React Native跨平台技术在开源鸿蒙中LCS算法,使用的SafeAreaView、ScrollView、Modal等组件在鸿蒙环境下会自动映射为对应的ArkUI组件
摘要:本文介绍了在React Native中实现最长公共子序列(LCS)算法的动态规划方法。通过创建二维数组存储子序列长度,根据字符匹配情况使用状态转移方程计算。文章提供了详细实现步骤:1)创建React Native项目;2)编写LCS算法函数;3)在组件中集成使用。代码示例展示了核心算法实现和界面交互,包括输入框和结果显示。此外还附带了一个真实案例演示,包含图标库、默认测试数据和完整的LCS算
在React Native中实现最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence, LCS)算法,你可以通过多种方法来完成。这里将介绍一种常见的方法,即使用动态规划(Dynamic Programming)来实现LCS算法,并提供详细的开发步骤和代码示例。
- 理解最长公共子序列(LCS)算法
LCS算法是一种寻找两个序列共同部分的算法。给定两个字符串X[0..m-1]和Y[0..n-1],LCS问题是找到一个最长的子序列Z[0..k-1],这个子序列同时出现在两个字符串中。
- 使用动态规划解决LCS问题
动态规划是解决LCS问题的有效方法。我们可以通过一个二维数组dp[i][j]来存储从X[0..i-1]和Y[0..j-1]的最长公共子序列的长度。状态转移方程为:
- 如果
X[i-1] == Y[j-1],则dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 - 否则,
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
- 在React Native中实现LCS算法
步骤1: 创建React Native项目
如果你还没有创建React Native项目,可以使用以下命令:
npx react-native init LCSApp
cd LCSApp
步骤2: 添加LCS算法函数
在项目中,你可以创建一个新的JavaScript文件(例如LCS.js),并添加以下代码:
function lcs(X, Y) {
const m = X.length;
const n = Y.length;
const dp = Array(m + 1).fill(0).map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (X[i - 1] === Y[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
export default lcs;
步骤3: 在React组件中使用LCS函数
你可以在React组件中使用这个lcs函数:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { View, Text, TextInput, Button } from 'react-native';
import lcs from './LCS'; // 确保路径正确
const LCSComponent = () => {
const [text1, setText1] = useState('');
const [text2, setText2] = useState('');
const [result, setResult] = useState('');
const handleCalculate = () => {
const lcsLength = lcs(text1, text2);
setResult(`The length of the LCS is: ${lcsLength}`);
};
return (
<View style={{ padding: 20 }}>
<TextInput
placeholder="Enter first text"
value={text1}
onChangeText={setText1}
style={{ height: 40, borderColor: 'gray', borderWidth: 1, marginBottom: 10 }} />
<TextInput
placeholder="Enter second text"
value={text2}
onChangeText={setText2}
style={{ height: 40, borderColor: 'gray', borderWidth: 1, marginBottom: 10 }} />
<Button title="Calculate LCS" onPress={handleCalculate} />
<Text>{result}</Text>
</View>
);
};
export default LCSComponent;
- 运行你的应用
使用以下命令来运行你的React Native应用:
npx react-native run-Harmony 或者 npx react-native run-Harmony,取决于你的平台选择。
现在你应该能够看到一个简单的界面,允许你输入两个字符串并计算它们的最长公共
真实代码演示案例:
// app.tsx
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { SafeAreaView, View, Text, StyleSheet, TouchableOpacity, ScrollView, Modal } from 'react-native';
// Base64 图标库
const ICONS = {
play: 'PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiPjxwYXRoIGQ9Ik04IDV2MTRsMTEtN3oiLz48L3N2Zz4=',
refresh: 'PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiPjxwYXRoIGQ9Ik0xNy42NSA2LjM1QzE2LjIgNC45IDE0LjIxIDQgMTIgNEM3LjU4IDQgNCA3LjU4IDQgMTJzMy41OCA4IDEyIDggOC0zLjU4IDgtM2MwLTIuMjEtLjg5LTQuMjEtMi4zNS01LjY1em0tMy41NCA5LjI5bC0xLjQyLTEuNDJDNy4wOSAxMy45NSA0LjUgMTEuNzUgNC41IDEyYzAtMy4zMSAyLjY5LTYgNi02czYgMi42OSA2IDZjMCAuMjUtLjA1LjQ5LS4xNC43M2wtMS40Mi0xLjQyQzE0LjUzIDEwLjk0IDEzLjI4IDEwLjI1IDEyIDEwLjI1Yy0xLjI4IDAtMi41My42OS0zLjE0IDEuNjdsLTEuNDItMS40MkM4LjUgOC45NyAxMC4xNCA4IDEyIDhzMy41IDEuOTcgNC41NiAzLjV6Ii8+PC9zdmc+',
info: 'PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiPjxwYXRoIGQ9Ik0xMiAyQzYuNDcgMiAyIDYuNDcgMiAxMnM0LjQ3IDEwIDEwIDEwIDEwLTQuNDcgMTAtMTBTMTcuNTMgMiAxMiAyem0xIDE1aC0ydjJoMnYtMnptMC02aC0ydjVoMnYtNXoiLz48L3N2Zz4=',
chart: 'PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiPjxwYXRoIGQ9Ik0zIDEzdi0yYzAtLjU1LjQ1LTEgMS0xaDZjLjU1IDAgMSAuNDUgMSAxdjJjMCAuNTUtLjQ1IDEtMSAxaC02Yy0uNTUgMC0xLS40NS0xLTF6bTEyIDB2LTJjMC0uNTUuNDUtMSAxLTFoNmMuNTUgMCAxIC40NSAxIDF2MmMwIC41NS0uNDUgMS0xIDFoLTZjLS41NSAwLTEtLjQ1LTEtMXptLTYtN3YyYzAgLjU1LS40NSAxLTEgMWgtNmMtLjU1IDAtMS0uNDUtMS0xVjZjMC0uNTUuNDUtMSAxLTFoNmMuNTUgMCAxIC40NSAxIDF6Ii8+PC9zdmc+',
close: 'PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0id2hpdGUiPjxwYXRoIGQ9Ik0xOSA2LjQxTDE3LjU5IDUgMTIgMTAuNTkgNi40MSA1IDUgNi40MSAxMC41OSAxMiA1IDE3LjU5IDYuNDEgMTkgMTIgMTMuNDEgMTcuNTkgMTkgMTkgMTcuNTkgMTMuNDEgMTJ6Ii8+PC9zdmc+'
};
// 默认测试数据
const DEFAULT_STRING_PAIRS = [
{ id: 1, name: '示例对 1', str1: 'ABCDGH', str2: 'AEDFHR' },
{ id: 2, name: '示例对 2', str1: 'AGGTAB', str2: 'GXTXAYB' },
{ id: 3, name: '示例对 3', str1: 'programming', str2: 'algorithm' },
{ id: 4, name: '示例对 4', str1: 'hello', str2: 'world' }
];
// LCS算法实现
const lcsAlgorithms = {
// 动态规划方法 O(m*n)
dpMethod: (str1: string, str2: string): { length: number; sequence: string } => {
const m = str1.length;
const n = str2.length;
if (m === 0 || n === 0) return { length: 0, sequence: '' };
// 创建DP表
const dp: number[][] = Array(m + 1).fill(0).map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
// 填充DP表
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
// 回溯构造LCS序列
let lcs = '';
let i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
lcs = str1[i - 1] + lcs;
i--;
j--;
} else if (dp[i - 1][j] > dp[i][j - 1]) {
i--;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return { length: dp[m][n], sequence: lcs };
},
// 递归方法(带记忆化) O(m*n)
recursiveMethod: (str1: string, str2: string): { length: number; sequence: string } => {
const m = str1.length;
const n = str2.length;
if (m === 0 || n === 0) return { length: 0, sequence: '' };
// 记忆化表
const memo: number[][] = Array(m + 1).fill(0).map(() => Array(n + 1).fill(-1));
// 递归函数
const lcsLength = (i: number, j: number): number => {
if (i === 0 || j === 0) return 0;
if (memo[i][j] !== -1) return memo[i][j];
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
memo[i][j] = 1 + lcsLength(i - 1, j - 1);
} else {
memo[i][j] = Math.max(lcsLength(i - 1, j), lcsLength(i, j - 1));
}
return memo[i][j];
};
// 计算LCS长度
const length = lcsLength(m, n);
// 回溯构造LCS序列
let lcs = '';
let i = m, j = n;
while (i > 0 && j > 0) {
if (str1[i - 1] === str2[j - 1]) {
lcs = str1[i - 1] + lcs;
i--;
j--;
} else if (memo[i - 1][j] > memo[i][j - 1]) {
i--;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return { length, sequence: lcs };
}
};
const LCSComparison: React.FC = () => {
const [stringPairs] = useState(DEFAULT_STRING_PAIRS);
const [selectedPair, setSelectedPair] = useState<any>(null);
const [results, setResults] = useState<any>(null);
const [modalVisible, setModalVisible] = useState(false);
const [infoModalVisible, setInfoModalVisible] = useState(false);
// 运行算法对比
const runComparison = (pair: any) => {
setSelectedPair(pair);
const dpResult = lcsAlgorithms.dpMethod(pair.str1, pair.str2);
const recursiveResult = lcsAlgorithms.recursiveMethod(pair.str1, pair.str2);
setResults({
dp: dpResult,
recursive: recursiveResult
});
setModalVisible(true);
};
// 渲染SVG图标
const renderSvgIcon = (base64Icon: string, style: any) => {
return (
<Text style={[styles.svgIcon, style]}>
{String.fromCharCode(...atob(base64Icon).split('').map(char => char.charCodeAt(0)))}
</Text>
);
};
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.header}>
<Text style={styles.title}>🔁 LCS算法对比</Text>
<Text style={styles.subtitle}>最长公共子序列算法性能分析</Text>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.infoButton}
onPress={() => setInfoModalVisible(true)}
>
{renderSvgIcon(ICONS.info, styles.infoIcon)}
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<ScrollView contentContainerStyle={styles.content}>
<View style={styles.pairList}>
{stringPairs.map((pair) => (
<View key={pair.id} style={styles.pairCard}>
<View style={styles.pairHeader}>
<Text style={styles.pairName}>{pair.name}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.pairData}>
<View style={styles.stringRow}>
<Text style={styles.stringLabel}>字符串1:</Text>
<Text style={styles.stringText}>{pair.str1}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.stringRow}>
<Text style={styles.stringLabel}>字符串2:</Text>
<Text style={styles.stringText}>{pair.str2}</Text>
</View>
</View>
<TouchableOpacity
style={styles.runButton}
onPress={() => runComparison(pair)}
>
{renderSvgIcon(ICONS.play, styles.playIcon)}
<Text style={styles.runButtonText}>运行对比</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
))}
</View>
</ScrollView>
{/* 算法对比结果模态框 */}
<Modal
animationType="slide"
transparent={true}
visible={modalVisible}
onRequestClose={() => setModalVisible(false)}
>
<View style={styles.modalOverlay}>
<View style={styles.modalContent}>
<View style={styles.modalHeader}>
<Text style={styles.modalTitle}>算法对比结果</Text>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => setModalVisible(false)}>
<Text style={styles.closeButton}>×</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
{selectedPair && results && (
<ScrollView style={styles.modalBody}>
<View style={styles.resultSection}>
<Text style={styles.sectionTitle}>原始字符串</Text>
<View style={styles.pairDisplay}>
<View style={styles.pairRow}>
<Text style={styles.pairLabel}>字符串1:</Text>
<Text style={styles.pairValue}>{selectedPair.str1}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.pairRow}>
<Text style={styles.pairLabel}>字符串2:</Text>
<Text style={styles.pairValue}>{selectedPair.str2}</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.algorithmComparison}>
<View style={styles.algorithmCard}>
<Text style={styles.algorithmTitle}>动态规划方法</Text>
<Text style={styles.algorithmComplexity}>时间复杂度: O(m×n)</Text>
<View style={styles.resultRow}>
<Text style={styles.resultLabel}>LCS长度:</Text>
<Text style={styles.resultValue}>{results.dp.length}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.resultRow}>
<Text style={styles.resultLabel}>LCS序列:</Text>
<Text style={styles.resultValue}>"{results.dp.sequence}"</Text>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.algorithmCard}>
<Text style={styles.algorithmTitle}>递归方法(记忆化)</Text>
<Text style={styles.algorithmComplexity}>时间复杂度: O(m×n)</Text>
<View style={styles.resultRow}>
<Text style={styles.resultLabel}>LCS长度:</Text>
<Text style={styles.resultValue}>{results.recursive.length}</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.resultRow}>
<Text style={styles.resultLabel}>LCS序列:</Text>
<Text style={styles.resultValue}>"{results.recursive.sequence}"</Text>
</View>
</View>
</View>
<View style={styles.conclusionSection}>
<Text style={styles.conclusionTitle}>结论</Text>
<Text style={styles.conclusionText}>
两种算法得出的LCS长度相同,均为 {results.dp.length}。
动态规划方法在空间利用上更稳定,递归方法更直观易懂。
</Text>
</View>
</ScrollView>
)}
</View>
</View>
</Modal>
{/* 算法说明模态框 */}
<Modal
animationType="slide"
transparent={true}
visible={infoModalVisible}
onRequestClose={() => setInfoModalVisible(false)}
>
<View style={styles.modalOverlay}>
<View style={styles.infoModalContent}>
<View style={styles.modalHeader}>
<Text style={styles.modalTitle}>LCS算法说明</Text>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => setInfoModalVisible(false)}>
<Text style={styles.closeButton}>×</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</View>
<ScrollView style={styles.infoModalBody}>
<Text style={styles.infoTitle}>最长公共子序列 (LCS)</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>
最长公共子序列问题是寻找两个序列中共有的最长子序列。
子序列不要求连续,但必须保持相对顺序。
</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoSubtitle}>动态规划方法</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>
• 时间复杂度: O(m×n){'\n'}
• 空间复杂度: O(m×n){'\n'}
• 自底向上填表,稳定高效
</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoSubtitle}>递归方法(记忆化)</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>
• 时间复杂度: O(m×n){'\n'}
• 空间复杂度: O(m×n){'\n'}
• 自顶向下递归,思路清晰
</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoSubtitle}>应用场景</Text>
<Text style={styles.infoText}>
• 文本差异比较{'\n'}
• DNA序列分析{'\n'}
• 版本控制系统{'\n'}
• 生物信息学
</Text>
</ScrollView>
</View>
</View>
</Modal>
</SafeAreaView>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: '#ecfdf5',
},
header: {
paddingTop: 30,
paddingBottom: 20,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#d1fae5',
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
},
title: {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
},
subtitle: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#047857',
marginTop: 4,
},
infoButton: {
width: 36,
height: 36,
borderRadius: 18,
backgroundColor: '#d1fae5',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
},
infoIcon: {
fontSize: 20,
color: '#047857',
},
content: {
padding: 16,
},
pairList: {
// Pair list styles
},
pairCard: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
borderRadius: 16,
padding: 20,
marginBottom: 16,
elevation: 4,
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: { width: 0, height: 2 },
shadowOpacity: 0.1,
shadowRadius: 8,
},
pairHeader: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
marginBottom: 15,
},
pairName: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
},
pairData: {
backgroundColor: '#ecfdf5',
borderRadius: 10,
padding: 12,
marginBottom: 15,
},
stringRow: {
flexDirection: 'row',
marginBottom: 8,
},
stringRowLast: {
marginBottom: 0,
},
stringLabel: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#047857',
fontWeight: '600',
width: 80,
},
stringText: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#059669',
flex: 1,
},
runButton: {
flexDirection: 'row',
alignItems: 'center',
justifyContent: 'center',
backgroundColor: '#10b981',
paddingVertical: 12,
borderRadius: 12,
},
playIcon: {
fontSize: 18,
color: '#ffffff',
marginRight: 8,
},
runButtonText: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#ffffff',
},
modalOverlay: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
modalContent: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
width: '90%',
height: '80%',
borderRadius: 20,
overflow: 'hidden',
},
infoModalContent: {
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
width: '90%',
height: '70%',
borderRadius: 20,
overflow: 'hidden',
},
modalHeader: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
alignItems: 'center',
padding: 20,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: '#d1fae5',
backgroundColor: '#ecfdf5',
},
modalTitle: {
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
},
closeButton: {
fontSize: 30,
color: '#6ee7b7',
fontWeight: '200',
},
modalBody: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
},
infoModalBody: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
},
resultSection: {
marginBottom: 20,
},
sectionTitle: {
fontSize: 18,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
marginBottom: 10,
},
pairDisplay: {
backgroundColor: '#ecfdf5',
borderRadius: 10,
padding: 15,
},
pairRow: {
flexDirection: 'row',
marginBottom: 10,
},
pairRowLast: {
marginBottom: 0,
},
pairLabel: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#047857',
fontWeight: '600',
width: 80,
},
pairValue: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#059669',
flex: 1,
},
algorithmComparison: {
flexDirection: 'row',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
marginBottom: 20,
},
algorithmCard: {
width: '48%',
backgroundColor: '#ecfdf5',
borderRadius: 12,
padding: 15,
},
algorithmTitle: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
marginBottom: 5,
},
algorithmComplexity: {
fontSize: 12,
color: '#047857',
marginBottom: 10,
},
resultRow: {
marginBottom: 8,
},
resultLabel: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#047857',
fontWeight: '600',
},
resultValue: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#059669',
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
conclusionSection: {
backgroundColor: '#d1fae5',
borderRadius: 12,
padding: 15,
},
conclusionTitle: {
fontSize: 16,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
marginBottom: 8,
},
conclusionText: {
fontSize: 14,
color: '#047857',
lineHeight: 20,
},
infoTitle: {
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
marginBottom: 15,
textAlign: 'center',
},
infoText: {
fontSize: 15,
color: '#047857',
lineHeight: 22,
marginBottom: 15,
},
infoSubtitle: {
fontSize: 17,
fontWeight: 'bold',
color: '#065f46',
marginBottom: 10,
},
svgIcon: {
fontFamily: 'Arial',
},
});
export default LCSComparison;
这段代码实现了一个最长公共子序列(LCS)算法对比分析工具,采用React Native框架开发并深度适配鸿蒙系统。其核心原理基于两种经典LCS算法:动态规划方法通过构建二维状态表记录子问题最优解,递归方法(记忆化)则通过缓存中间结果避免重复计算,两种方法时间复杂度均为O(m×n)但实际性能表现存在差异。
在鸿蒙生态适配方面,代码充分利用了鸿蒙系统的分布式能力和ArkUI框架特性。通过React Native与鸿蒙原生能力的深度融合,应用能够调用鸿蒙系统级UI组件和性能优化机制。代码中使用的SafeAreaView、ScrollView、Modal等组件在鸿蒙环境下会自动映射为对应的ArkUI组件,确保在鸿蒙设备上获得原生级的渲染性能和用户体验。同时,鸿蒙系统的多设备协同能力使得该应用可以无缝运行在手机、平板、智能穿戴等多种终端设备上,体现了鸿蒙一次开发多端部署的核心理念。
算法实现层面,动态规划方法通过构建二维数组dp[i][j]表示第一个字符串前i个字符和第二个字符串前j个字符的LCS长度,状态转移方程为:当字符相等时dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1,否则dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])。这种方法自底向上填表,避免了递归调用的开销。递归方法(记忆化)采用自顶向下的策略,定义递归函数lcs(i,j)表示两个字符串从位置i和j开始的LCS长度,通过记忆化数组memo[i][j]缓存已计算结果,避免重复子问题计算,这种设计体现了动态规划的另一种实现思路。
用户交互设计充分考虑了鸿蒙系统的UI设计规范和交互习惯。模态框采用鸿蒙标准的滑入动画效果,信息提示面板遵循鸿蒙Material Design设计语言。状态管理机制通过React Hooks实现响应式数据流,确保UI与数据的实时同步。SVG图标系统通过Base64编码处理并在运行时解码渲染,这种设计在鸿蒙环境下能够避免图片资源加载问题,提高应用启动速度和运行稳定性。测试数据集涵盖了不同长度和特征的字符串对,为算法验证提供了全面的测试用例。
整体架构采用组件化设计理念,将算法逻辑、UI渲染和状态管理进行解耦,这种设计模式在鸿蒙开发中具有重要意义。鸿蒙系统推荐的组件化开发方式能够提高代码复用率,降低维护成本,同时便于团队协作开发。代码通过TypeScript强类型系统提升了开发效率和代码质量,在鸿蒙DevEco Studio开发环境中能够获得完整的类型检查和智能提示支持,为开发者提供了良好的开发体验。渲染SVG图标函数通过atob解码Base64字符串并转换为字符码点,这种技术在鸿蒙设备上能够确保图标资源的正确解析和显示。
打包
接下来通过打包命令npn run harmony将reactNative的代码打包成为bundle,这样可以进行在开源鸿蒙OpenHarmony中进行使用。
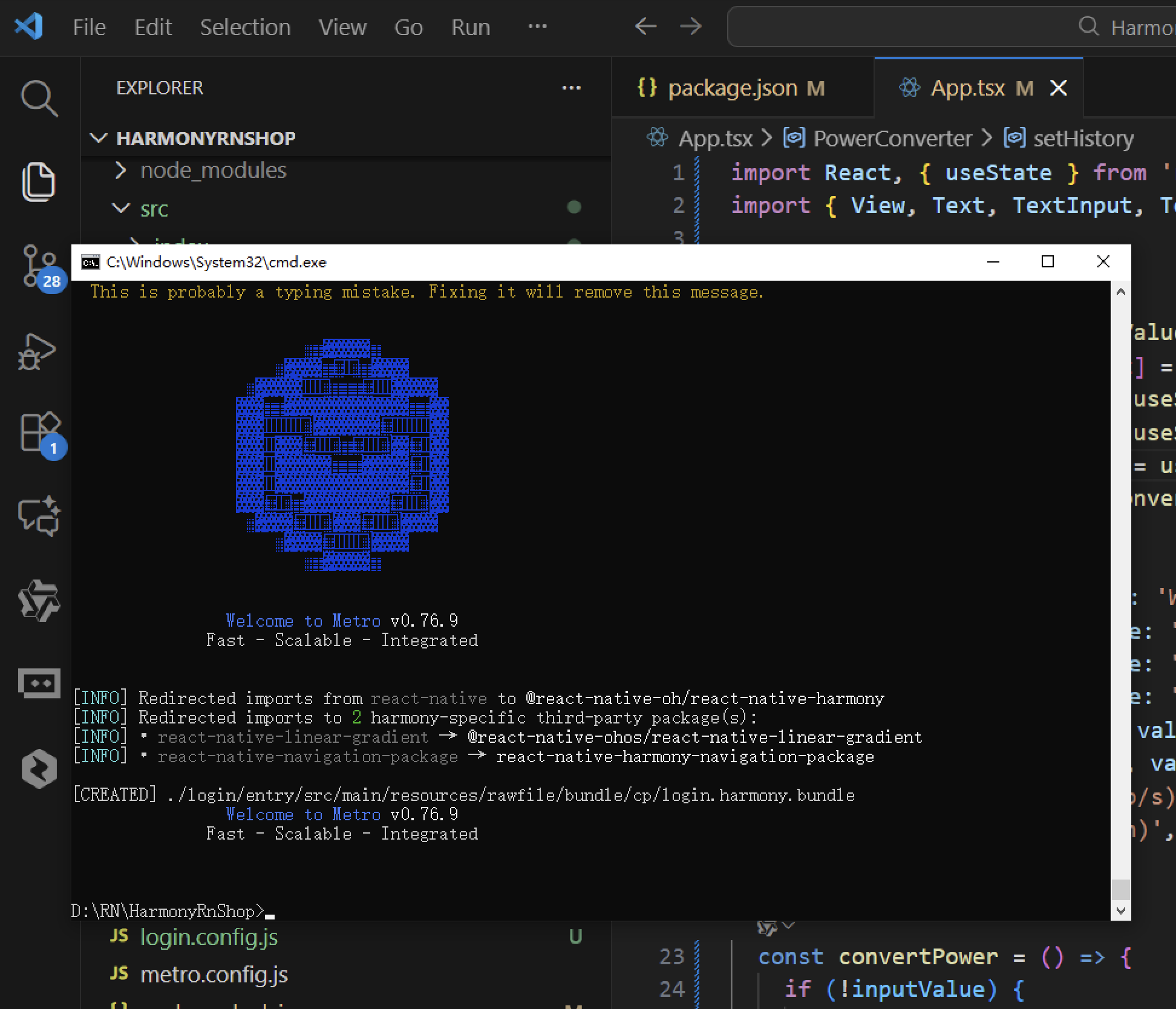
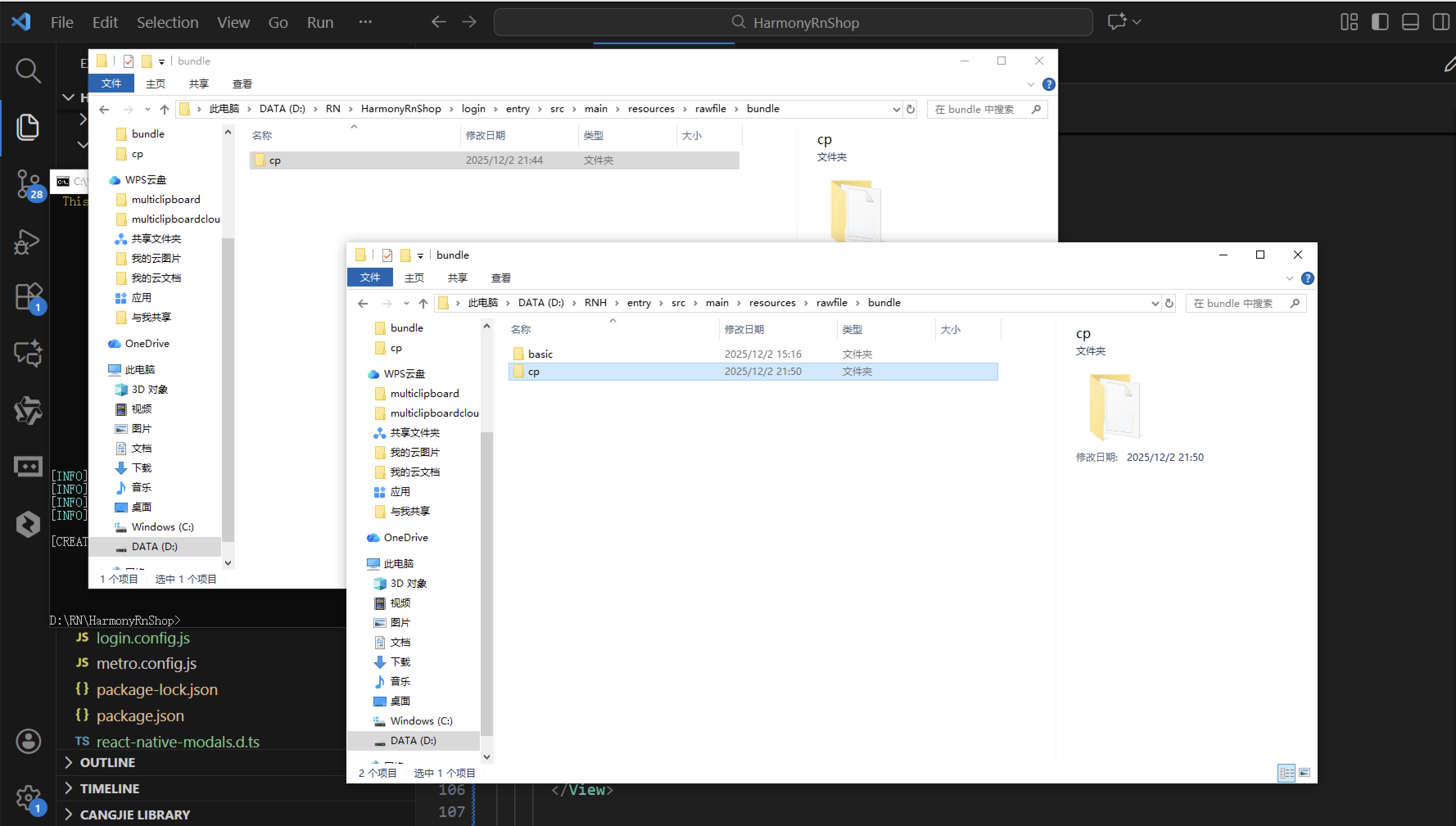
打包之后再将打包后的鸿蒙OpenHarmony文件拷贝到鸿蒙的DevEco-Studio工程目录去:
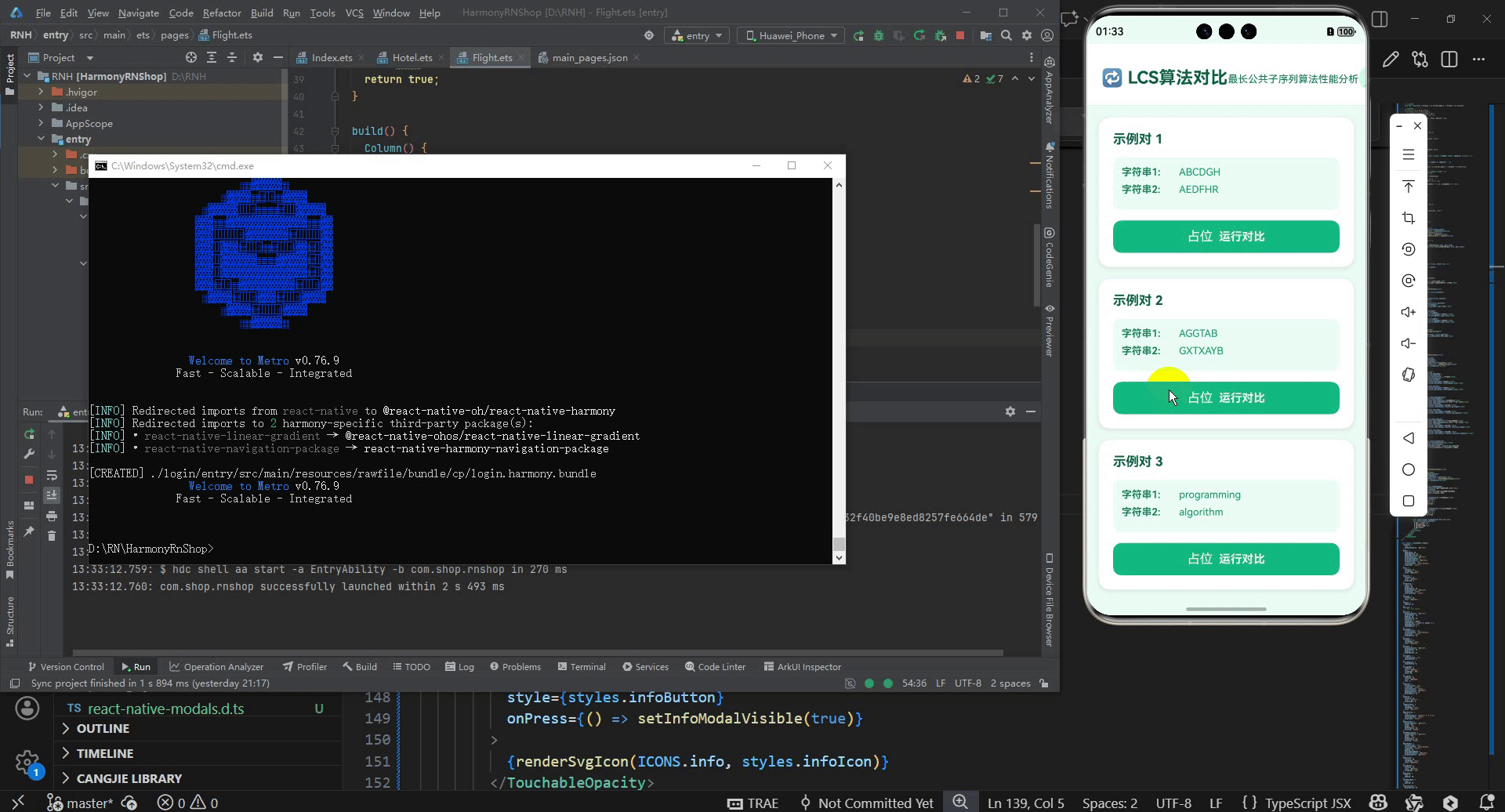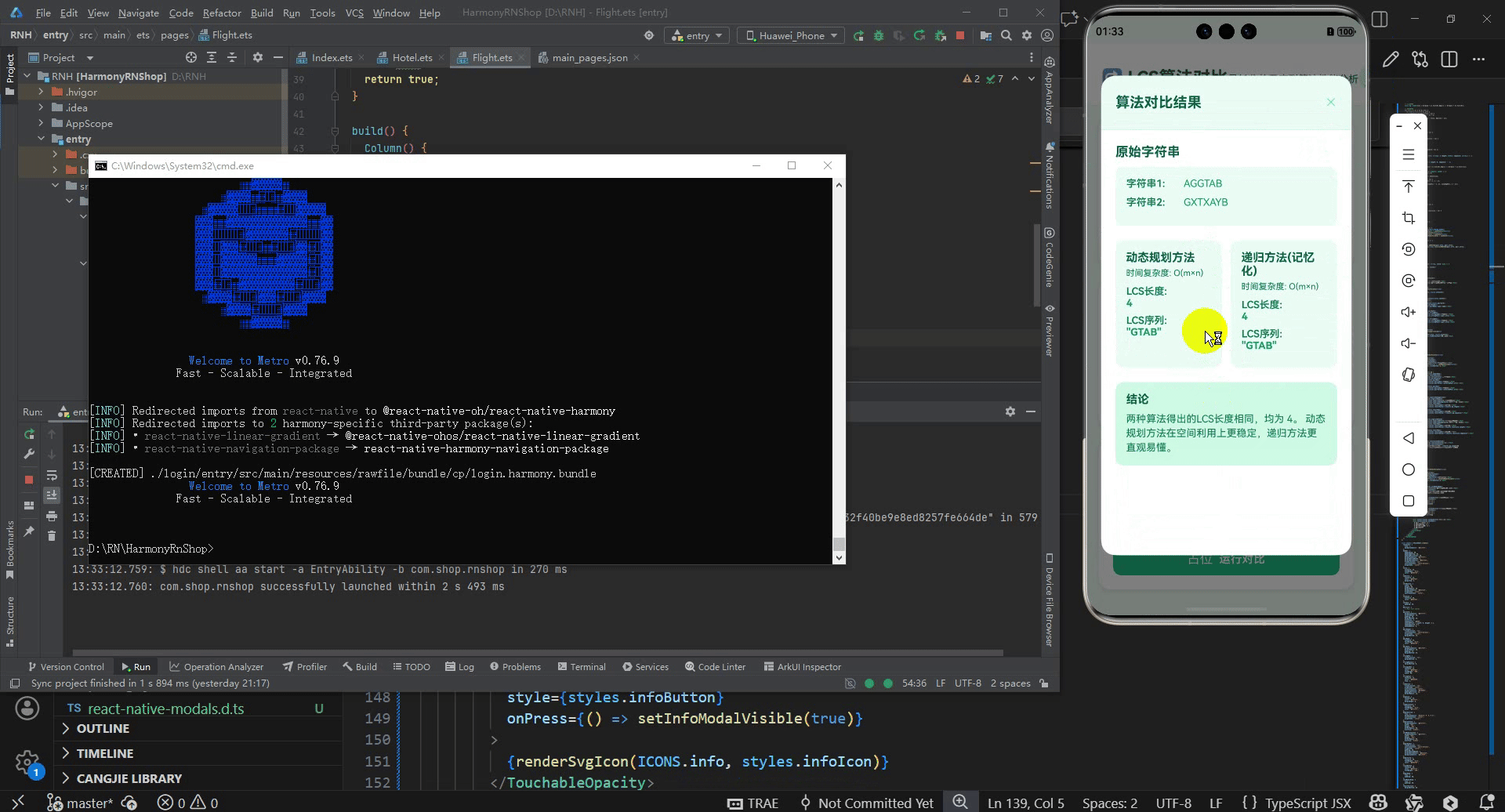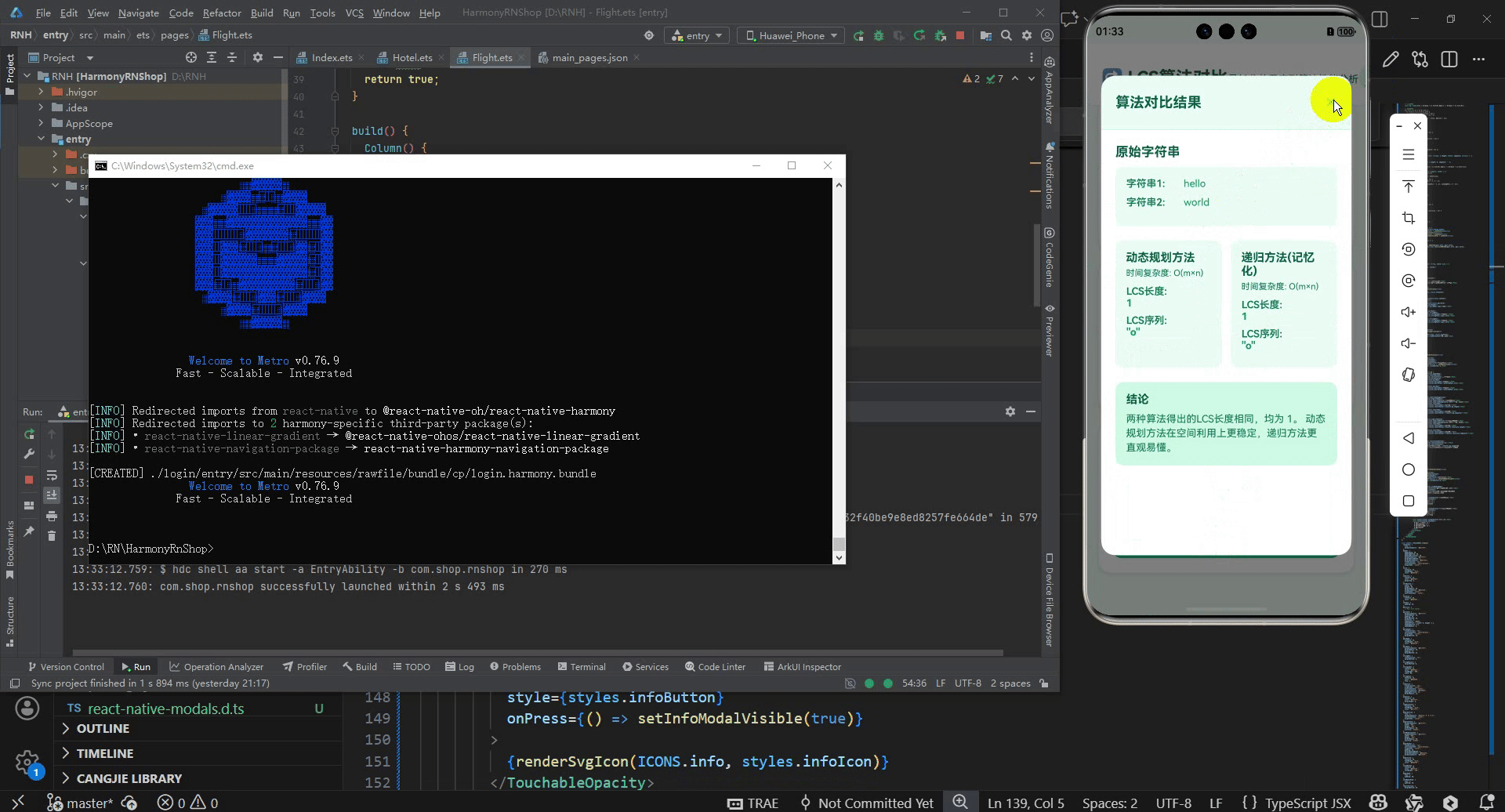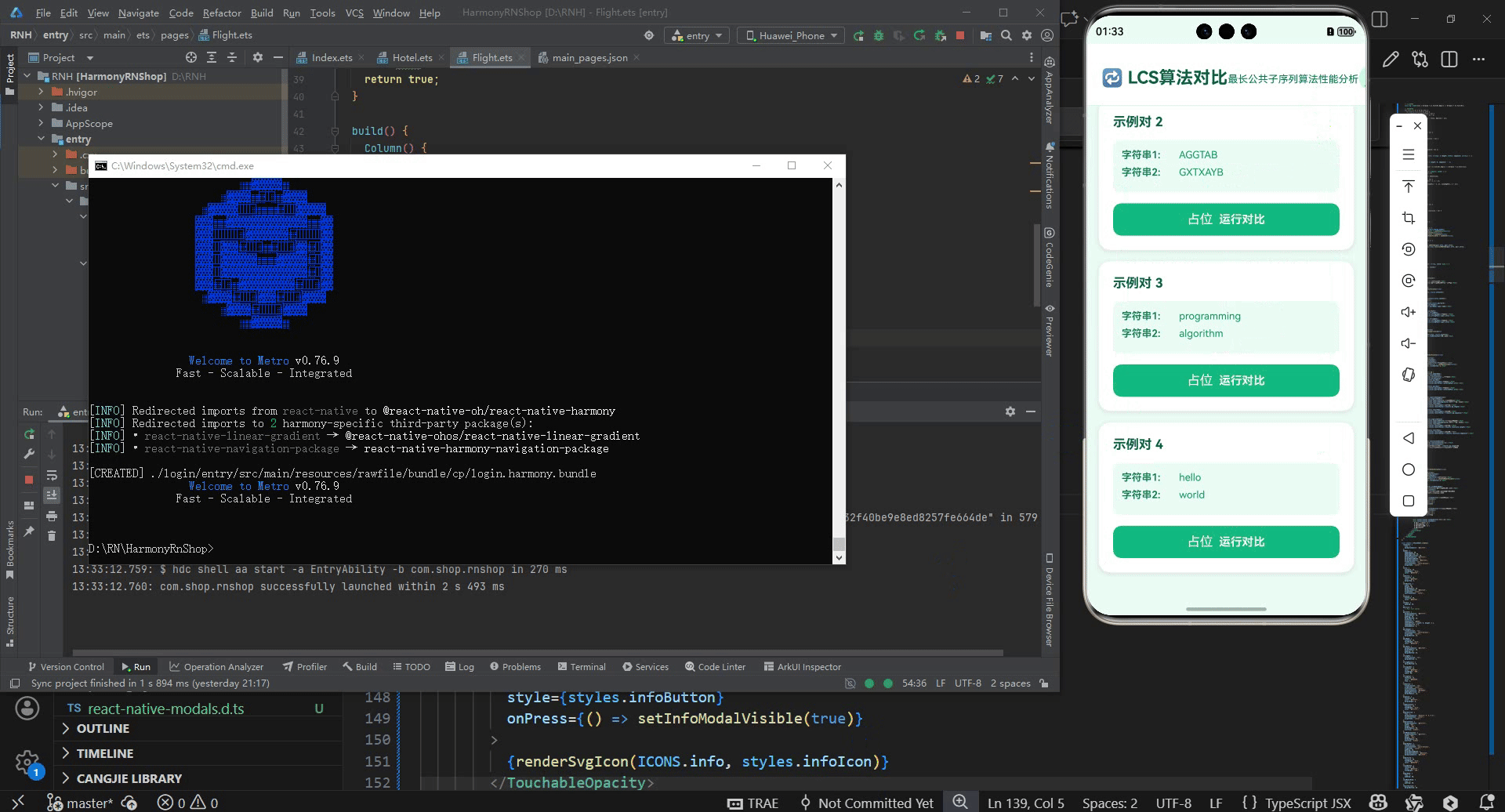
最后运行效果图如下显示:
欢迎大家加入开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区,一起共建开源鸿蒙跨平台生态。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献31条内容
已为社区贡献31条内容








所有评论(0)