thrift JAVA使用示例(可与C++/QT互相访问)
thrift JAVA使用示例(可与C++/QT互相访问)
·
thrift JAVA使用示例(可与C++/QT互相访问)
JAVA客户端、服务器端/QT客户端、服务器端
接 上一篇文章 搭建C++的thrift环境之后,本文继续实现thrift的JAVA服务器端和客户端,thrift仍然使用上一篇使用的add.thrift。
//add.thrift
//a + b
service AddService{
i32 add(1: i32 num1, 2: i32 num2)
}
(1)生成java接口文件
thrift -r --gen java add.thrift
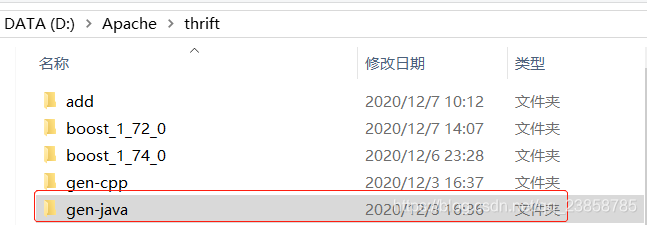

(2)编写java客户端和服务端
本文使用IDEA编辑器,首先新建项目,并添加Maven依赖。
java对thrift的支持很完善,只需要引入maven,不像c++一样需要自行编译依赖库。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.thrift/libthrift -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>
<artifactId>libthrift</artifactId>
<version>0.13.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.slf4j/slf4j-nop -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId>
<version>1.7.21</version>
</dependency>
项目的整体目录如下:

- AddClient:客户端
- AddServer:服务器端
- AddService:thrift文件产生的代码,主要是Iface和client
- AddServiceImpl:接口的实现类
在Addservice中,Iface是个接口文件,主要是用来被服务器端的程序继承和重写的,Iface里面定义了方法的接口,在服务器端的程序中应当实现这个接口,而client程序中定义了add 方法,而add方法中又调用了send_add和 recv_add 用来发送请求和接受反馈,具体通信的细节不用用户去考虑,thrift已经帮我们完全生成好了,只需要我们具体实现add的方法即可。
AddServiceImpl.java:实现了AddService的Iface接口
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
public class AddServiceImpl implements AddService.Iface{
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2) throws TException {
System.out.println("num1:" + num1);
System.out.println("num2:" + num2);
return num1 + num2;
}
}
AddClient.java:调用AddService的client即可,client调用add方法,向服务器传递参数,并接受服务器返回的信息。
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
public class AddClient {
public static final String SERVER_IP = "localhost";
public static final int SERVER_PORT = 9090;
public static final int TIMEOUT = 30000;
public void startClient(int a, int b) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
// 创建TTransport
transport = new TSocket(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT, TIMEOUT);
// 创建TProtocol 协议要与服务端一致
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
// 创建client
AddService.Client client = new AddService.Client(protocol);
// 建立连接
transport.open();
// client调用server端方法
int result = client.add(a,b);
System.out.println("thirft client result =: " + result);
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 请求结束,断开连接
if (null != transport) {
transport.close();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddClient client = new AddClient();
client.startClient(1, 2);
}
}
AddServer.java:impl文件只会在服务器端被调用,来规定服务器端返回的信息
import org.apache.thrift.TProcessor;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TSimpleServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
public class AddServer {
public static final int SERVER_PORT = 9090;
public void startServer() {
try {
System.out.println("HelloService TSimpleServer start ....");
// Transport 简单的单线程服务模型,一般用于测试
TServerSocket serverTransport = new TServerSocket(SERVER_PORT);
// Processor
TProcessor tprocessor = new AddService.Processor<AddService.Iface>(new AddServiceImpl());
TServer.Args tArgs = new TServer.Args(serverTransport);
tArgs.processor(tprocessor);
tArgs.protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocol.Factory());
// Server
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(tArgs);
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Server start error!!!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddServer server = new AddServer();
server.startServer();
}
}
与上一篇文章的QT实例合起来,可以通过thrift实现java和c++的互相调用。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)