字符函数和字符串函数(二)
一、strcpy的使用和模拟使用
1.1.函数strcpy
char * strcpy ( char * destination, const char * source );
1.2.strcpy的作用:
复制字符串 将源字符串指向的C字符串复制到目标数组指向的数组中,包括终止空字符(并在该位置停止)。
1.3strcpy的使用
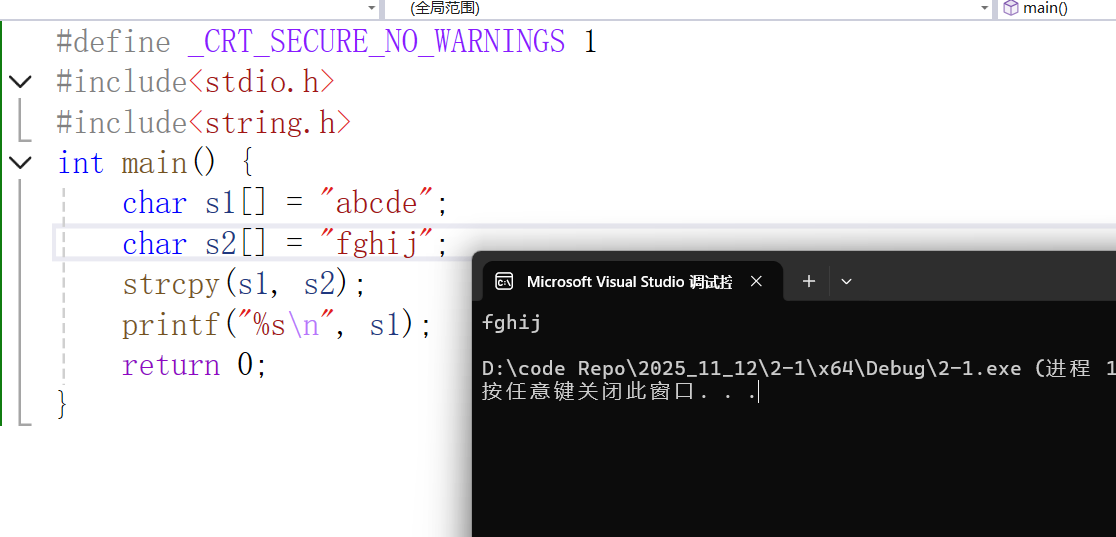
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
char s1[] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghij";
strcpy(s1, s2);
printf("%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
1.4strcpy的模拟实现
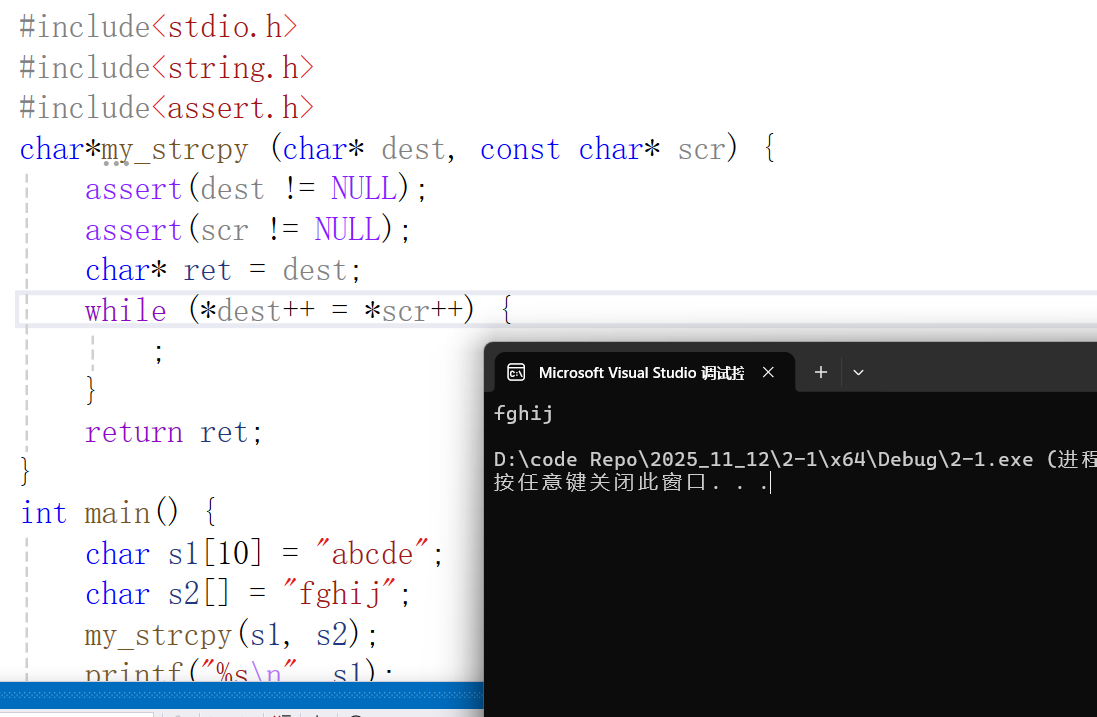
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
char*my_strcpy (char* dest, const char* scr) {
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(scr != NULL);
char* ret = dest;
while (*dest++ = *scr++) {
;
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
char s1[10] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghij";
my_strcpy(s1, s2);
printf("%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
二、strcat的使用及模拟实现
2.1.函数strcat
char * strcat ( char * destination, const char * source );
2.2.strcat的作用
连接字符串 将源字符串的副本追加到目标字符串。目标字符串中的终止空字符会被源字符串的第一个字符覆盖,并且在目标字符串中由两者连接形成的新字符串的末尾会包含一个空字符。
2.3.strcat的使用
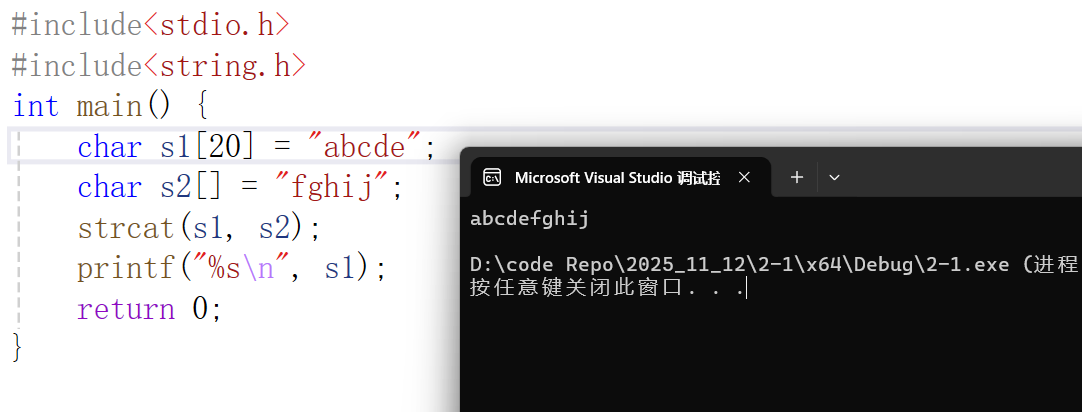 代码如下(可自行测试):
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
char s1[20] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghij";
strcat(s1, s2);
printf("%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
2.4.strcat的模拟实现
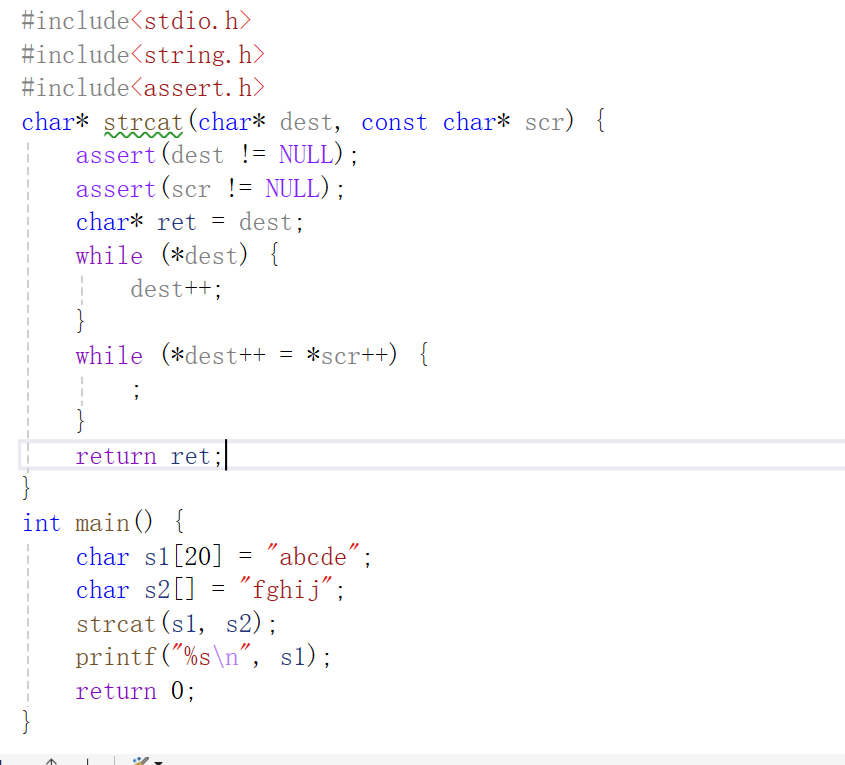
运行结果如下:
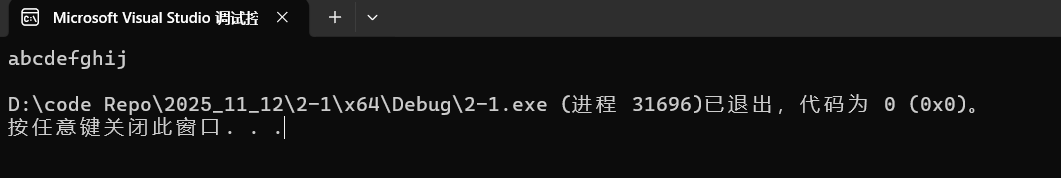 代码如下(可自行测试):
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
char* strcat(char* dest, const char* scr) {
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(scr != NULL);
char* ret = dest;
while (*dest) {
dest++;
}
while (*dest++ = *scr++) {
;
}
return ret;
}
int main() {
char s1[20] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghij";
strcat(s1, s2);
printf("%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
三、strcmp的使用和模拟实现
3.1.函数strcmp
int strcmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2 );
3.2.strcmp的作用
比较两个字符串
比较C字符串str1和C字符串str2。
此函数从每个字符串的第一个字符开始比较。如果它们相等,则继续比较后续字符对,直到字符不同或直到遇到终止空字符为止。
3.3.strcmp的使用
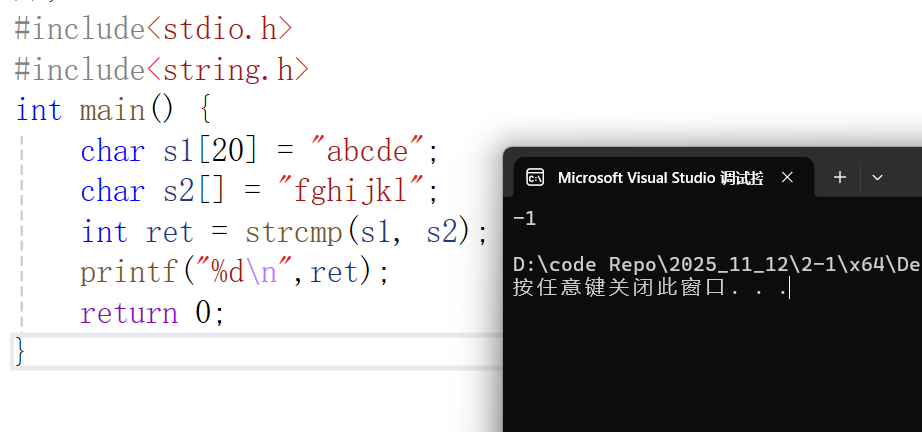
注:这里讨论字符串s1比字符串s2小的情况,大于和等于的情况可自行比较
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
char s1[20] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghijkl";
int ret = strcmp(s1, s2);
printf("%d\n",ret);
return 0;
}
3.4.strcmp的模拟实现
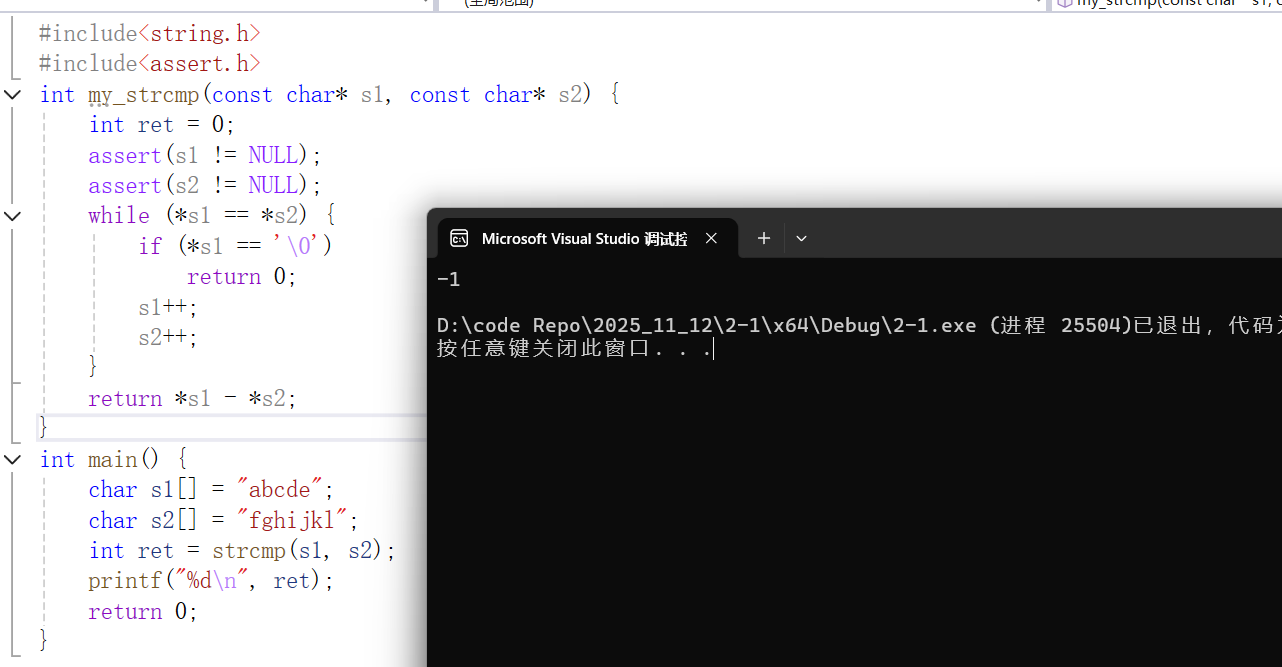
代码如下(可自行测试):
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
int my_strcmp(const char* s1, const char* s2) {
int ret = 0;
assert(s1 != NULL);
assert(s2 != NULL);
while (*s1 == *s2) {
if (*s1 == '\0')
return 0;
s1++;
s2++;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}
int main() {
char s1[] = "abcde";
char s2[] = "fghijkl";
int ret = strcmp(s1, s2);
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)