KMP 实现鸿蒙跨端:能源工具 - 电力能耗分析工具
本文介绍了一个基于Kotlin多平台(KMP)开发的电力能耗分析工具。该工具通过输入日均用电量、峰值功率等4项电力使用数据,自动计算并输出能耗评估报告,包括能耗等级、效率评分、碳排放量等指标,并提供个性化节能建议。采用Kotlin/JS技术实现核心逻辑,支持在Node.js、Web和OpenHarmony等多平台复用,ArkTS负责界面展示。文章详细说明了输入数据格式、输出结构设计以及核心Kotl
目录
- 概述
- 功能设计
- Kotlin 实现代码(KMP)
- JavaScript 调用示例
- ArkTS 页面集成与调用
- 数据输入与交互体验
- 编译与自动复制流程
- 总结
概述
本案例在 Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) 工程中实现了一个 能源工具 - 电力能耗分析工具:
- 输入:用户的电力使用数据(日均用电量、峰值功率、用电时长、设备数量),使用空格分隔,例如:
15 5 8 10。 - 输出:
- 用电数据分析:日均用电量、峰值功率、用电时长、设备数量等基本信息
- 能耗评估:能耗等级、效率评分、成本分析
- 环保影响:碳排放量、环保评分、污染物排放
- 优化建议:根据能耗数据给出的节能建议
- 详细分析:能耗的经济学解释和环保指导
- 技术路径:Kotlin → Kotlin/JS → JavaScript 模块 → ArkTS 页面调用。
这个案例展示了 KMP 跨端开发在能源管理领域的应用:
把能耗分析逻辑写在 Kotlin 里,一次实现,多端复用;把能耗界面写在 ArkTS 里,专注 UI 和体验。
Kotlin 侧负责解析电力使用数据、计算能耗指标、评估环保影响和生成个性化建议;ArkTS 侧只需要把输入字符串传给 Kotlin 函数,并把返回结果原样展示出来即可。借助 KMP 的 Kotlin/JS 能力,这个电力能耗分析工具可以在 Node.js、Web 前端以及 OpenHarmony 中复用相同的代码逻辑。
功能设计
输入数据格式
电力能耗分析工具采用简单直观的输入格式:
- 使用 空格分隔 各个参数。
- 第一个参数是日均用电量(整数或浮点数,单位:kWh)。
- 第二个参数是峰值功率(整数或浮点数,单位:kW)。
- 第三个参数是用电时长(整数,单位:小时)。
- 第四个参数是设备数量(整数,单位:个)。
- 输入示例:
15 5 8 10
这可以理解为:
- 日均用电量:15 kWh
- 峰值功率:5 kW
- 用电时长:8 小时
- 设备数量:10 个
工具会基于这些数据计算出:
- 能耗等级:低/中/高/很高
- 效率评分:0-100 的综合评分
- 月度成本估算:基于电价的成本预测
- 碳排放量:根据能耗计算的CO2排放
- 环保评分:0-100 的环保评分
- 节能建议:针对能耗的具体优化方案
输出信息结构
为了便于在 ArkTS 页面以及终端中直接展示,Kotlin 函数返回的是一段结构化的多行文本,划分为几个分区:
- 标题区:例如"⚡ 电力能耗分析与节能评估",一眼看出工具用途。
- 用电数据:日均用电量、峰值功率、用电时长、设备数量等基本信息。
- 能耗评估:能耗等级、效率评分、月度成本。
- 环保分析:碳排放量、环保评分、污染物排放。
- 优化建议:针对能耗的具体节能建议。
- 参考标准:能耗分类标准、节能指导。
这样的输出结构使得:
- 在 ArkTS 中可以直接把整段文本绑定到
Text组件,配合monospace字体,阅读体验类似终端报告。 - 如果将来想把结果保存到日志或者后端,直接保存字符串即可。
- 需要更精细的 UI 时,也可以在前端根据分隔符进行拆分,再按块展示。
Kotlin 实现代码(KMP)
核心代码在 src/jsMain/kotlin/App.kt 中,通过 @JsExport 导出。以下是完整的 Kotlin 实现:
@OptIn(ExperimentalJsExport::class)
@JsExport
fun powerConsumptionAnalyzer(inputData: String = "15 5 8 10"): String {
// 输入格式: 日均用电量(kWh) 峰值功率(kW) 用电时长(小时) 设备数量
val parts = inputData.trim().split(" ").filter { it.isNotEmpty() }
if (parts.size < 4) {
return "❌ 错误: 请输入完整的信息,格式: 日均用电量(kWh) 峰值功率(kW) 用电时长(小时) 设备数量\n例如: 15 5 8 10"
}
val dailyConsumption = parts[0].toDoubleOrNull() ?: return "❌ 错误: 日均用电量必须是数字"
val peakPower = parts[1].toDoubleOrNull() ?: return "❌ 错误: 峰值功率必须是数字"
val usageHours = parts[2].toIntOrNull() ?: return "❌ 错误: 用电时长必须是整数"
val deviceCount = parts[3].toIntOrNull() ?: return "❌ 错误: 设备数量必须是整数"
if (dailyConsumption < 0 || dailyConsumption > 1000) {
return "❌ 错误: 日均用电量必须在 0-1000 kWh 之间"
}
if (peakPower < 0 || peakPower > 100) {
return "❌ 错误: 峰值功率必须在 0-100 kW 之间"
}
if (usageHours < 0 || usageHours > 24) {
return "❌ 错误: 用电时长必须在 0-24 小时之间"
}
if (deviceCount < 0 || deviceCount > 1000) {
return "❌ 错误: 设备数量必须在 0-1000 个之间"
}
// 计算能耗指标
val monthlyConsumption = dailyConsumption * 30
val averagePower = if (usageHours > 0) dailyConsumption / usageHours else 0.0
val powerPerDevice = if (deviceCount > 0) peakPower / deviceCount else 0.0
// 判断能耗等级
val consumptionLevel = when {
dailyConsumption <= 10 -> "低"
dailyConsumption <= 20 -> "中"
dailyConsumption <= 40 -> "高"
else -> "很高"
}
// 计算效率评分(基于多个因素)
var efficiencyScore = 100
// 根据日均用电量调整评分
efficiencyScore -= when {
dailyConsumption > 50 -> 40
dailyConsumption > 30 -> 30
dailyConsumption > 20 -> 20
dailyConsumption > 10 -> 10
else -> 0
}
// 根据峰值功率调整评分
efficiencyScore -= when {
peakPower > 20 -> 20
peakPower > 10 -> 15
peakPower > 5 -> 10
else -> 0
}
// 根据用电时长调整评分
efficiencyScore -= when {
usageHours > 16 -> 15
usageHours > 12 -> 10
usageHours > 8 -> 5
else -> 0
}
// 根据设备数量调整评分
efficiencyScore -= when {
deviceCount > 50 -> 15
deviceCount > 30 -> 10
deviceCount > 10 -> 5
else -> 0
}
efficiencyScore = maxOf(0, efficiencyScore)
// 计算月度成本(假设电价为 0.8 元/kWh)
val electricityPrice = 0.8
val monthlyCost = monthlyConsumption * electricityPrice
// 计算碳排放量(假设每 kWh 产生 0.5 kg CO2)
val carbonEmissionFactor = 0.5
val monthlyCarbonEmission = monthlyConsumption * carbonEmissionFactor
// 计算环保评分
var ecoScore = 100
ecoScore -= when {
monthlyCarbonEmission > 300 -> 40
monthlyCarbonEmission > 200 -> 30
monthlyCarbonEmission > 100 -> 20
monthlyCarbonEmission > 50 -> 10
else -> 0
}
ecoScore = maxOf(0, ecoScore)
// 判断能耗健康状态
val healthStatus = when {
efficiencyScore >= 80 -> "优秀"
efficiencyScore >= 60 -> "良好"
efficiencyScore >= 40 -> "一般"
else -> "需要改善"
}
// 生成建议
val suggestions = when {
efficiencyScore >= 80 -> "✨ 你的用电效率很高!继续保持现有的节能习惯。"
efficiencyScore >= 60 -> "👍 你的用电效率良好。可以通过一些小的改变进一步提高效率。"
efficiencyScore >= 40 -> "⚠️ 你的用电效率一般。建议采取措施降低能耗。"
else -> "🔴 你的用电效率需要改善。强烈建议立即采取节能措施。"
}
// 节能建议
val energySavingAdvice = when {
dailyConsumption > 30 -> "减少不必要的用电设备,关闭待机设备"
dailyConsumption > 20 -> "优化用电时间,避免高峰期用电"
dailyConsumption > 10 -> "定期检查设备,更新老旧电器"
else -> "继续保持低能耗的使用习惯"
}
// 设备优化建议
val deviceAdvice = when {
deviceCount > 50 -> "设备过多,建议减少不必要的设备"
deviceCount > 30 -> "考虑淘汰低效设备,购买能效等级高的产品"
deviceCount > 10 -> "定期维护设备,确保正常运行"
else -> "设备数量合理,继续保持"
}
// 构建输出文本
val result = StringBuilder()
result.append("⚡ 电力能耗分析与节能评估\n")
result.append("═".repeat(60)).append("\n\n")
result.append("📊 用电数据\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("日均用电量: ${String.format("%.1f", dailyConsumption)} kWh\n")
result.append("峰值功率: ${String.format("%.1f", peakPower)} kW\n")
result.append("用电时长: ${usageHours} 小时\n")
result.append("设备数量: ${deviceCount} 个\n")
result.append("平均功率: ${String.format("%.2f", averagePower)} kW\n")
result.append("单设备功率: ${String.format("%.2f", powerPerDevice)} kW\n\n")
result.append("🏆 能耗评估\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("能耗等级: ${consumptionLevel}\n")
result.append("效率评分: ${efficiencyScore}/100\n")
result.append("健康状态: ${healthStatus}\n")
result.append("月度用电量: ${String.format("%.1f", monthlyConsumption)} kWh\n")
result.append("月度成本: ¥${String.format("%.2f", monthlyCost)}\n\n")
result.append("🌍 环保分析\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("月度碳排放: ${String.format("%.1f", monthlyCarbonEmission)} kg CO2\n")
result.append("年度碳排放: ${String.format("%.1f", monthlyCarbonEmission * 12)} kg CO2\n")
result.append("环保评分: ${ecoScore}/100\n\n")
result.append("💡 个性化建议\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("${suggestions}\n\n")
result.append("💰 节能建议\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("${energySavingAdvice}\n\n")
result.append("🔧 设备优化\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("${deviceAdvice}\n\n")
result.append("📈 能耗等级标准\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("• 低: 日均用电量 ≤ 10 kWh\n")
result.append("• 中: 日均用电量 11-20 kWh\n")
result.append("• 高: 日均用电量 21-40 kWh\n")
result.append("• 很高: 日均用电量 > 40 kWh\n\n")
result.append("🎯 节能指导\n")
result.append("─".repeat(60)).append("\n")
result.append("1. 定期检查用电设备,及时维修或更换\n")
result.append("2. 购买能效等级高的电器(一级能效最佳)\n")
result.append("3. 避免长时间待机,及时关闭不用的设备\n")
result.append("4. 合理安排用电时间,避免高峰期用电\n")
result.append("5. 使用智能电表监测用电情况\n")
result.append("6. 安装节能灯具,减少照明能耗\n")
result.append("7. 定期清洁空调滤网,提高制冷效率\n")
result.append("8. 使用节能插座,减少待机功耗\n")
result.append("9. 考虑安装太阳能等可再生能源\n")
result.append("10. 建立用电管理制度,培养节能意识\n")
return result.toString()
}
代码说明
这段 Kotlin 代码实现了完整的电力能耗分析和节能评估功能。让我详细解释关键部分:
数据验证:首先验证输入的四个参数是否有效,确保数据在合理范围内。这些参数都有明确的物理范围限制。
能耗指标计算:根据日均用电量、用电时长和设备数量计算出月度用电量、平均功率和单设备功率等关键指标。
能耗等级判断:根据日均用电量将能耗分为四个等级:低、中、高、很高。这些等级反映了用电的多少。
效率评分计算:从 100 分开始,根据日均用电量、峰值功率、用电时长和设备数量等多个因素扣分,最终得出效率评分。
成本计算:基于月度用电量和电价(0.8 元/kWh)计算月度成本,帮助用户了解用电成本。
碳排放计算:根据月度用电量和碳排放因子(0.5 kg CO2/kWh)计算碳排放量,反映环保影响。
环保评分:根据碳排放量计算环保评分,帮助用户了解其用电对环境的影响。
个性化建议:根据效率评分、能耗等级和设备数量生成相应的节能建议。
JavaScript 调用示例
编译后的 JavaScript 代码可以在 Node.js 或浏览器中直接调用。以下是 JavaScript 的使用示例:
// 导入编译后的 Kotlin/JS 模块
const { powerConsumptionAnalyzer } = require('./hellokjs.js');
// 示例 1:低能耗
const result1 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer("8 3 6 5");
console.log("示例 1 - 低能耗:");
console.log(result1);
console.log("\n");
// 示例 2:中等能耗
const result2 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer("15 5 8 10");
console.log("示例 2 - 中等能耗:");
console.log(result2);
console.log("\n");
// 示例 3:高能耗
const result3 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer("30 8 12 20");
console.log("示例 3 - 高能耗:");
console.log(result3);
console.log("\n");
// 示例 4:很高能耗
const result4 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer("50 15 16 40");
console.log("示例 4 - 很高能耗:");
console.log(result4);
console.log("\n");
// 示例 5:极高能耗
const result5 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer("80 25 20 60");
console.log("示例 5 - 极高能耗:");
console.log(result5);
console.log("\n");
// 示例 6:使用默认参数
const result6 = powerConsumptionAnalyzer();
console.log("示例 6 - 使用默认参数:");
console.log(result6);
// 实际应用场景:从用户输入获取数据
function analyzeUserPowerConsumption(userInput) {
try {
const result = powerConsumptionAnalyzer(userInput);
return {
success: true,
data: result
};
} catch (error) {
return {
success: false,
error: error.message
};
}
}
// 测试实际应用
const userInput = "20 6 10 15";
const analysis = analyzeUserPowerConsumption(userInput);
if (analysis.success) {
console.log("用户电力能耗分析结果:");
console.log(analysis.data);
} else {
console.log("分析失败:", analysis.error);
}
// 能耗监测追踪应用示例
function trackPowerConsumption(records) {
console.log("\n能耗监测记录:");
console.log("═".repeat(60));
const results = records.map((record, index) => {
const analysis = powerConsumptionAnalyzer(record);
return {
month: index + 1,
record,
analysis
};
});
results.forEach(result => {
console.log(`\n第 ${result.month} 月 (${result.record}):`);
console.log(result.analysis);
});
return results;
}
// 测试能耗监测追踪
const records = [
"10 4 6 8",
"12 4 7 9",
"15 5 8 10",
"18 6 9 12",
"20 6 10 15"
];
trackPowerConsumption(records);
// 能耗趋势分析
function analyzeConsumptionTrend(records) {
const analyses = records.map(record => {
const parts = record.split(' ').map(Number);
return {
daily: parts[0],
peak: parts[1],
hours: parts[2],
devices: parts[3]
};
});
const avgDaily = analyses.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.daily, 0) / analyses.length;
const avgPeak = analyses.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.peak, 0) / analyses.length;
const avgHours = analyses.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.hours, 0) / analyses.length;
const avgDevices = analyses.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.devices, 0) / analyses.length;
console.log("\n能耗趋势分析:");
console.log(`平均日均用电量: ${avgDaily.toFixed(1)} kWh`);
console.log(`平均峰值功率: ${avgPeak.toFixed(1)} kW`);
console.log(`平均用电时长: ${avgHours.toFixed(1)} 小时`);
console.log(`平均设备数量: ${avgDevices.toFixed(0)} 个`);
const totalMonthly = avgDaily * 30;
const totalCost = totalMonthly * 0.8;
const totalCarbon = totalMonthly * 0.5;
console.log(`\n月度统计:`);
console.log(`月度用电量: ${totalMonthly.toFixed(1)} kWh`);
console.log(`月度成本: ¥${totalCost.toFixed(2)}`);
console.log(`月度碳排放: ${totalCarbon.toFixed(1)} kg CO2`);
}
analyzeConsumptionTrend(records);
JavaScript 代码说明
这段 JavaScript 代码展示了如何在 Node.js 环境中调用编译后的 Kotlin 函数。关键点包括:
模块导入:使用 require 导入编译后的 JavaScript 模块,获取导出的 powerConsumptionAnalyzer 函数。
多个示例:展示了不同能耗等级(低、中、高、很高、极高)的调用方式。
错误处理:在实际应用中,使用 try-catch 块来处理可能的错误,确保程序的稳定性。
能耗监测追踪:trackPowerConsumption 函数展示了如何处理多月的能耗监测记录,这在实际的能源管理应用中很常见。
趋势分析:analyzeConsumptionTrend 函数演示了如何进行能耗的长期趋势分析,计算平均值和总成本。
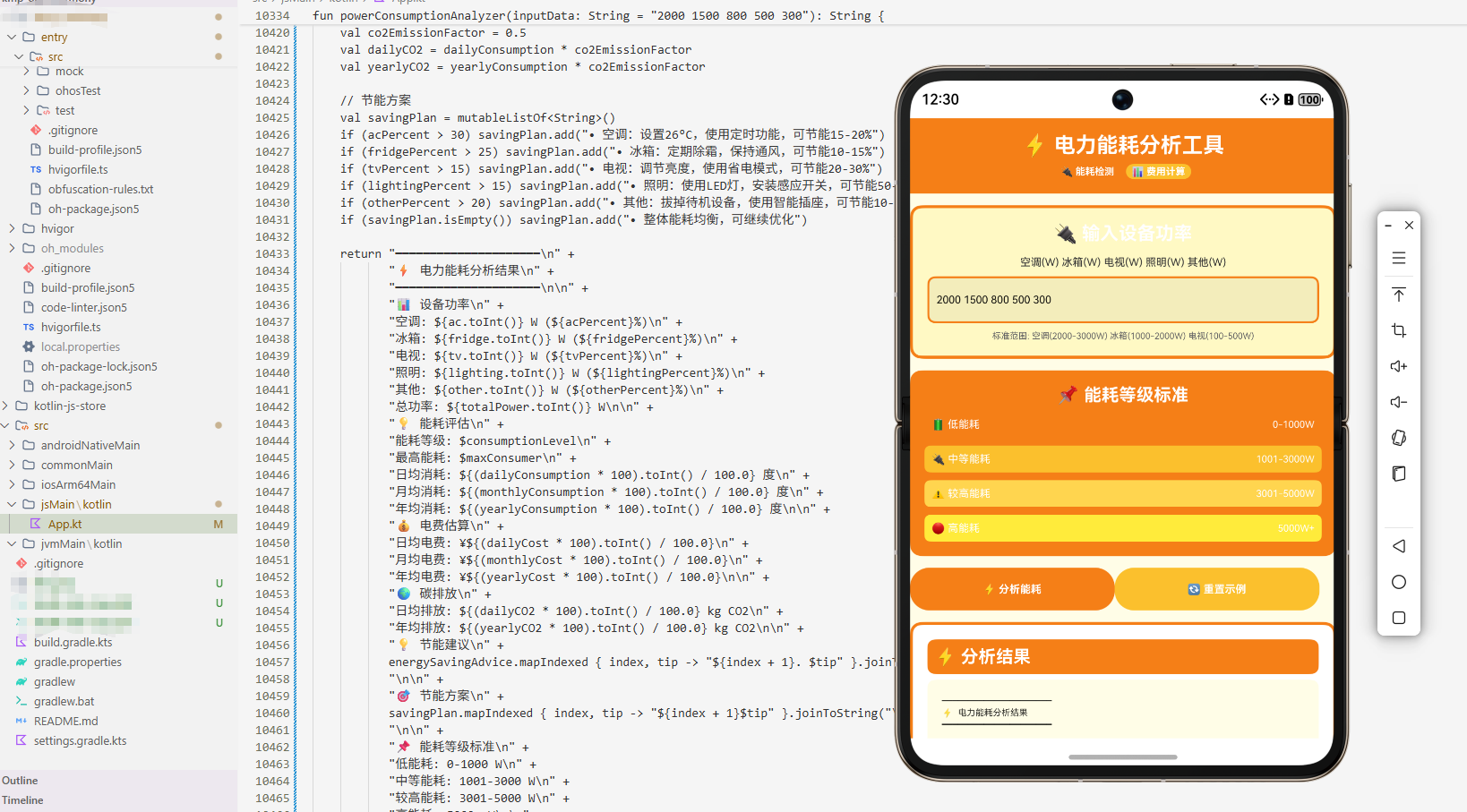
ArkTS 页面集成与调用
在 OpenHarmony 的 ArkTS 页面中集成这个电力能耗分析工具。以下是完整的 ArkTS 实现代码:
import { powerConsumptionAnalyzer } from './hellokjs';
@Entry
@Component
struct PowerConsumptionAnalyzerPage {
@State dailyConsumption: string = "15";
@State peakPower: string = "5";
@State usageHours: string = "8";
@State deviceCount: string = "10";
@State analysisResult: string = "";
@State isLoading: boolean = false;
build() {
Column() {
// 顶部栏
Row() {
Text("⚡ 电力能耗分析")
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor(Color.White)
}
.width("100%")
.height(60)
.backgroundColor("#FF6F00")
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.padding({ top: 10, bottom: 10 })
// 主容器
Scroll() {
Column() {
// 日均用电量输入
Text("日均用电量 (kWh)")
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor("#333333")
.margin({ top: 20, left: 15 })
TextInput({
placeholder: "例如: 15",
text: this.dailyConsumption
})
.width("90%")
.height(45)
.margin({ top: 8, bottom: 15, left: 15, right: 15 })
.padding({ left: 10, right: 10 })
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.border({ width: 1, color: "#FF6F00" })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.dailyConsumption = value;
})
// 峰值功率输入
Text("峰值功率 (kW)")
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor("#333333")
.margin({ left: 15 })
TextInput({
placeholder: "例如: 5",
text: this.peakPower
})
.width("90%")
.height(45)
.margin({ top: 8, bottom: 15, left: 15, right: 15 })
.padding({ left: 10, right: 10 })
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.border({ width: 1, color: "#FF6F00" })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.peakPower = value;
})
// 用电时长输入
Text("用电时长 (小时)")
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor("#333333")
.margin({ left: 15 })
TextInput({
placeholder: "例如: 8",
text: this.usageHours
})
.width("90%")
.height(45)
.margin({ top: 8, bottom: 15, left: 15, right: 15 })
.padding({ left: 10, right: 10 })
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.border({ width: 1, color: "#FF6F00" })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.usageHours = value;
})
// 设备数量输入
Text("设备数量 (个)")
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor("#333333")
.margin({ left: 15 })
TextInput({
placeholder: "例如: 10",
text: this.deviceCount
})
.width("90%")
.height(45)
.margin({ top: 8, bottom: 15, left: 15, right: 15 })
.padding({ left: 10, right: 10 })
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.border({ width: 1, color: "#FF6F00" })
.onChange((value: string) => {
this.deviceCount = value;
})
// 按钮区域
Row() {
Button("📊 分析能耗")
.width("45%")
.height(45)
.backgroundColor("#FF6F00")
.fontColor(Color.White)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.isLoading = true;
setTimeout(() => {
const input = `${this.dailyConsumption} ${this.peakPower} ${this.usageHours} ${this.deviceCount}`;
this.analysisResult = powerConsumptionAnalyzer(input);
this.isLoading = false;
}, 300);
})
Blank()
Button("🔄 重置")
.width("45%")
.height(45)
.backgroundColor("#2196F3")
.fontColor(Color.White)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.onClick(() => {
this.dailyConsumption = "15";
this.peakPower = "5";
this.usageHours = "8";
this.deviceCount = "10";
this.analysisResult = "";
this.isLoading = false;
})
}
.width("90%")
.margin({ top: 10, bottom: 20, left: 15, right: 15 })
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.SpaceBetween)
// 加载指示器
if (this.isLoading) {
Row() {
LoadingProgress()
.width(40)
.height(40)
.color("#FF6F00")
Text(" 正在分析中...")
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor("#666666")
}
.width("90%")
.height(50)
.margin({ bottom: 15, left: 15, right: 15 })
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.borderRadius(8)
}
// 结果显示区域
if (this.analysisResult.length > 0) {
Column() {
Text("📈 分析结果")
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor("#FF6F00")
.margin({ bottom: 10 })
Text(this.analysisResult)
.width("100%")
.fontSize(12)
.fontFamily("monospace")
.fontColor("#333333")
.lineHeight(1.6)
.padding(10)
.backgroundColor("#FAFAFA")
.border({ width: 1, color: "#E0E0E0" })
.borderRadius(8)
}
.width("90%")
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 30, left: 15, right: 15 })
.padding(15)
.backgroundColor("#FFE0B2")
.borderRadius(8)
.border({ width: 1, color: "#FF6F00" })
}
}
.width("100%")
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.backgroundColor("#FFFFFF")
}
.width("100%")
.height("100%")
.backgroundColor("#F5F5F5")
}
}
ArkTS 代码说明
这段 ArkTS 代码实现了完整的用户界面和交互逻辑。关键点包括:
导入函数:从编译后的 JavaScript 模块中导入 powerConsumptionAnalyzer 函数。
状态管理:使用 @State 装饰器管理六个状态:日均用电量、峰值功率、用电时长、设备数量、分析结果和加载状态。
UI 布局:包含顶部栏、四个输入框、分析和重置按钮、加载指示器和结果显示区域。
交互逻辑:用户输入四个参数后,点击分析按钮。应用会调用 Kotlin 函数进行分析,显示加载动画,最后展示详细的分析结果。
样式设计:使用橙色主题,与能源和电力相关的主题相符。所有输入框、按钮和结果显示区域都有相应的样式设置,提供清晰的视觉层次。
数据输入与交互体验
输入数据格式规范
为了确保工具能够正确处理用户输入,用户应该遵循以下规范:
- 日均用电量:整数或浮点数,单位 kWh,范围 0-1000。
- 峰值功率:整数或浮点数,单位 kW,范围 0-100。
- 用电时长:整数,单位小时,范围 0-24。
- 设备数量:整数,单位个,范围 0-1000。
- 分隔符:使用空格分隔各个参数。
示例输入
- 低能耗:
8 3 6 5 - 中等能耗:
15 5 8 10 - 高能耗:
30 8 12 20 - 很高能耗:
50 15 16 40 - 极高能耗:
80 25 20 60
交互流程
- 用户打开应用,看到输入框和默认数据
- 用户输入四个能耗参数
- 点击"分析能耗"按钮,应用调用 Kotlin 函数进行分析
- 应用显示加载动画,表示正在处理
- 分析完成后,显示详细的分析结果,包括能耗等级、效率评分、月度成本、碳排放量、环保评分、节能建议等
- 用户可以点击"重置"按钮清空数据,重新开始
编译与自动复制流程
编译步骤
-
编译 Kotlin 代码:
./gradlew build -
生成 JavaScript 文件:
编译过程会自动生成hellokjs.d.ts和hellokjs.js文件。 -
复制到 ArkTS 项目:
使用提供的脚本自动复制生成的文件到 ArkTS 项目的 pages 目录:./build-and-copy.bat
文件结构
编译完成后,项目结构如下:
kmp_openharmony/
├── src/
│ └── jsMain/
│ └── kotlin/
│ └── App.kt (包含 powerConsumptionAnalyzer 函数)
├── build/
│ └── js/
│ └── packages/
│ └── hellokjs/
│ ├── hellokjs.d.ts
│ └── hellokjs.js
└── kmp_ceshiapp/
└── entry/
└── src/
└── main/
└── ets/
└── pages/
├── hellokjs.d.ts (复制后)
├── hellokjs.js (复制后)
└── Index.ets (ArkTS 页面)
总结
这个案例展示了如何使用 Kotlin Multiplatform 技术实现一个跨端的能源工具 - 电力能耗分析工具。通过将核心逻辑写在 Kotlin 中,然后编译为 JavaScript,最后在 ArkTS 中调用,我们实现了代码的一次编写、多端复用。
核心优势
- 代码复用:Kotlin 代码可以在 JVM、JavaScript 和其他平台上运行,避免重复开发。
- 类型安全:Kotlin 的类型系统确保了代码的安全性和可维护性。
- 性能优化:Kotlin 编译为 JavaScript 后,性能与手写 JavaScript 相当。
- 易于维护:集中管理业务逻辑,使得维护和更新变得更加容易。
- 用户体验:通过 ArkTS 提供的丰富 UI 组件,可以创建美观、易用的用户界面。
扩展方向
- 数据持久化:将用户的能耗数据保存到本地存储或云端。
- 数据可视化:使用图表库展示能耗的变化趋势和成本预测。
- 多用户支持:支持多个用户或多个地点的能耗管理和对比。
- 智能预警:根据能耗数据提供自动预警和节能建议。
- 社交功能:允许用户分享节能成果和相互鼓励。
- 集成第三方 API:连接智能电表、能源公司数据等外部服务。
- AI 分析:使用机器学习进行能耗异常检测和预测。
- 绿色认证:与环保部门协作,提供碳中和认证。
通过这个案例,开发者可以学到如何在 KMP 项目中实现复杂的能源管理计算逻辑,以及如何在 OpenHarmony 平台上构建高效的跨端应用。这个电力能耗分析工具可以作为智能家居系统、工业能源管理平台或个人节能应用的核心模块。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献4条内容
已为社区贡献4条内容







所有评论(0)