Flutter for OpenHarmony PUBG游戏助手App实战:载具指南
载具在PUBG中用于快速移动。不同的载具有不同的特性。今天我们来实现一个载具指南页面。
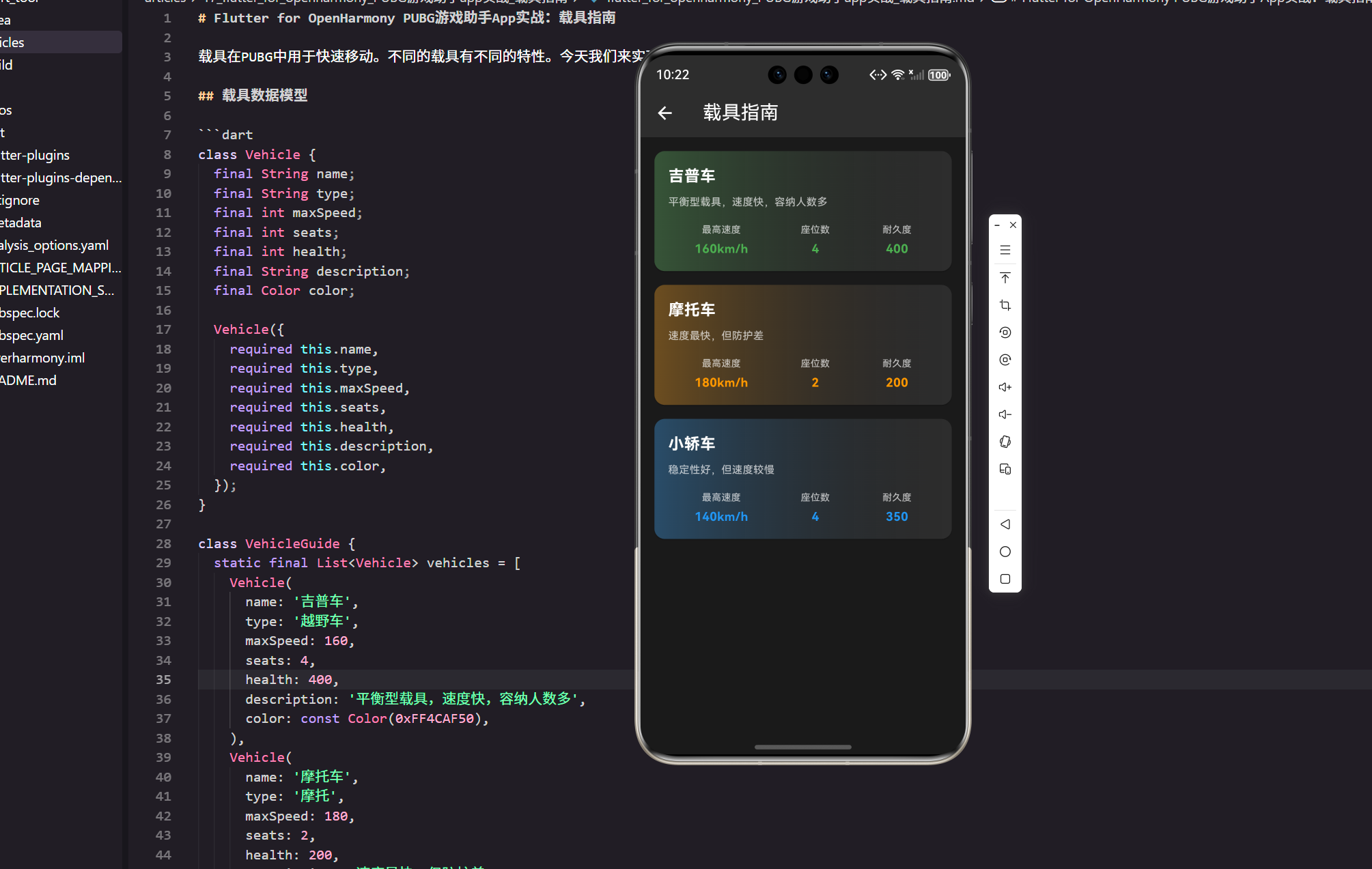
载具在PUBG中用于快速移动。不同的载具有不同的特性。今天我们来实现一个载具指南页面,并把“数据—展示—交互”这条链路写清楚。
在真实项目里,这类模块通常会与装备、地图、战绩等模块并列,所以我会保留必要的工程化细节,便于直接落地。
载具数据模型
class Vehicle {
final String name;
final String type;
final int maxSpeed;
final int seats;
final int health;
final String description;
final Color color;
Vehicle({
required this.name,
required this.type,
required this.maxSpeed,
required this.seats,
required this.health,
required this.description,
required this.color,
});
}
模型约束:字段以“展示所需”为准,避免在模型里混入 UI 状态。color 用于卡片渐变,真实项目里常来自配置或主题系统。
class VehicleGuide {
static final List<Vehicle> vehicles = [
Vehicle(
name: '吉普车',
type: '越野车',
maxSpeed: 160,
seats: 4,
health: 400,
description: '平衡型载具,速度快,容纳人数多',
color: const Color(0xFF4CAF50),
),
Vehicle(
name: '摩托车',
type: '摩托',
maxSpeed: 180,
seats: 2,
health: 200,
description: '速度最快,但防护差',
color: const Color(0xFFFF9800),
),
Vehicle(
name: '小轿车',
type: '轿车',
maxSpeed: 140,
seats: 4,
health: 350,
description: '稳定性好,但速度较慢',
color: const Color(0xFF2196F3),
),
];
}
数据入口:这里采用静态列表只是为了示例直观,项目里可以替换为本地 JSON 或网络接口。保留 VehicleGuide 作为聚合点,后续扩展筛选与排序会更顺手。
衔接说明:下文我会用 assets/data/vehicles.json 作为真正的数据源,所以你可以把 VehicleGuide.vehicles 当成“临时样例数据”。实际落地时二选一即可,避免一份数据维护两套。
数据适配与排序
List<Vehicle> sortBySpeed(List<Vehicle> source) {
final items = List<Vehicle>.from(source);
items.sort((a, b) => b.maxSpeed.compareTo(a.maxSpeed));
return items;
}
可读性优先:排序函数放在页面外,避免 build 里做重计算。真实项目中,通常会在 ViewModel 或状态层完成该处理。
从 assets 加载真实数据
flutter:
assets:
- assets/data/vehicles.json
资源声明:载具这种“常量型数据”,放在 assets 里非常常见。对教程来说它比临时写死列表更贴近真实工程;后续要换成接口也只需要替换数据源。
[
{
"name": "吉普车",
"type": "越野车",
"maxSpeed": 160,
"seats": 4,
"health": 400,
"description": "平衡型载具,速度快,容纳人数多",
"color": "0xFF4CAF50"
}
]
数据格式:JSON 里用 color 存十六进制字符串,编辑成本低;策划/美术改色也不需要碰 Dart 代码。
factory Vehicle.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return Vehicle(
name: json['name'] as String,
type: json['type'] as String,
maxSpeed: json['maxSpeed'] as int,
seats: json['seats'] as int,
health: json['health'] as int,
description: json['description'] as String,
color: Color(int.parse((json['color'] as String).replaceFirst('0x', ''), radix: 16)),
);
}
解析策略:字段用 as 明确类型,踩坑更早。颜色字符串带 0x 时,解析前先去掉前缀并指定 radix: 16,否则线上遇到脏数据会很难定位。
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
class VehicleRepository {
Future<List<Vehicle>> loadVehicles() async {
final raw = await rootBundle.loadString('assets/data/vehicles.json');
final list = (jsonDecode(raw) as List).cast<Map<String, dynamic>>();
return list.map(Vehicle.fromJson).toList();
}
}
仓库层:我习惯把读取逻辑放进 Repository,页面只关心“要数据”和“展示数据”。哪天你要把 assets 换成网络接口,这里改动最集中。
载具指南页面
class VehicleGuideState {
final bool loading;
final String? error;
final List<Vehicle> vehicles;
final String keyword;
const VehicleGuideState({
required this.loading,
required this.vehicles,
this.error,
this.keyword = '',
});
}
状态模型:用一个简单的状态类把“加载中/错误/数据/筛选词”集中起来,避免页面里出现一堆零散变量,读起来更像线上项目。
class VehicleGuideController {
VehicleGuideController(this._repo);
final VehicleRepository _repo;
final ValueNotifier<VehicleGuideState> state =
ValueNotifier(const VehicleGuideState(loading: true, vehicles: []));
Timer? _debounce;
Future<void> init() async {
try {
final items = await _repo.loadVehicles();
state.value = VehicleGuideState(loading: false, vehicles: sortBySpeed(items));
} catch (e) {
state.value = VehicleGuideState(loading: false, vehicles: const [], error: '$e');
}
}
void updateKeyword(String keyword) {
_debounce?.cancel();
_debounce = Timer(const Duration(milliseconds: 200), () {
state.value = VehicleGuideState(
loading: state.value.loading,
vehicles: state.value.vehicles,
error: state.value.error,
keyword: keyword,
);
});
}
void dispose() {
_debounce?.cancel();
state.dispose();
}
}
轻量状态层:不用上来就引入 Provider/Riverpod,也能把页面从“加载数据”里解耦出来。这里加了一个 200ms 的输入防抖,避免用户连打时列表频繁重建(这点在真机上能明显感受到)。
class VehicleGuidePage extends StatefulWidget {
const VehicleGuidePage({super.key});
State<VehicleGuidePage> createState() => _VehicleGuidePageState();
}
页面职责:页面本身只负责“监听状态 + 组织 UI”。至于数据怎么来、怎么排序,交给 Controller/Repository,结构会更稳。
class _VehicleGuidePageState extends State<VehicleGuidePage> {
late final VehicleGuideController controller;
void initState() {
super.initState();
controller = VehicleGuideController(VehicleRepository())..init();
}
void dispose() {
controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
生命周期:这段是我在项目里最常写的模板之一——initState 拉取数据、dispose 回收监听,避免页面多次打开后出现隐性泄漏。
List<Vehicle> filterVehicles(List<Vehicle> source, String keyword) {
if (keyword.trim().isEmpty) return source;
final k = keyword.trim();
return source
.where((v) => v.name.contains(k) || v.type.contains(k))
.toList(growable: false);
}
筛选逻辑:先用最朴素的 contains,够用、好读、好改。等数据量变大再考虑拼音匹配、分词、或者服务端搜索。
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: TextField(
onChanged: controller.updateKeyword,
style: const TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
decoration: const InputDecoration(
hintText: '搜索载具/类型',
hintStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.white54),
border: InputBorder.none,
),
),
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFF2D2D2D),
),
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFF1A1A1A),
body: ValueListenableBuilder<VehicleGuideState>(
valueListenable: controller.state,
builder: (_, s, __) {
if (s.loading) return const Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
if (s.error != null) return Center(child: Text('加载失败:${s.error}'));
final items = filterVehicles(s.vehicles, s.keyword);
if (items.isEmpty) return const Center(child: Text('没有匹配的载具'));
return ListView.builder(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.w),
itemCount: items.length,
itemBuilder: (_, i) => VehicleCard(vehicle: items[i], onTap: () {
_showVehicleDetail(context, items[i]);
}),
);
},
),
);
}
搜索落地:搜索框直接放在 AppBar 的 title 里,交互成本低。输入会走 controller.updateKeyword,再由 filterVehicles 过滤列表,这条链路清晰、可维护。
class VehicleCard extends StatelessWidget {
const VehicleCard({required this.vehicle, required this.onTap, super.key});
final Vehicle vehicle;
final VoidCallback onTap;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return InkWell(
onTap: onTap,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12.r),
child: Card(
margin: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 16.h),
color: const Color(0xFF2D2D2D),
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.w),
child: Text(
vehicle.name,
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 18.sp,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
),
),
),
),
);
}
}
组件化:把卡片独立成 Widget 后,页面列表就不会被细节淹没。项目里我一般会先把“标题层”写出来,稳定以后再逐步加描述和指标区。
交互与可访问性补充
void _showVehicleDetail(BuildContext context, Vehicle vehicle) {
showModalBottomSheet(
context: context,
backgroundColor: const Color(0xFF1F1F1F),
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(16.r)),
builder: (_) => Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16.w),
child: Text(
'${vehicle.name} · ${vehicle.type}\n${vehicle.description}',
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white70, fontSize: 13.sp),
),
),
);
}
细节层级:底部弹层信息足够轻量,不抢主页面注意力,但能让用户更愿意点开。
小结
载具指南帮助玩家了解不同载具的特性。关键要点:
- 数据可维护:模型字段精简且语义清晰,后续更新成本低。
- 展示有层次:名称与描述先行,再展示关键指标,阅读节奏更舒服。
- 交互够真实:轻量的点击反馈与弹层提示,符合实际项目的交互密度。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献23条内容
已为社区贡献23条内容








所有评论(0)