C++ | 浅谈 Qt 事件
目录一、事件二、事件回调函数1.计时器事件 timerEvent相关方法【扩展】2.鼠标事件相关方法鼠标事件回调的重写三、事件的分发event()一、事件事件(event)是由系统或者 Qt 本身在不同的时刻发出的。一些事件在对用户操作做出响应时发出,如鼠标、键盘事件;另一些事件则是由系统自动发出,如计时器事件。Qt 中所有事件类都继承于QEvent类。Qt 程序在main()函数创建一个QApp
目录
一、事件
事件(event)是由系统或者 Qt 本身在不同的时刻发出的。一些事件在对用户操作做出响应时发出,如鼠标、键盘事件;另一些事件则是由系统自动发出,如计时器事件。
Qt 中所有事件类都继承于QEvent类。Qt 程序在main()函数创建一个QApplication对象,然后调用了它的exec()函数,这个函数就是开始 Qt 的事件循环。在执行exec()函数之后,程序将进入事件循环来监听应用程序的事件。当事件发生时,Qt 将创建一个事件对象,在事件对象创建完毕后,Qt 将这个事件对象传递给QObject的event()函数。
event()函数并不直接处理事件,而是按照事件对象的类型分派给特定的事件处理函数,也就是说,event()函数负责事件的分发。
二、事件处理器
1.计时器事件 timerEvent
重写timerEvent事件处理器来实现计时器功能【startTimer()与timerEvent搭配使用】
-
相关方法
int QObject::startTimer(int interval, Qt::TimerType timerType = Qt::CoarseTimer);
Starts a timer and returns a timer identifier, or returns zero if it could not start a timer.
int QTimerEvent::timerId() const
Returns the unique timer identifier, which is the same identifier as returned from QObject::startTimer().
void QObject::killTimer(int id)
Kills the timer with timer identifier, id.The timer identifier is returned by startTimer() when a timer event is started.
//.h文件:
int timer1_id;
int timer2_id;
void timerEvent(QTimerEvent *ev) override;
//.cpp文件:
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QTimer>
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//启动定时器startTimer
timer1_id = startTimer(1000);
timer2_id = startTimer(2000);
//关闭定时器
connect(ui->stopBtn,&QPushButton::clicked,[=](){
killTimer(timer1_id);
killTimer(timer2_id);
});
}
//重写timerEvent事件
void Widget::timerEvent(QTimerEvent *ev)
{
if(ev->timerId()==timer1_id)
{
static int num1=1;
ui->label_2->setText(QString::number(num1++));
}
if(ev->timerId()==timer2_id)
{
static int num2=1;
ui->label_3->setText(QString::number(num2++));
}
}【扩展】
使用QTimer类实现计时器功能:
- 相关方法
void QTimer::start(int msec)
Starts or restarts the timer with a timeout interval of msec milliseconds.
If the timer is already running, it will be stopped and restarted.
Stops the timer.
This signal is emitted when the timer times out.
//每500毫秒num加1
QTimer *timer=new QTimer(this);
timer->start(500);
connect(timer,&QTimer::timeout,this,[=](){
static int num=1;
ui->label_7->setText(QString::number(num++));
});
connect(ui->stopBtn,&QPushButton::clicked,[=](){
timer->stop();
});2.鼠标事件
-
相关方法
Qt::MouseButton QMouseEvent::button() const
Returns the button that caused the event.Note that the returned value is always Qt::NoButton for mouse move events.
Qt::MouseButtons QMouseEvent::buttons() const
Returns the button state when the event was generated. The button state is a combination of Qt::LeftButton, Qt::RightButton, Qt::MidButton using the OR operator. For mouse move events, this is all buttons that are pressed down. For mouse press and double click events this includes the button that caused the event. For mouse release events this excludes the button that caused the event.
官方文档意思就是说:
QMouseEvent::button()返回 发生了该事件的按钮,对于鼠标移动事件,该函数返回Qt::NoButton;
QMouseEvent::buttons()返回 发生事件时哪些按钮还处于按下状态 。
-
鼠标事件处理器的重写
自定义一个Label类,继承自QWidget,重写鼠标相关事件回调。
//mylabel.h
#ifndef MYLABEL_H
#define MYLABEL_H
#include <QWidget>
class MyLabel : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MyLabel(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
///鼠标进入
void enterEvent(QEvent *event) override;
///鼠标离开
void leaveEvent(QEvent *event) override;
///鼠标按下
void mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override;
///鼠标释放
void mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override;
///鼠标移动
void mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override;
///鼠标双击
void mouseDoubleClickEvent(QMouseEvent *event) override;
};
#endif // MYLABEL_H
//mylabel.cpp
#include "mylabel.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QMouseEvent>
MyLabel::MyLabel(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent)
{
}
void MyLabel::enterEvent(QEvent *event)
{
qDebug()<<"鼠标进入";
}
void MyLabel::leaveEvent(QEvent *event)
{
qDebug()<<"鼠标离开";
}
void MyLabel::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if(event->button()==Qt::MouseButton::LeftButton)
{
qDebug()<<"左键按下";
QString str=QString("按下,当前窗口坐标:x=%1,y=%2").arg(event->x()).arg(event->y());
qDebug()<<str;
QString str1=QString("按下,基于桌面坐标:x=%1,y=%2").arg(event->globalX()).arg(event->globalY());
qDebug()<<str1;
}
}
void MyLabel::mouseReleaseEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if(event->button()==Qt::MouseButton::LeftButton)
{
qDebug()<<"左键释放";
QString str=QString("释放,当前窗口坐标:x=%1,y=%2").arg(event->x()).arg(event->y());
qDebug()<<str;
QString str1=QString("释放,基于桌面坐标:x=%1,y=%2").arg(event->globalX()).arg(event->globalY());
qDebug()<<str1;
}
}
void MyLabel::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
//无法用event->button()判断,需要用组合按钮 event->buttons(),并且用与操作符
if(event->buttons() & Qt::MouseButton::LeftButton)
{
qDebug()<<"鼠标移动"<<event->pos();
}
if(event->buttons() & Qt::MouseButton::AllButtons)
{
qDebug()<<"任意按钮按下移动";
}
}
void MyLabel::mouseDoubleClickEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
if(event->button()==Qt::MouseButton::LeftButton)
{
qDebug()<<"左键双击";
}
}
【扩展:mouseMoveEvent自动触发】
实现自定义MyLabel后,我们在UI界面中放入一个Widget容器,取名mylabel,把它提升为MyLabel后,便可以触发相关鼠标事件来输出相关信息。值得注意的是,mouseMoveEvent需要按下鼠标后移动才可以触发,如何实现不按下鼠标只鼠标移动的情况下自动触发mouseMoveEvent呢?
QWidget中有一个mouseTracking属性,该属性用于设置是否追踪鼠标。只有鼠标被追踪时,mouseMoveEvent()才会发出。如果mouseTracking是 false(默认即是),组件在至少一次鼠标点击之后,才能够被追踪,也就是能够发出mouseMoveEvent()事件。如果mouseTracking为 true,则mouseMoveEvent()直接可以被发出。
ui->mylabel->setMouseTracking(true);三、事件的分发event()
[override virtual protected] bool QWidget::event(QEvent *event)
事件对象创建完毕后,Qt 将这个事件对象传递给QObject的event()函数。event()函数并不直接处理事件,而是将这些事件对象按照它们不同的类型,分发给不同的事件处理器(event handler)。所以,如果我们在事件分发之前想做一些操作,重写event()函数便可以实现。
bool event(QEvent *event) override;event()返回bool值,当我们在某件事件分发之前做了一些操作,并返回true的话,表示该事件已经被识别并且处理,此时Qt 会认为这个事件已经处理完毕,不会再将这个事件发送给其它对象,而是会继续处理事件队列中的下一事件。
比如我们在事件分发之前要处理MyLabel的鼠标按下事件,而且不需要Qt将鼠标按下事件再发送给事件对象(鼠标按下的时候,不会触发之前重写的MyLabel::mousePressEvent()),我们可以这么干:
bool MyLabel::event(QEvent *event)
{
if(event->type()==QEvent::MouseButtonPress)
{
QMouseEvent *ev=static_cast<QMouseEvent *>(event);
QString str=QString("event,按下,当前窗口坐标:x=%1,y=%2").arg(ev->x()).arg(ev->y());
qDebug()<<str;
return true;
}
return QWidget::event(event);//调用父类的event()函数继续转发
}*如果我们不屏蔽某个事件,建议只重写事件处理器,因为重写event()函数需要十分注意父类的同名函数的调用,一不留神就可能出现问题。
四、事件过滤器
[virtual] bool QObject::eventFilter(QObject *watched, QEvent *event)
void QObject::installEventFilter(QObject *filterObj)
事件过滤器的调用时间是watched对象接收到事件对象之前,也就是在event()事件分发之前。我们可以重写eventFilter处理器配合installEventFilter()来过滤某个事件。
eventFilter()创建了过滤器,installEventFilter()为安装过滤器。installEventFilter()可以调用多次,依据后进先出的原则,最后一个安装的会第一个执行。
installEventFilter()是QObject的函数,所以一切对象,包括QLabel、QApplication等都可以添加事件过滤器。需要注意的是,事件过滤器和被安装过滤器的组件必须在同一个进程,否则过滤器不起作用。另外,当我们为QApplication添加事件过滤器后(即全局的事件过滤器),会严重降低整个应用程序的事件分发效率,所以要避免安装全局的事件过滤器。
1.为MyLabel安装事件过滤器
1.修改mylabel.h并在mylabel.cpp中重写该过滤器。
//mylabel.h文件
bool eventFilter(QObject *obj,QEvent *ev) override;
//mylabel.cpp文件
bool MyLabel::eventFilter(QObject *obj, QEvent *ev)
{
if(obj==this)
{
if(ev->type()==QMouseEvent::MouseButtonPress)
{
QMouseEvent* event= static_cast<QMouseEvent*>(ev);
qDebug()<<"override MyLabel eventFilter"<<event->pos();
return true;
}
}
return QObject::eventFilter(obj,ev);
}2.在MyLabel的构造函数中安装过滤器:
MyLabel::MyLabel(QWidget *parent) : QWidget(parent)
{
this->installEventFilter(this);
}此时运行程序,当我们按下按钮的时候,不会触发event()事件分发,更不会触发之前重写的MyLabel::mousePressEvent()函数,因为在事件分发之前我们在事件过滤器中停止了鼠标按下的事件。
2.为MyLabel的对象安装过滤器
修改mainwindow.h文件并在mainwindow.cpp中安装、重写过滤器:
//mainwindow.h文件:
bool eventFilter(QObject *obj,QEvent *ev) override;
//mainwindow.cpp文件:
ui->mylabel->installEventFilter(this);
bool MainWindow::eventFilter(QObject *obj, QEvent *ev)
{
if(obj==ui->mylabel)
{
if(ev->type()==QMouseEvent::MouseButtonPress)
{
QMouseEvent* event= static_cast<QMouseEvent*>(ev);
qDebug()<<"override eventFilter"<<event->pos();
return true;
}
}
return QObject::eventFilter(obj,ev);
}此时运行程序,当我们按下按钮的时候,不会触发MyLabel中的事件过滤器、event()事件分发及mousePressEvent()函数,因为在事件分发之前我们在MyLabel对象的事件过滤器中停止了鼠标按下的事件。
五、QCoreApplication::notify()
QObject、QCoreApplication、QGuiApplication、QApplication之间的关系如下:
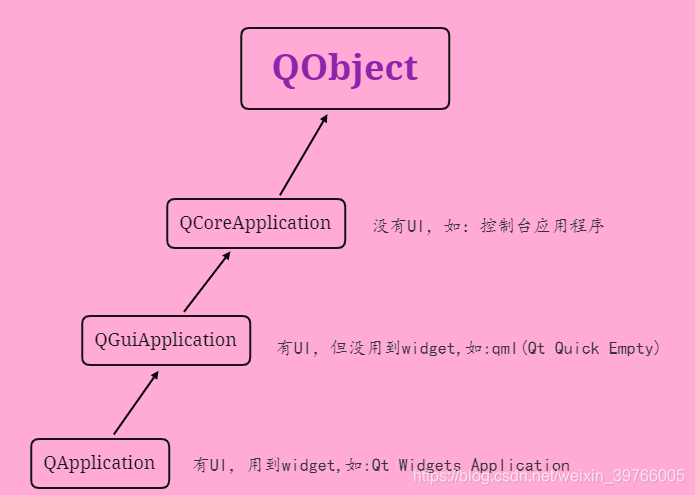
在QCoreApplication类中, 存在notify()方法,Qt事件的调用最终都会追溯到该函数,所以它的控制权最大。该函数会将event发送给receiver,也就是调用receiver->event(event)。
[virtual] bool QCoreApplication::notify(QObject *receiver, QEvent *event)
这个函数为任意线程的任意对象的任意事件调用,因此,它不存在事件过滤器的线程的问题。不过我们并不推荐这么做,因为notify()函数只有一个(QCoreApplication是单例的),而事件过滤器要灵活得多。
六、总结
对比event()事件分发和eventfilter()事件过滤器:
1.QWidget下event()是protected(虽然QObject的event()是public的),而QObject的eventfilter()是public的(QWidget没有对eventfilter()重写),因此我们可以向任何QObject子类安装事件过滤器。
2.事件过滤器在目标对象接收到事件之前进行处理,如果我们将某个事件过滤掉,目标对象根本看不到这个事件。而event()虽然可以拦截,但它也接受到了事件对象。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献3条内容
已为社区贡献3条内容






所有评论(0)