。
日期 emoji 的选择
我们用 📅 这个 emoji 来表示日期。为什么选这个?
首先,它是一个日历图标,语义明确。用户一看就知道后面跟的是日期。
其次,它在各个平台上的显示效果都比较一致。有些 emoji 在不同平台上差异很大,但日历 emoji 相对稳定。
最后,它的视觉重量适中。不会太抢眼,也不会被忽略。
当然,也可以用其他方式表示日期:
- 文字前缀:
截止:2024-12-30 - 图标组件:使用 react-native-vector-icons 的日历图标
- 不加前缀:直接显示日期
每种方式都有优缺点。emoji 的优点是简洁、跨平台、不需要额外依赖。缺点是无法自定义样式(大小、颜色)。
性能考虑
在任务列表中,每个任务卡片都会渲染日期。如果任务很多,需要考虑性能。
当前的实现没有性能问题,因为日期只是一个简单的字符串显示。但如果加上日期格式化、相对日期计算等功能,就需要注意了。
避免在渲染时做复杂计算
// 不好的做法:每次渲染都计算
<Text>{formatRelativeDate(item.dueDate)}</Text>
// 好的做法:使用 useMemo 缓存
const formattedDate = useMemo(() => formatRelativeDate(item.dueDate), [item.dueDate]);
<Text>{formattedDate}</Text>
使用 FlatList 的优化特性
我们的列表使用了 FlatList,它会自动回收屏幕外的列表项,只渲染可见的部分。这对于长列表的性能很重要。
<FlatList
data={filteredTasks}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
renderItem={({item, index}) => <TaskItem item={item} index={index} />}
// ...
/>
keyExtractor 很重要,它告诉 FlatList 如何识别每个列表项。使用稳定的 key(如 id)可以避免不必要的重新渲染。
日期功能的测试要点
如果要为日期功能写测试,需要考虑这些场景:
1. 日期显示正确
// 任务的 dueDate 应该正确显示在界面上
expect(screen.getByText('📅 2024-12-30')).toBeTruthy();
2. 今日任务统计正确
// 需要 mock Date.now() 来控制"今天"是哪一天
jest.useFakeTimers().setSystemTime(new Date('2024-12-30'));
// 然后验证今日任务数量
3. 新任务的默认日期正确
// 添加任务后,dueDate 应该是 7 天后
const newTask = tasks[0];
const expectedDate = new Date(Date.now() + 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000).toISOString().split('T')[0];
expect(newTask.dueDate).toBe(expectedDate);
4. 时区边界情况
// 在 UTC 时间接近午夜时,本地日期可能与 UTC 日期不同
// 需要测试这种边界情况
与其他功能的联动
日期不是孤立的功能,它与应用的其他部分有联动:
与筛选功能联动
虽然当前没有实现按日期筛选,但这是一个常见需求。用户可能想看"今天到期的任务"或"本周到期的任务"。
与排序功能联动
按截止日期排序是很自然的需求。把最紧急的任务排在前面,帮助用户优先处理。
与通知功能联动
在任务到期前发送提醒通知。这需要后台服务或本地通知的支持。
与统计功能联动
除了"今日任务",还可以统计"本周任务"、"已过期任务"等。
这些功能的实现都依赖于日期字段。选择一个好的日期格式(如 ISO 字符串),可以让这些功能的实现更简单。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献9条内容
已为社区贡献9条内容








所有评论(0)